C1403_Final Exam p. 1 Friday, January 23, 2004 Printed Last Name
... 55. A compound has the empirical formula CoCl3·4NH3. One mole of the compound yields one mole of silver chloride when treated with silver nitrate. Ammonia is not removed by treatment with concentrated sulfuric acid. The formula for the compound is best represented by a. Co(NH3)4Cl3 b. [Co(NH3)Cl2]C ...
... 55. A compound has the empirical formula CoCl3·4NH3. One mole of the compound yields one mole of silver chloride when treated with silver nitrate. Ammonia is not removed by treatment with concentrated sulfuric acid. The formula for the compound is best represented by a. Co(NH3)4Cl3 b. [Co(NH3)Cl2]C ...
ch19 MSJ jlm
... The Ag|Ag+ half-cell has a higher reduction potential than the Cu|Cu2+ half-cell. This means that the Ag/Ag+ half-cell will more readily undergo reduction when compared to the Cu/Cu2+ halfcell, and the Cu|Cu2+ half-cell will undergo oxidation. The Ag|Ag+ standard reduction potential is Eored = +0.8 ...
... The Ag|Ag+ half-cell has a higher reduction potential than the Cu|Cu2+ half-cell. This means that the Ag/Ag+ half-cell will more readily undergo reduction when compared to the Cu/Cu2+ halfcell, and the Cu|Cu2+ half-cell will undergo oxidation. The Ag|Ag+ standard reduction potential is Eored = +0.8 ...
CHE-310 Organic Chemistry I_
... For alkyl halides, alcohols and ethers, be able to name compounds correctly (nomenclature). Where necessay, be able to specify congiguration in the name. Know the two new mechanisms that we have learned in these chapters: SN2, SN1. Know which mechanisms go with which reactions under which conditions ...
... For alkyl halides, alcohols and ethers, be able to name compounds correctly (nomenclature). Where necessay, be able to specify congiguration in the name. Know the two new mechanisms that we have learned in these chapters: SN2, SN1. Know which mechanisms go with which reactions under which conditions ...
TIPS for NET-IONIC EQUATIONS A.P. Chemistry (long form)
... Reactions of coordination compounds and ions are not covered in depth on the exam but you will sometimes see them in the reaction-writing section and they are easy enough to complete with a few basic principles in mind. Most can be recognized by the choice of reactants: generally a transition metal ...
... Reactions of coordination compounds and ions are not covered in depth on the exam but you will sometimes see them in the reaction-writing section and they are easy enough to complete with a few basic principles in mind. Most can be recognized by the choice of reactants: generally a transition metal ...
Utah - Wavefunction, Inc.
... In a chemical reaction new substances are formed as atoms and molecules are rearranged. The concept of atoms explains the conservation of matter, since the number of atoms stays the same in a chemical reaction no matter how they are rearranged; the total mass stays the same. Although ...
... In a chemical reaction new substances are formed as atoms and molecules are rearranged. The concept of atoms explains the conservation of matter, since the number of atoms stays the same in a chemical reaction no matter how they are rearranged; the total mass stays the same. Although ...
Chapter 4 - GEOCITIES.ws
... Redox Reactions Oxidation-Reduction called Redox An Oxidation-reduction reaction involves the transfer of electrons. In a REDOX Reaction, one substance loses electrons as it is oxidized, the other substance gains electrons and is reduced. Use oxidation numbers to help keep track of where the electr ...
... Redox Reactions Oxidation-Reduction called Redox An Oxidation-reduction reaction involves the transfer of electrons. In a REDOX Reaction, one substance loses electrons as it is oxidized, the other substance gains electrons and is reduced. Use oxidation numbers to help keep track of where the electr ...
Final review packet
... 1. Compare the parts of an atom based on location, charge and mass: - proton - neutron - electron 2. Define: - isotope - ion - atomic number - mass number - atomic mass unit 3. How many neutrons does U-238 have? 4. Write isotope notation for the particle that contains 17 neutrons and 15 protons. 5. ...
... 1. Compare the parts of an atom based on location, charge and mass: - proton - neutron - electron 2. Define: - isotope - ion - atomic number - mass number - atomic mass unit 3. How many neutrons does U-238 have? 4. Write isotope notation for the particle that contains 17 neutrons and 15 protons. 5. ...
19-Oct
... the mole proportions of chemical reactions. Stoichiometric ratio: The ratio of any two species (reactants or products) in a balanced chemical reaction. ...
... the mole proportions of chemical reactions. Stoichiometric ratio: The ratio of any two species (reactants or products) in a balanced chemical reaction. ...
Test 9 Review - Evan`s Chemistry Corner
... negative. Endothermic reactions are reactions in which energy is absorbed. This means the potential energy of the products is higher than the potential energy of the reactants and ΔH is positive. Catalysts reduce the activation energy but have no effect on the change in enthalpy. ...
... negative. Endothermic reactions are reactions in which energy is absorbed. This means the potential energy of the products is higher than the potential energy of the reactants and ΔH is positive. Catalysts reduce the activation energy but have no effect on the change in enthalpy. ...
Assistant Professor Chemistry, Class-2, Advt No. 84/2016
... Which of the following species does not have metal-metal bond (A) Fe2(CO)9 ...
... Which of the following species does not have metal-metal bond (A) Fe2(CO)9 ...
File
... When electrons move from one area to another they produce an electric current (electricity!). Since redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons, these chemical reactions can be used to produce electricity. ...
... When electrons move from one area to another they produce an electric current (electricity!). Since redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons, these chemical reactions can be used to produce electricity. ...
REACTION PREDICTION
... learn to write net ionic equations, you will write three different equations for each reaction. Steps in writing net ionic equations: 1. Write the complete molecular equation. (This is the type of equation that you are accustomed to writing.) 2. Write the complete ionic equation. To do this, you mus ...
... learn to write net ionic equations, you will write three different equations for each reaction. Steps in writing net ionic equations: 1. Write the complete molecular equation. (This is the type of equation that you are accustomed to writing.) 2. Write the complete ionic equation. To do this, you mus ...
- Cypress HS
... Many chemical reactions, especially those of organic substances, do not go to completion. Rather, they come to a point of chemical equilibrium before the reactants are fully converted to products. At the point of equilibrium, the concentrations of all reactants remain constant with time. The positio ...
... Many chemical reactions, especially those of organic substances, do not go to completion. Rather, they come to a point of chemical equilibrium before the reactants are fully converted to products. At the point of equilibrium, the concentrations of all reactants remain constant with time. The positio ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry
... • Ordinarily, when a chemical reaction is carried out in the laboratory, energy is evolved as heat • CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) à CO2 (g) + H2O (ℓ) ΔE = -885 kJ • The combustion of methane in a Bunsen burner produces nearly 885 kJ of heat per mol • The decrease in volume that takes place is a 1% ...
... • Ordinarily, when a chemical reaction is carried out in the laboratory, energy is evolved as heat • CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) à CO2 (g) + H2O (ℓ) ΔE = -885 kJ • The combustion of methane in a Bunsen burner produces nearly 885 kJ of heat per mol • The decrease in volume that takes place is a 1% ...
Advanced Chemistry
... (a) Determine the order of the reaction with respect to each reactant, Br2(g) and NO(g). In each case, explain your reasoning or provide calculations to justify your answer. Order of reaction for NO: look at experiments 3 + 4 (keep [Br2] constant). The initial [NO] in run 3 is 2x the initial [NO] of ...
... (a) Determine the order of the reaction with respect to each reactant, Br2(g) and NO(g). In each case, explain your reasoning or provide calculations to justify your answer. Order of reaction for NO: look at experiments 3 + 4 (keep [Br2] constant). The initial [NO] in run 3 is 2x the initial [NO] of ...
Fundamentals of Theoretical Organic Chemistry Lecture 1
... Some of the mathematical models given in Figure1.1.2-8, together with other formulas not shown on figure, can be combined to compute internal potential energies. The equations may be combined in a number of possible ways. The combined equations, collectively referred to as “force - fields”, incorpor ...
... Some of the mathematical models given in Figure1.1.2-8, together with other formulas not shown on figure, can be combined to compute internal potential energies. The equations may be combined in a number of possible ways. The combined equations, collectively referred to as “force - fields”, incorpor ...
Chemical Industry
... oxidation state, but nitrogen in NO2 has a higher oxidation state than that in KNO2. ...
... oxidation state, but nitrogen in NO2 has a higher oxidation state than that in KNO2. ...
chem10chp7spr08
... Predict the product – has already been given, but we’ll learn how to do this later Write the correct chemical formulas – keep working on this __Al(s) + __Cl2(g) __AlCl3(s) Not mass balanced Balance equation using the correct stoich coefficients 1 Al & 2 Cl 1 Al & 3 Cl 2 Cl vs. 3 Cl: Find least c ...
... Predict the product – has already been given, but we’ll learn how to do this later Write the correct chemical formulas – keep working on this __Al(s) + __Cl2(g) __AlCl3(s) Not mass balanced Balance equation using the correct stoich coefficients 1 Al & 2 Cl 1 Al & 3 Cl 2 Cl vs. 3 Cl: Find least c ...
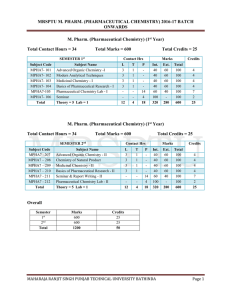
mrsptu m. pharm. (pharmaceutical chemistry) 2016
... Optical Isomerism in Compounds Containing No Chiral Atom: Biphenyls, Allenes, Compounds with Exocylic Double Bonds, Spiranes, Chirality due to a Helical Shape, Chirality caused by Restricted Rotation of other Types. Cis-Trans Isomerism: Resulting from Double Bonds, Monocyclic Compounds, Fused Ring S ...
... Optical Isomerism in Compounds Containing No Chiral Atom: Biphenyls, Allenes, Compounds with Exocylic Double Bonds, Spiranes, Chirality due to a Helical Shape, Chirality caused by Restricted Rotation of other Types. Cis-Trans Isomerism: Resulting from Double Bonds, Monocyclic Compounds, Fused Ring S ...
NC Exam Questions - Rosshall Academy
... (d) Aldehydes can also be formed by the reaction of some alcohols with copper(II) oxide. Name the type of alcohol that would react with copper(II) oxide to form an aldehyde. ...
... (d) Aldehydes can also be formed by the reaction of some alcohols with copper(II) oxide. Name the type of alcohol that would react with copper(II) oxide to form an aldehyde. ...
CHEMISTRY 110 LECTURE
... 2. A crucial reaction for the maintenance of plant and animal life is the conversion of oxygen gas to ozone gas[O3(g)] in the lower part of the stratosphere. How many molecules of oxygen gas are needed to produce 17.0 moles of ozone (O 3)? ...
... 2. A crucial reaction for the maintenance of plant and animal life is the conversion of oxygen gas to ozone gas[O3(g)] in the lower part of the stratosphere. How many molecules of oxygen gas are needed to produce 17.0 moles of ozone (O 3)? ...
Solutions
... ‣ If a double displacement reaction forms CO2 (g), H2S (g), or NH3 (g) gases this irreversible reaction will drive equilibrium forward. ‣ If a double displacement reaction forms H2CO3 (aq) or NH4Cl (aq) these decompose to gases and drive equilibrium forward. NaOH(aq) + NH4Cl(aq) ⇄ Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) ...
... ‣ If a double displacement reaction forms CO2 (g), H2S (g), or NH3 (g) gases this irreversible reaction will drive equilibrium forward. ‣ If a double displacement reaction forms H2CO3 (aq) or NH4Cl (aq) these decompose to gases and drive equilibrium forward. NaOH(aq) + NH4Cl(aq) ⇄ Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) ...