summer fun - West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
oxidation and reduction
... a) Oxidation and reduction are brought about by substances referred to as oxidising agents and reducing agents. Define each of these substances in terms of electrons. Oxidising agent ..................................................................................................................... ...
... a) Oxidation and reduction are brought about by substances referred to as oxidising agents and reducing agents. Define each of these substances in terms of electrons. Oxidising agent ..................................................................................................................... ...
35 - TAMU Chemistry
... Note: >50% of all O2 from photosynthesis comes from photoplankton in oceans • The cycle continues when decay, respiration and combustion take O2 back to CO2 and H2O. Q What would happen if the oxygen cycle did not maintain O2 concentration in air at ~21%? ...
... Note: >50% of all O2 from photosynthesis comes from photoplankton in oceans • The cycle continues when decay, respiration and combustion take O2 back to CO2 and H2O. Q What would happen if the oxygen cycle did not maintain O2 concentration in air at ~21%? ...
Document
... 2 H2(g)+ O2(g) → 2 H2O(g) + heat ΔH = – 483.6 kJ Characteristics of Enthalpy (1) Enthalpy is an extensive property (2) ΔH for a reaction is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to ΔH for reverse reaction (3) ΔH for a reaction depends on states of reactants and products (gas, liquid) ...
... 2 H2(g)+ O2(g) → 2 H2O(g) + heat ΔH = – 483.6 kJ Characteristics of Enthalpy (1) Enthalpy is an extensive property (2) ΔH for a reaction is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to ΔH for reverse reaction (3) ΔH for a reaction depends on states of reactants and products (gas, liquid) ...
An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be chemically
... Compound: a pure substance that is formed when atoms of two or more different elements combine and create a new material with properties completely unlike those of its constituent elements. ...
... Compound: a pure substance that is formed when atoms of two or more different elements combine and create a new material with properties completely unlike those of its constituent elements. ...
www.studyguide.pk
... (c) The energy of activation for the formation of CH3Cl is 16 kJ mol–1. Use this figure and your answer to (a)(i) to complete the reaction pathway diagram below showing the formation of CH3Cl from CH4 and Cl2. Show clearly the intermediate organic species and the final products. Indicate on your ske ...
... (c) The energy of activation for the formation of CH3Cl is 16 kJ mol–1. Use this figure and your answer to (a)(i) to complete the reaction pathway diagram below showing the formation of CH3Cl from CH4 and Cl2. Show clearly the intermediate organic species and the final products. Indicate on your ske ...
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
... - Group 1A metals give up one electron to become monopositive ion (Na+) - Group 2A metals give up two electrons to become a dipositive ion (Ca2+) - Group 3A give up three electrons (Al3+) ; - Transition metals give up a variable number of electrons. C. Oxidizing Agent- the substance that causes oxid ...
... - Group 1A metals give up one electron to become monopositive ion (Na+) - Group 2A metals give up two electrons to become a dipositive ion (Ca2+) - Group 3A give up three electrons (Al3+) ; - Transition metals give up a variable number of electrons. C. Oxidizing Agent- the substance that causes oxid ...
Raman Spectroscopy
... absorbed light must always result into chemical reaction. The absorbed light may simply bring about phenomena such as fluorescence, phosphorescence etc., Similarly, the absorbed light energy may be simply converted into thermal energy e.g. in case of potassium permanganate solution, the light energy ...
... absorbed light must always result into chemical reaction. The absorbed light may simply bring about phenomena such as fluorescence, phosphorescence etc., Similarly, the absorbed light energy may be simply converted into thermal energy e.g. in case of potassium permanganate solution, the light energy ...
Comparing Free Energies
... our system, the total entropy of the system plus its surroundings should increase. This means, the difference between the total entropy after and before the process should be positive (DSTOT > 0). This does not imply that the change of entropy in the chemical system (DSsys) should also be larger tha ...
... our system, the total entropy of the system plus its surroundings should increase. This means, the difference between the total entropy after and before the process should be positive (DSTOT > 0). This does not imply that the change of entropy in the chemical system (DSsys) should also be larger tha ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... 36 Chlorine reacts with hot concentrated aqueous sodium hydroxide according to the equation ...
... 36 Chlorine reacts with hot concentrated aqueous sodium hydroxide according to the equation ...
APEF – Equilibrium and Reaction Rate Multiple Choice Answers
... 13. Which phrase could be a definition of the activation energy of a reaction? A. the energy gained by reactant molecules to undergo a reaction B. the energy supplied by the attractive forces between molecules C. the energy supplied by a catalyst D. the heat content of the products minus that of the ...
... 13. Which phrase could be a definition of the activation energy of a reaction? A. the energy gained by reactant molecules to undergo a reaction B. the energy supplied by the attractive forces between molecules C. the energy supplied by a catalyst D. the heat content of the products minus that of the ...
Section 1 Describing Chemical Reactions Chapter 8
... • One of the compounds formed is usually a precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of the solution, or a molecular compound, usually water. • The other compound is often soluble and remains dissolved in solution. ...
... • One of the compounds formed is usually a precipitate, an insoluble gas that bubbles out of the solution, or a molecular compound, usually water. • The other compound is often soluble and remains dissolved in solution. ...
Click here to Ch 06.2 Covalent Bonding_Lewis Structures
... If carbon is present in the molecule it will ALWAYS be the center atom. If it is not, the atom with the least electronegativity will be the center. Hydrogen will NEVER be the center. A good thing to do is to bond all the atoms together by single bonds, and then add the multiple bonds using the rul ...
... If carbon is present in the molecule it will ALWAYS be the center atom. If it is not, the atom with the least electronegativity will be the center. Hydrogen will NEVER be the center. A good thing to do is to bond all the atoms together by single bonds, and then add the multiple bonds using the rul ...
Combined
... (b) Suggest a chemical test to distinguish each of the following pairs of solutions. Each test should include the reagent(s), the expected observation with each compound and the chemical equation(s) (i) ...
... (b) Suggest a chemical test to distinguish each of the following pairs of solutions. Each test should include the reagent(s), the expected observation with each compound and the chemical equation(s) (i) ...
Enthalpy
... Iron can be reacted with nitrogen to yield iron nitride in the reaction: 3 Fe (s) + N2(g) Fe3N2(s) 10.0 g Fe and 2.00 g N2 are placed in a calorimeter at 25.0°C and the reaction triggered. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (INCLUDING WATER) is 14.7 kJ/°C. If the final temperature of the calorim ...
... Iron can be reacted with nitrogen to yield iron nitride in the reaction: 3 Fe (s) + N2(g) Fe3N2(s) 10.0 g Fe and 2.00 g N2 are placed in a calorimeter at 25.0°C and the reaction triggered. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (INCLUDING WATER) is 14.7 kJ/°C. If the final temperature of the calorim ...
enthalpy of reaction
... Iron can be reacted with nitrogen to yield iron nitride in the reaction: 3 Fe (s) + N2(g) Fe3N2(s) 10.0 g Fe and 2.00 g N2 are placed in a calorimeter at 25.0°C and the reaction triggered. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (INCLUDING WATER) is 14.7 kJ/°C. If the final temperature of the calorim ...
... Iron can be reacted with nitrogen to yield iron nitride in the reaction: 3 Fe (s) + N2(g) Fe3N2(s) 10.0 g Fe and 2.00 g N2 are placed in a calorimeter at 25.0°C and the reaction triggered. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (INCLUDING WATER) is 14.7 kJ/°C. If the final temperature of the calorim ...
AP - 04 - Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
... o Determine the oxidation numbers of everything in H2S, S8, Na2SO3, and SO42(a) When bonded to a nonmetal, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 (rule 3b). Because the H2S molecule is neutral, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal zero (rule 4). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we h ...
... o Determine the oxidation numbers of everything in H2S, S8, Na2SO3, and SO42(a) When bonded to a nonmetal, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 (rule 3b). Because the H2S molecule is neutral, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal zero (rule 4). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we h ...
2. The Magic of Chemical Reactions
... Corrosion can be prevented by using -----. The chemical formula of rust is ------. When acids and alkalis react together, ------ and ------ are formed. ...
... Corrosion can be prevented by using -----. The chemical formula of rust is ------. When acids and alkalis react together, ------ and ------ are formed. ...
chemistry advanced may 2010 marking scheme
... (ii) Explain giving essential experimental detail how a pure sample of butanal could be isolated from the distillate given that the boiling point of butanal is 75oC. ...
... (ii) Explain giving essential experimental detail how a pure sample of butanal could be isolated from the distillate given that the boiling point of butanal is 75oC. ...
The s-Block Elements
... 2. For Group II sulphates, the cations are much smaller than the anions. The changing in size of cations does not cause a significant change in H lattice (proportional to 1/(r+ + r-). However, the changing in size of cations does cause H hydration (proportional to 1/r+ and 1/r-) to become less exo ...
... 2. For Group II sulphates, the cations are much smaller than the anions. The changing in size of cations does not cause a significant change in H lattice (proportional to 1/(r+ + r-). However, the changing in size of cations does cause H hydration (proportional to 1/r+ and 1/r-) to become less exo ...
dutch national chemistry olympiad
... 3p 6 Explain by using information from Binas Table 57A that the amount of NO decreases when the gas mixture is cooled down. Mention the numerical value of this information in your explanation. Assume that this information also applies in the conditions present in diesel motors. The temperature of ...
... 3p 6 Explain by using information from Binas Table 57A that the amount of NO decreases when the gas mixture is cooled down. Mention the numerical value of this information in your explanation. Assume that this information also applies in the conditions present in diesel motors. The temperature of ...
CHEMISTRY SAMPLE PAPER - I
... (b) the reduction of Cr2O3 with AI is thermodynamically feasible, yet it does not occur at room temperature. (c) pine oil is used in froth floatation method. 3 23. Explain the following facts (a) transition metals act as catalysts. (b) chromium group elements have the highest melting points in their ...
... (b) the reduction of Cr2O3 with AI is thermodynamically feasible, yet it does not occur at room temperature. (c) pine oil is used in froth floatation method. 3 23. Explain the following facts (a) transition metals act as catalysts. (b) chromium group elements have the highest melting points in their ...
Normality Primer
... when the titration reaction is unknown or just not used. Consequently, definitions for these terms vary depending on the type of chemical reaction that is being used for the titration. The two most common types of reactions for which normality is used are acid‐base reactions and redox (reduction ...
... when the titration reaction is unknown or just not used. Consequently, definitions for these terms vary depending on the type of chemical reaction that is being used for the titration. The two most common types of reactions for which normality is used are acid‐base reactions and redox (reduction ...
Double Displacement Reactions
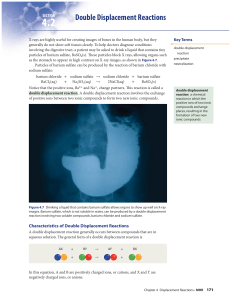
... Figure 4.7 Drinking a liquid that contains barium sulfate allows organs to show up well on X-ray images. Barium sulfate, which is not soluble in water, can be produced by a double displacement reaction involving two soluble compounds, barium chloride and sodium sulfate. ...
... Figure 4.7 Drinking a liquid that contains barium sulfate allows organs to show up well on X-ray images. Barium sulfate, which is not soluble in water, can be produced by a double displacement reaction involving two soluble compounds, barium chloride and sodium sulfate. ...