`A` LEVEL H2 CHEMISTRY ORGANIC REACTIONS SUMMARY By
... (f) describe hydrogen bonding, using ammonia and water as examples of molecules containing -NH and -OH groups (g) explain the terms bond energy, bond length and bond polarity and use them to compare the reactivities of covalent bonds (h) describe intermolecular forces (van der Waals’ forces), based ...
... (f) describe hydrogen bonding, using ammonia and water as examples of molecules containing -NH and -OH groups (g) explain the terms bond energy, bond length and bond polarity and use them to compare the reactivities of covalent bonds (h) describe intermolecular forces (van der Waals’ forces), based ...
Document
... Graphite is a non metal but can conduct electricity. This is because graphite has free(delocalised electrons) HT Graphite has free electrons because each carbon atom is covalently bonded to 3 others leaving 1 electron free per carbon atom. Graphite has strong covalent bonds and weak intermolecular f ...
... Graphite is a non metal but can conduct electricity. This is because graphite has free(delocalised electrons) HT Graphite has free electrons because each carbon atom is covalently bonded to 3 others leaving 1 electron free per carbon atom. Graphite has strong covalent bonds and weak intermolecular f ...
Chemistry
... Molecular formula and Kekule’s structure. Stability and carbon-carbon bond lengths of benzene, resonance structure, MO picture. Aromaticity: Huckel rule, aromatic ions, Aromatic electrophilic substitution –Mechanism of nitration, halogenation, sulphonation, Friedel-Craft reaction. Effect of substitu ...
... Molecular formula and Kekule’s structure. Stability and carbon-carbon bond lengths of benzene, resonance structure, MO picture. Aromaticity: Huckel rule, aromatic ions, Aromatic electrophilic substitution –Mechanism of nitration, halogenation, sulphonation, Friedel-Craft reaction. Effect of substitu ...
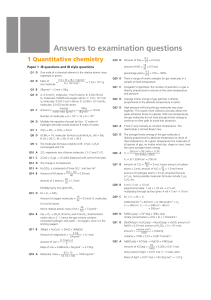
Stoichiometry intro
... Remember that the coefficients from a balanced reaction represent the ratio of the moles of substances that react and form during a chemical reaction. These numbers are fixed - they do not change We can use these ratios to predict the amounts of substances that react and form in a reaction when ...
... Remember that the coefficients from a balanced reaction represent the ratio of the moles of substances that react and form during a chemical reaction. These numbers are fixed - they do not change We can use these ratios to predict the amounts of substances that react and form in a reaction when ...
1 Discussion questions 22.1 Consult literature sources and list the
... 22.11 The addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes has played a fundamental role in the investigation of organic reaction mechanisms. In one study (M.J. Haugh and D.R. Dalton, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 97, 5674 (1975)), high pressures of hydrogen chloride (up to 25 atm) and propene (up to 5 atm) were exami ...
... 22.11 The addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes has played a fundamental role in the investigation of organic reaction mechanisms. In one study (M.J. Haugh and D.R. Dalton, J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 97, 5674 (1975)), high pressures of hydrogen chloride (up to 25 atm) and propene (up to 5 atm) were exami ...
Chem 2A Final Review
... SOF3- (S is the central atom) 74. Draw a 3-D diagram for each molecule and indicate if the molecule is polar or non-polar. a. OF2 b. PBr3 75. Draw the 3-D structure. Give the VSEPR electron-pair name, the molecular shape name for the following. a. NF3 b. CCl4 c. CF3+ 76. Draw and example of hydrogen ...
... SOF3- (S is the central atom) 74. Draw a 3-D diagram for each molecule and indicate if the molecule is polar or non-polar. a. OF2 b. PBr3 75. Draw the 3-D structure. Give the VSEPR electron-pair name, the molecular shape name for the following. a. NF3 b. CCl4 c. CF3+ 76. Draw and example of hydrogen ...
Solutions (DOC format, upgraded July 20)
... kJ·mol–1. The ordinate is log p = 1.2. The ratio of the lengths of the line segments from this point to the borders of the phase coexistence curve (blue and red line segments in the figure below) is equal to the ratio of the number of moles of methane in vapor and liquid phases. One can find that ab ...
... kJ·mol–1. The ordinate is log p = 1.2. The ratio of the lengths of the line segments from this point to the borders of the phase coexistence curve (blue and red line segments in the figure below) is equal to the ratio of the number of moles of methane in vapor and liquid phases. One can find that ab ...
SAT - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... • The number of unpaired valence electrons in a nonmetal tells you how many covalent bonds that atom can form with other nonmetals or how many electrons it wants to gain from metals to form an ion. • The number of valence electrons in a metal tells you how many electrons the metal will lose to nonme ...
... • The number of unpaired valence electrons in a nonmetal tells you how many covalent bonds that atom can form with other nonmetals or how many electrons it wants to gain from metals to form an ion. • The number of valence electrons in a metal tells you how many electrons the metal will lose to nonme ...
Example 1-2
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
chem A exercise package C
... regions, such as for oxygen, will result in the gain of two electrons. This process of overlapping atoms is called covalent bonding. The substance that results from covalent bonding is called a covalent substance. The process of overlapping atoms will keep occurring for a particular atom until it ha ...
... regions, such as for oxygen, will result in the gain of two electrons. This process of overlapping atoms is called covalent bonding. The substance that results from covalent bonding is called a covalent substance. The process of overlapping atoms will keep occurring for a particular atom until it ha ...
chemical reaction
... decomposition, single-displacement, and doubledisplacement reactions. • Classify a reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement, or combustion reaction. • List three kinds of synthesis reactions and six kinds of decomposition reactions. ...
... decomposition, single-displacement, and doubledisplacement reactions. • Classify a reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement, or combustion reaction. • List three kinds of synthesis reactions and six kinds of decomposition reactions. ...
Example 7.1: The following decomposition was studied at a given
... Determination of the Rate Law In the previous section we noted that the order of each reactant could be determined experimentally by measuring the initial rate of reaction over a range of initial concentrations. If we do this for each reactant then it is possible to determine the overall order of th ...
... Determination of the Rate Law In the previous section we noted that the order of each reactant could be determined experimentally by measuring the initial rate of reaction over a range of initial concentrations. If we do this for each reactant then it is possible to determine the overall order of th ...
PREPARATORY PROBLEMS (Theoretical)
... 5. Based on your answers on questions (3)-(4) and using the formula above calculate l. How does this value compare with the structure of retinal molecule? ...
... 5. Based on your answers on questions (3)-(4) and using the formula above calculate l. How does this value compare with the structure of retinal molecule? ...
PREPARATORY PROBLEMS (Theoretical)
... 5. Based on your answers on questions (3)-(4) and using the formula above calculate l. How does this value compare with the structure of retinal molecule? ...
... 5. Based on your answers on questions (3)-(4) and using the formula above calculate l. How does this value compare with the structure of retinal molecule? ...
PREPARATORY PROBLEMS
... 5. Based on your answers on questions (3)-(4) and using the formula above calculate l. How does this value compare with the structure of retinal molecule? ...
... 5. Based on your answers on questions (3)-(4) and using the formula above calculate l. How does this value compare with the structure of retinal molecule? ...
CHAPTER TWO SOLID STATE REACTIONS 2.0 Introduction The
... five coordination sites have been observed to be occupied by water and the 1,10phenanthroline ligand. This provided yet another facile example in which the solid state reaction produced new compounds which are not accessible in solution media. Many other solid state reactions of this type, in which ...
... five coordination sites have been observed to be occupied by water and the 1,10phenanthroline ligand. This provided yet another facile example in which the solid state reaction produced new compounds which are not accessible in solution media. Many other solid state reactions of this type, in which ...
mc_ch08 - MrBrownsChem1LCHS
... decomposition, single-displacement, and doubledisplacement reactions. • Classify a reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement, or combustion reaction. • List three kinds of synthesis reactions and six kinds of decomposition reactions. ...
... decomposition, single-displacement, and doubledisplacement reactions. • Classify a reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement, or combustion reaction. • List three kinds of synthesis reactions and six kinds of decomposition reactions. ...
Chapter 4 Solution Chemistry
... attraction among the particles of the solute (solutesolute interactions) and the forces of attraction between the solvent molecules and the particles in the solute (solvent-solute interactions). Which interactions are stronger determines whether the solute dissolves. ...
... attraction among the particles of the solute (solutesolute interactions) and the forces of attraction between the solvent molecules and the particles in the solute (solvent-solute interactions). Which interactions are stronger determines whether the solute dissolves. ...
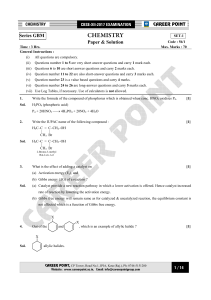
- Career Point Kota
... resonance hence the reactivity reduce" (b) CH3–NH2 is more basic then C6H5–NH2 Because In case of aniline the L.P of –NH2 (amino group) are in conjugation with benzene ring due to which e– density less available on N-atom hence higher the "electron density on N-atom more will be the basicity." ...
... resonance hence the reactivity reduce" (b) CH3–NH2 is more basic then C6H5–NH2 Because In case of aniline the L.P of –NH2 (amino group) are in conjugation with benzene ring due to which e– density less available on N-atom hence higher the "electron density on N-atom more will be the basicity." ...
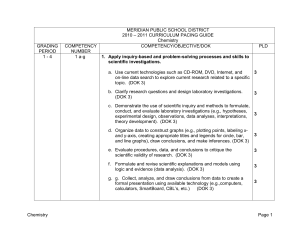
MERIDIAN PUBLIC SCHOOL DISTRICT
... 2. Demonstrate an understanding of the atomic model of matter by explaining atomic structure and chemical bonding. b. Research and explain crucial contributions and critical experiments of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, de Broglie, and Schrődinger and describe how each discovery contributed to t ...
... 2. Demonstrate an understanding of the atomic model of matter by explaining atomic structure and chemical bonding. b. Research and explain crucial contributions and critical experiments of Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, de Broglie, and Schrődinger and describe how each discovery contributed to t ...
Kinetics of Excited-State Ti(a5F)
... As the result of these values, the Reynolds number of our flow tube is about half of that of the flow tube of RW, and this gives 8 cm of the distance necessary for He to develop its characteristic parabolic velocity profile. Therefore, we believe that the flow in our tube is fully developed at the f ...
... As the result of these values, the Reynolds number of our flow tube is about half of that of the flow tube of RW, and this gives 8 cm of the distance necessary for He to develop its characteristic parabolic velocity profile. Therefore, we believe that the flow in our tube is fully developed at the f ...
Chemical Kinetics
... proceeds, the loss of reactants (and the increase in product) will be stoichiometrically linked. Setting the loss of reactants (or appearance of product) = x, we get ...
... proceeds, the loss of reactants (and the increase in product) will be stoichiometrically linked. Setting the loss of reactants (or appearance of product) = x, we get ...
Redox Introduction
... particle to another. 2. Oxidation is the process by which electrons are apparently removed from an atom or group of atoms. 3. Reduction is the process by which electrons are apparently added to atoms or groups of atoms. 3. Any substance in a reaction which loses electrons is a reducing agent. 4. Any ...
... particle to another. 2. Oxidation is the process by which electrons are apparently removed from an atom or group of atoms. 3. Reduction is the process by which electrons are apparently added to atoms or groups of atoms. 3. Any substance in a reaction which loses electrons is a reducing agent. 4. Any ...