Textbook PowerPoint
... Sensory information from body Occipital lobe Interprets visual information Temporal lobe Hearing, balance, some emotions and motivations ...
... Sensory information from body Occipital lobe Interprets visual information Temporal lobe Hearing, balance, some emotions and motivations ...
Chapter 15 - Austin Community College
... • The BBB is absent in some places of the 3rd and 4th ventricles at patches called circumventricular organs where some substances may pass into the brain tissue. ...
... • The BBB is absent in some places of the 3rd and 4th ventricles at patches called circumventricular organs where some substances may pass into the brain tissue. ...
leadership
... Most importantly: Dualism fails to scientifically explain Where and how the nonphysical soul/mind connects with the ...
... Most importantly: Dualism fails to scientifically explain Where and how the nonphysical soul/mind connects with the ...
Topic Presentation: Biopsychology
... i. After Ashley permanently damaged her left frontal lobe and lost the ability to speak (though she can still understand speech) she was able to recover some of her speech due ...
... i. After Ashley permanently damaged her left frontal lobe and lost the ability to speak (though she can still understand speech) she was able to recover some of her speech due ...
the brain
... • Is the visual cortex – Receives, integrates and processes visual information – Clinically referred to as Brodmann area 17 ...
... • Is the visual cortex – Receives, integrates and processes visual information – Clinically referred to as Brodmann area 17 ...
Step back and look at the Science
... Neuroscience and Psychology …or between : Cognitive models of information processing And structures and processes in the brain ...
... Neuroscience and Psychology …or between : Cognitive models of information processing And structures and processes in the brain ...
Aotearoa Neuroscience Postdoctoral Fellow Projects
... CBR PIs: Dr Maurice A Curtis and Dr Henry J Waldvogel The inhibitory system in the human brain plays a critical role during development and continues to impact on normal brain function as well as being a major drug target for known neuroactive pharmaceuticals and in novel drug design. How the inhibi ...
... CBR PIs: Dr Maurice A Curtis and Dr Henry J Waldvogel The inhibitory system in the human brain plays a critical role during development and continues to impact on normal brain function as well as being a major drug target for known neuroactive pharmaceuticals and in novel drug design. How the inhibi ...
brain and cranial nerves
... --they are concerned with the reception and interpretation of sensory impulses. --Sensory areas are: Primary somatosensory area. Primary visual area. Primary auditory area. Primary gustatory area. ii. Motor areas: --control and govern muscular movements --areas are: primary motor area. Broca’s speec ...
... --they are concerned with the reception and interpretation of sensory impulses. --Sensory areas are: Primary somatosensory area. Primary visual area. Primary auditory area. Primary gustatory area. ii. Motor areas: --control and govern muscular movements --areas are: primary motor area. Broca’s speec ...
Central Nervous System
... Other sulci form the boundaries of the temporal lobe and the occipital lobe. ...
... Other sulci form the boundaries of the temporal lobe and the occipital lobe. ...
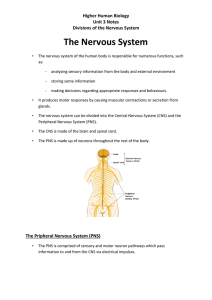
The Nervous System - Cathkin High School
... Divisions of the Nervous System 1. The information from left eye went to the right (cerebral) hemisphere. 2. The right hemisphere controls / moves the left hand (so the patient points to “HE”). 3. The information from right eye went to the left hemisphere. 4. Information cannot be transferred to the ...
... Divisions of the Nervous System 1. The information from left eye went to the right (cerebral) hemisphere. 2. The right hemisphere controls / moves the left hand (so the patient points to “HE”). 3. The information from right eye went to the left hemisphere. 4. Information cannot be transferred to the ...
Brain and NS Quiz
... • The parietal lobes are involved with touch and movement in the environment • The temporal lobes are involved in hearing and language ...
... • The parietal lobes are involved with touch and movement in the environment • The temporal lobes are involved in hearing and language ...
Everson Nervous system I. Functional/ Anatomical Divisions A
... 2. functions concern sensations 3. integrates sensory info for cerebrum interpretation v. Cerebrum (Cerebral hemispheres) 1. Right and left cerebral hemispheres a. Separated by longitudinal fissure b. Connected by Corpus callosum c. Sulci and gyri (grooves and bumps) d. Each contain a lateral ventri ...
... 2. functions concern sensations 3. integrates sensory info for cerebrum interpretation v. Cerebrum (Cerebral hemispheres) 1. Right and left cerebral hemispheres a. Separated by longitudinal fissure b. Connected by Corpus callosum c. Sulci and gyri (grooves and bumps) d. Each contain a lateral ventri ...
Brain Plasticity
... musicians, and lowest in non-musicians in several brain areas involved in playing music: motor regions, anterior superior parietal areas and inferior temporal areas. Finally, Draganski and colleagues (2006) recently showed that extensive learning of abstract information can also trigger some plastic ...
... musicians, and lowest in non-musicians in several brain areas involved in playing music: motor regions, anterior superior parietal areas and inferior temporal areas. Finally, Draganski and colleagues (2006) recently showed that extensive learning of abstract information can also trigger some plastic ...
The Brain!
... controlling our instincts (brain stem), our emotions (limbic system), and our thoughts (cortex). The brain is also divided into the left and right hemispheres, or halves. The left side is often known as the detail oriented, get to the point, speech and happiness center; while the right side is kno ...
... controlling our instincts (brain stem), our emotions (limbic system), and our thoughts (cortex). The brain is also divided into the left and right hemispheres, or halves. The left side is often known as the detail oriented, get to the point, speech and happiness center; while the right side is kno ...
Nervous System Notes File
... iv. Left Hemisphere: language, reasoning and the ability to analyze and think critically about math and science v. Right Hemisphere: process music, art and spatial relationships vi. Both Hemispheres have 4 Lobes or sections 1. The Frontal Lobe – Controls Voluntary movements; has a role in the use o ...
... iv. Left Hemisphere: language, reasoning and the ability to analyze and think critically about math and science v. Right Hemisphere: process music, art and spatial relationships vi. Both Hemispheres have 4 Lobes or sections 1. The Frontal Lobe – Controls Voluntary movements; has a role in the use o ...
Step back and look at the Science
... Neuroscience and Psychology …or between : Cognitive models of information processing And structures and processes in the brain ...
... Neuroscience and Psychology …or between : Cognitive models of information processing And structures and processes in the brain ...
Step back and look at the Science
... Neuroscience and Psychology …or between : Cognitive models of information processing And structures and processes in the brain ...
... Neuroscience and Psychology …or between : Cognitive models of information processing And structures and processes in the brain ...
Myers AP - Unit 3B
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
... above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. ...
Biological Bases
... Old brain parts are what exist in very young children, and the new brain develops later The old brain developed first according to evolution The old brain becomes more active as we grow older The new brain deals with new information, while the old brain deals with information gathered when we were c ...
... Old brain parts are what exist in very young children, and the new brain develops later The old brain developed first according to evolution The old brain becomes more active as we grow older The new brain deals with new information, while the old brain deals with information gathered when we were c ...
Payton
... • made of two things: • Flap- side lobe • wrinkles • brains vary in size and in the number of "folds" on their surface • brains are remarkably similar in overall structure Animal Brains (vertebrates) Brain/Body Weight linear relationship between body weight and brain weight • above the line, your br ...
... • made of two things: • Flap- side lobe • wrinkles • brains vary in size and in the number of "folds" on their surface • brains are remarkably similar in overall structure Animal Brains (vertebrates) Brain/Body Weight linear relationship between body weight and brain weight • above the line, your br ...
Chapter 2 - bobcat
... • You central nervous system’s hungry brain activates and guides the muscles of your arm and hand via your peripheral nervous system’s motor neurons. • As you pick up the fork, your brain processes the information from your sensory nervous system, enabling it to continue to guide the fork to your ...
... • You central nervous system’s hungry brain activates and guides the muscles of your arm and hand via your peripheral nervous system’s motor neurons. • As you pick up the fork, your brain processes the information from your sensory nervous system, enabling it to continue to guide the fork to your ...
The Teenage Brain - Welcome to Senior Biology
... Speaking Awareness of abilities Self-control “do the right thing” ...
... Speaking Awareness of abilities Self-control “do the right thing” ...
Answer Key
... 6. During an action potential, the electrical state of the axon becomes: A) polarized, as positively charged atoms are admitted. B) polarized, as negatively charged atoms are admitted. C) depolarized, as positively charged atoms are admitted. D) depolarized, as negatively charged atoms are admitted ...
... 6. During an action potential, the electrical state of the axon becomes: A) polarized, as positively charged atoms are admitted. B) polarized, as negatively charged atoms are admitted. C) depolarized, as positively charged atoms are admitted. D) depolarized, as negatively charged atoms are admitted ...
Lateralization of brain function

The longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. The hemispheres exhibit strong, but not complete, bilateral symmetry in both structure and function. For example, structurally, the lateral sulcus generally is longer in the left hemisphere than in the right hemisphere, and functionally, Broca's area and Wernicke's area are located in the left cerebral hemisphere for about 95% of right-handers, but about 70% of left-handers.Broad generalizations are often made in ""pop"" psychology about one side or the other having characteristic labels, such as ""logical"" for the left side or ""creative"" for the right. These labels are not supported by studies on lateralization, as lateralization does not add specialized usage from either hemisphere. Both hemispheres contribute to both kinds of processes, and experimental evidence provides little support for correlating the structural differences between the sides with such broadly defined functional differences.The extent of any modularity, or specialization of brain function by area, remains under investigation. If a specific region of the brain, or even an entire hemisphere, is injured or destroyed, its functions can sometimes be assumed by a neighboring region in the same hemisphere or the corresponding region in the other hemisphere, depending upon the area damaged and the patient's age. When injury interferes with pathways from one area to another, alternative (indirect) connections may develop to communicate information with detached areas, despite the inefficiencies.Brain function lateralization is evident in the phenomena of right- or left-handedness and of right or left ear preference, but a person's preferred hand is not a clear indication of the location of brain function. Although 95% of right-handed people have left-hemisphere dominance for language, 18.8% of left-handed people have right-hemisphere dominance for language function. Additionally, 19.8% of the left-handed have bilateral language functions. Even within various language functions (e.g., semantics, syntax, prosody), degree (and even hemisphere) of dominance may differ.Additionally, although some functions are lateralized, these are only a tendency. The trend across many individuals may also vary significantly as to how any specific function is implemented. The areas of exploration of this causal or effectual difference of a particular brain function include its gross anatomy, dendritic structure, and neurotransmitter distribution. The structural and chemical variance of a particular brain function, between the two hemispheres of one brain or between the same hemisphere of two different brains, is still being studied. Short of having undergone a hemispherectomy (removal of a cerebral hemisphere), no one is a ""left-brain only"" or ""right-brain only"" person.