Ecology unit ch 2-5
... plants and animals interact. You are probably familiar with interdependence among animals and plants linked by a food web. In addition, we will look at other types of interactions which occur as a result of adaptation, such as the mutually beneficial relationship between honey guide birds and badger ...
... plants and animals interact. You are probably familiar with interdependence among animals and plants linked by a food web. In addition, we will look at other types of interactions which occur as a result of adaptation, such as the mutually beneficial relationship between honey guide birds and badger ...
Food webs in space: On the interplay of dynamic instability and
... One of the core ideas of island biogeographic theory is that area can influence community structure via colonization and extinction. All else being equal, a species is more likely to be found on a large island, than a small island, because the large island provides a larger target for colonization a ...
... One of the core ideas of island biogeographic theory is that area can influence community structure via colonization and extinction. All else being equal, a species is more likely to be found on a large island, than a small island, because the large island provides a larger target for colonization a ...
AP Ecology Review Questions 51-56
... 9. Provide 2 different examples of the relationship between behavioral trait and natural selection. Why does this relationship “make sense”? 10. The statement can be made that “there are risks and benefits” to everything.” How does this relate to the optimal foraging theory? 11. What is generally th ...
... 9. Provide 2 different examples of the relationship between behavioral trait and natural selection. Why does this relationship “make sense”? 10. The statement can be made that “there are risks and benefits” to everything.” How does this relate to the optimal foraging theory? 11. What is generally th ...
Alternative stable states and regional community structure
... previous occupant reduced resource levels below what is required for invasion by another species. Thus, species may alter the local environment in ways that favor later colonization by conspecifics. To consider the dynamics of such a system, we modified Model 1 to include a latency period after a spec ...
... previous occupant reduced resource levels below what is required for invasion by another species. Thus, species may alter the local environment in ways that favor later colonization by conspecifics. To consider the dynamics of such a system, we modified Model 1 to include a latency period after a spec ...
Comparative studies of terrestrial vertebrates in urban areas
... Conservation and management questions are at the interface between questions raised by ecologists studying cities and urban residents. Management questions are shaped by the two sometimes conflicting goals for wildlife conservation in cities: to maintain regional biodiversity, and to provide opportu ...
... Conservation and management questions are at the interface between questions raised by ecologists studying cities and urban residents. Management questions are shaped by the two sometimes conflicting goals for wildlife conservation in cities: to maintain regional biodiversity, and to provide opportu ...
Lesson Overview
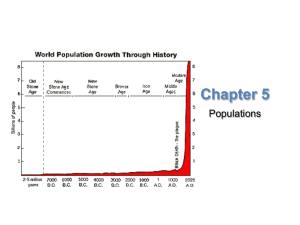
... This kind of exponential growth could not continue forever. Two centuries ago, English economist Thomas Malthus suggested that only war, famine, and disease could limit human population growth. ...
... This kind of exponential growth could not continue forever. Two centuries ago, English economist Thomas Malthus suggested that only war, famine, and disease could limit human population growth. ...
LOTPL_MWRA - University of Massachusetts Boston
... Disadvantages of this project: • No physical vouchers - if a detail is not captured by the photographer, it is lost (ID can be hard) • More likely to miss “skittish” creatures • Biased towards larger, more eye-catching organisms • Biased against anything that is good at hiding, or is in the soil (r ...
... Disadvantages of this project: • No physical vouchers - if a detail is not captured by the photographer, it is lost (ID can be hard) • More likely to miss “skittish” creatures • Biased towards larger, more eye-catching organisms • Biased against anything that is good at hiding, or is in the soil (r ...
Ecology2 - WordPress.com
... – Pioneer species in secondary succession are usually plants that begin to grow in the disturbed area. – This is much faster than primary succession ...
... – Pioneer species in secondary succession are usually plants that begin to grow in the disturbed area. – This is much faster than primary succession ...
Density-dependent dispersal may explain the mid
... sign of wilting or any other damage; A. Mashanova, unpubl. data]. The above reasons make P. alni a convenient species to study density-dependent emigration (which is the first stage of dispersal). Another useful feature of P. alni biology is that immigration into colonised patches is negligible— whe ...
... sign of wilting or any other damage; A. Mashanova, unpubl. data]. The above reasons make P. alni a convenient species to study density-dependent emigration (which is the first stage of dispersal). Another useful feature of P. alni biology is that immigration into colonised patches is negligible— whe ...
Ecology: Organisms and their environment
... observed a scene like this before. What was recently a clear, grass-filled field or lawn is now crowded with hundreds, perhaps thousands, of bright yellow dandelions. Why do these plants crop up so quickly and in such large numbers? Dandelions are a problem to gardeners, but to population biologists ...
... observed a scene like this before. What was recently a clear, grass-filled field or lawn is now crowded with hundreds, perhaps thousands, of bright yellow dandelions. Why do these plants crop up so quickly and in such large numbers? Dandelions are a problem to gardeners, but to population biologists ...
Population Ecology and Ecosystems Ecology Human Population
... technology may further increase carrying capacity • Eventually, densitydependent factors will slow growth ...
... technology may further increase carrying capacity • Eventually, densitydependent factors will slow growth ...
Interaction between competition and predation in cave stream
... is simply the average of niche breadths for each sampling dah.. (see Table 1), and total niche breadth is computed by using the average habitat frequency over all sampling dates (Fig. 1). If niches are different at different times, total niche breadth will be greater than average niche breadth. If n ...
... is simply the average of niche breadths for each sampling dah.. (see Table 1), and total niche breadth is computed by using the average habitat frequency over all sampling dates (Fig. 1). If niches are different at different times, total niche breadth will be greater than average niche breadth. If n ...
Natural Selection Activity
... 7. Measure the variation in the Surviving Population Collect the remaining paper squares from the paper and sort them by shade. Record the number of each shade of the remaining paper squares. 8. Create a new generation Simulate reproduction among the paper squares by adding two paper squares for eac ...
... 7. Measure the variation in the Surviving Population Collect the remaining paper squares from the paper and sort them by shade. Record the number of each shade of the remaining paper squares. 8. Create a new generation Simulate reproduction among the paper squares by adding two paper squares for eac ...
Maureen McClung - Biology Department | UNC Chapel Hill
... repeatedly by many scientists over the last century (see reviews in Schoener 1989; Griesemer 1992). Even the identity of the first person to use the term “niche” as it relates to ecology is unresolved. However, most authors agree that it was Joseph Grinnell (1917b) who popularized its use in his pap ...
... repeatedly by many scientists over the last century (see reviews in Schoener 1989; Griesemer 1992). Even the identity of the first person to use the term “niche” as it relates to ecology is unresolved. However, most authors agree that it was Joseph Grinnell (1917b) who popularized its use in his pap ...
Maureen McClung - Biology Department | UNC Chapel Hill
... repeatedly by many scientists over the last century (see reviews in Schoener 1989; Griesemer 1992). Even the identity of the first person to use the term “niche” as it relates to ecology is unresolved. However, most authors agree that it was Joseph Grinnell (1917b) who popularized its use in his pap ...
... repeatedly by many scientists over the last century (see reviews in Schoener 1989; Griesemer 1992). Even the identity of the first person to use the term “niche” as it relates to ecology is unresolved. However, most authors agree that it was Joseph Grinnell (1917b) who popularized its use in his pap ...
Overgrazing - IDC Technologies
... In many parts of Africa subsistence farmers practice high density animal occupancy that produces sub-optimal yields per animal, with high, even if unsustainable, yields per hectare. Some argue that there is remarkably little reliable data available to fully understand the syndromes of overgrazing, a ...
... In many parts of Africa subsistence farmers practice high density animal occupancy that produces sub-optimal yields per animal, with high, even if unsustainable, yields per hectare. Some argue that there is remarkably little reliable data available to fully understand the syndromes of overgrazing, a ...
The Value of Animal Behavior in Evaluations of Restoration Success
... often play more significant ecological roles than others and/or are of greater conservation concern than others. For example, one or a few species may be particularly important seed dispersers or pollinators in a system (e.g., Wenny & Levey 1998; Ricketts 2004). Thus, a more strategic use of resourc ...
... often play more significant ecological roles than others and/or are of greater conservation concern than others. For example, one or a few species may be particularly important seed dispersers or pollinators in a system (e.g., Wenny & Levey 1998; Ricketts 2004). Thus, a more strategic use of resourc ...
Species-Area Relationship for Stream Fishes
... a stream may be viewed conceptually as an archipelago, albeit with two important differences from true islands. First, single patches of habitat are generally too small to support self-sustaining populations of fish. In this regard, stream habitats are analogous to small woodlots for bird population ...
... a stream may be viewed conceptually as an archipelago, albeit with two important differences from true islands. First, single patches of habitat are generally too small to support self-sustaining populations of fish. In this regard, stream habitats are analogous to small woodlots for bird population ...
Mahogany Glider (Petaurus gracilis)
... fragmented band of forest extending around 140km from Toomulla north of Townsville to Tully and up to 40km inland. The mahogany glider requires a relatively open forest structure for efficient gliding and tends to avoid dense vegetation such as rainforest. ...
... fragmented band of forest extending around 140km from Toomulla north of Townsville to Tully and up to 40km inland. The mahogany glider requires a relatively open forest structure for efficient gliding and tends to avoid dense vegetation such as rainforest. ...
A General Approach to the Modelling of Trophic Chains
... Mass conservation is a controversial issue in population dynamics. Some authors have argued that population dynamics models do not have to conform to ...
... Mass conservation is a controversial issue in population dynamics. Some authors have argued that population dynamics models do not have to conform to ...
Effect of human disturbance on long
... enable managers to make informed decisions about how land is accessed. This becomes increasingly important when new areas of habitat are being created with the aim of increasing population numbers of target species. If the areas being created are also subject to human disturbance, it is possible tha ...
... enable managers to make informed decisions about how land is accessed. This becomes increasingly important when new areas of habitat are being created with the aim of increasing population numbers of target species. If the areas being created are also subject to human disturbance, it is possible tha ...
Research Guidelines - IUCN Otter Specialist Group
... There is, of course, a kind of ‘glamour factor’ attached to any otter research, especially in behavioural studies, as it involves highly charismatic species, and the general public often envies those who are able to do research on them and spend time with otters in the field. Scientific research att ...
... There is, of course, a kind of ‘glamour factor’ attached to any otter research, especially in behavioural studies, as it involves highly charismatic species, and the general public often envies those who are able to do research on them and spend time with otters in the field. Scientific research att ...
Population Ecology
... Population Dispersion Population dispersion is how individuals of a species are arranged in their environment. There are three kinds. Clumped dispersion is usually due to a species being concentrated in areas most favourable for survival (ex. Cattails in wet soils lining ponds or lakes) or social b ...
... Population Dispersion Population dispersion is how individuals of a species are arranged in their environment. There are three kinds. Clumped dispersion is usually due to a species being concentrated in areas most favourable for survival (ex. Cattails in wet soils lining ponds or lakes) or social b ...
How can we apply theories of habitat selection to wildlife
... occupied by the population. Thus, if two species occupy completely separate habitats, average competition is zero. If a small number of individuals occupy the preferred habitat of their competitor the average competitive effect will be less than when a large number of individuals co-occupy the same ...
... occupied by the population. Thus, if two species occupy completely separate habitats, average competition is zero. If a small number of individuals occupy the preferred habitat of their competitor the average competitive effect will be less than when a large number of individuals co-occupy the same ...