protein
... catabolism (breakdown) of proteins in food, and then delivered to the cells by the blood vessels. Inside the cells, they are used for anabolism (building) of proteins or undergo deamination (removal of the amine functional group) for ATP production in cellular ...
... catabolism (breakdown) of proteins in food, and then delivered to the cells by the blood vessels. Inside the cells, they are used for anabolism (building) of proteins or undergo deamination (removal of the amine functional group) for ATP production in cellular ...
Biochemistry Practice Questions
... nucleotides in each original strand to produce two new complete DNA strands. The diagram below shows a simple model of this process. The letters A, T, C, and G represent the four nucleotides. ...
... nucleotides in each original strand to produce two new complete DNA strands. The diagram below shows a simple model of this process. The letters A, T, C, and G represent the four nucleotides. ...
Lecture 5
... • The amount of DNA that eukaryotes have varies; the amount of DNA is not necessarily related to the complexity (Amoeba proteus has a larger amount of DNA than Homo sapiens) • Eukaryotic chromosomes are integrated with proteins that help it fold (protein + DNA = chromatin) • Chromosomes become visib ...
... • The amount of DNA that eukaryotes have varies; the amount of DNA is not necessarily related to the complexity (Amoeba proteus has a larger amount of DNA than Homo sapiens) • Eukaryotic chromosomes are integrated with proteins that help it fold (protein + DNA = chromatin) • Chromosomes become visib ...
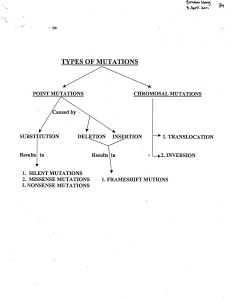
CHROMOSAL MUTATIONS SUBSTITUTION
... • For examp le: ACA and ACU both code for Threon ine. a.- : ACA : Threon ine The codon for Threo nine is If the third base 'A' is Substi tuted .,..: ACU : Still it is Threon ine. ...
... • For examp le: ACA and ACU both code for Threon ine. a.- : ACA : Threon ine The codon for Threo nine is If the third base 'A' is Substi tuted .,..: ACU : Still it is Threon ine. ...
RNA/DNA catalysts
... groups used for catalysis? structures formed? Know about transesterification & cleavage reactions Know four types of natural catalytic RNAs (group I introns, group II introns, RNase P, small self-cleaving), what reactions they perform, know basics of their secondary and tertiary structure, requireme ...
... groups used for catalysis? structures formed? Know about transesterification & cleavage reactions Know four types of natural catalytic RNAs (group I introns, group II introns, RNase P, small self-cleaving), what reactions they perform, know basics of their secondary and tertiary structure, requireme ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods
... washing and nucleic acids were isolated using the DNA Mini and the RNeasy kit (QIAGEN) according to the manufacturer's manuals. HIV-1 DNA absolute quantification and RNA relative quantification was determined by qPCR using the LightCycler480 Software (Roche, Mannheim, Germany). For absolute quantifi ...
... washing and nucleic acids were isolated using the DNA Mini and the RNeasy kit (QIAGEN) according to the manufacturer's manuals. HIV-1 DNA absolute quantification and RNA relative quantification was determined by qPCR using the LightCycler480 Software (Roche, Mannheim, Germany). For absolute quantifi ...
Acc_Bio_DNA_Webquest
... 18. Give an example of how an environmental factor can influence a trait. ...
... 18. Give an example of how an environmental factor can influence a trait. ...
PCT/MIA/8/2 ADD.2
... PCT Rule 13 specifies that the international application shall relate to one invention only or to a group of inventions so linked as to form a single general inventive concept (“requirement of unity of invention”). The rule further states that the requirement is fulfilled only when there is a techni ...
... PCT Rule 13 specifies that the international application shall relate to one invention only or to a group of inventions so linked as to form a single general inventive concept (“requirement of unity of invention”). The rule further states that the requirement is fulfilled only when there is a techni ...
Francis Harry Compton Crick – Nobel Lecture
... and cytosine in (presumably) random order will increase the incorporation of the amino acids phenylalanine, serine, leucine, and proline, and possibly threonine. By using polymers of different composition and assuming a triplet code one can deduce limited information about the composition of certain ...
... and cytosine in (presumably) random order will increase the incorporation of the amino acids phenylalanine, serine, leucine, and proline, and possibly threonine. By using polymers of different composition and assuming a triplet code one can deduce limited information about the composition of certain ...
Bulletin - Sigma
... AccuTaq LA Polymerase Mix combines Sigma’s high quality Taq DNA polymerase with a small amount of a thermostable proofreading enzyme. The result is an enzyme mix that amplifies genomic targets in excess of 20 kb. Using a less complex template, such as bacterial genomic and viral DNA, amplifications ...
... AccuTaq LA Polymerase Mix combines Sigma’s high quality Taq DNA polymerase with a small amount of a thermostable proofreading enzyme. The result is an enzyme mix that amplifies genomic targets in excess of 20 kb. Using a less complex template, such as bacterial genomic and viral DNA, amplifications ...
Chapter 13
... • Four types of bases are associated with the DNA structure: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). • The bases on each strand are properly aligned in a double-helix configuration, which is two strands of DNA coiled together. • As a result, adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pa ...
... • Four types of bases are associated with the DNA structure: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). • The bases on each strand are properly aligned in a double-helix configuration, which is two strands of DNA coiled together. • As a result, adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pa ...
DNA
... • Four types of bases are associated with the DNA structure: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). • The bases on each strand are properly aligned in a double-helix configuration, which is two strands of DNA coiled together. • As a result, adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pa ...
... • Four types of bases are associated with the DNA structure: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). • The bases on each strand are properly aligned in a double-helix configuration, which is two strands of DNA coiled together. • As a result, adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pa ...
here
... This course will provide background knowledge of five basic units of Biochemistry and the relationship between genes and proteins within the cell. Unit 1 deals with the molecules of life, DNA, RNA, nucleotides and the central dogma of molecular biology. Unit 2 covers the decoding of the genetic code ...
... This course will provide background knowledge of five basic units of Biochemistry and the relationship between genes and proteins within the cell. Unit 1 deals with the molecules of life, DNA, RNA, nucleotides and the central dogma of molecular biology. Unit 2 covers the decoding of the genetic code ...
A central problem in bioinformatics
... coordinates of proteins of average length ~400 residues: 16000 entries Not only are the individual databanks large, but their sizes are increasing as a very high rate. ...
... coordinates of proteins of average length ~400 residues: 16000 entries Not only are the individual databanks large, but their sizes are increasing as a very high rate. ...
Preview Sample 2
... are linked to glycerol, with the sugar’s third hydroxyl group attached to a phosphate group. Often a polar or ionized nitrogen-containing molecule is attached to the phosphate. Phospholipids, therefore, have a polar region as well as nonpolar ends and are thus amphipathic. Steroids: These are compos ...
... are linked to glycerol, with the sugar’s third hydroxyl group attached to a phosphate group. Often a polar or ionized nitrogen-containing molecule is attached to the phosphate. Phospholipids, therefore, have a polar region as well as nonpolar ends and are thus amphipathic. Steroids: These are compos ...
Chapter 8: Genetics
... 1. Mom and Dad are both heterozygous for freckles and a widow’s peak (both dominant traits). What are the possible phenotypes for their children? ...
... 1. Mom and Dad are both heterozygous for freckles and a widow’s peak (both dominant traits). What are the possible phenotypes for their children? ...
Author - Princeton ISD
... students often lose track of where amino acids originate from, and the purpose of protein synthesis. Once synthesized on the ribosome, proteins remain in their folded state. Students often believe that after a protein is released from the ribosomes, there are no further modifications that occur. All ...
... students often lose track of where amino acids originate from, and the purpose of protein synthesis. Once synthesized on the ribosome, proteins remain in their folded state. Students often believe that after a protein is released from the ribosomes, there are no further modifications that occur. All ...
CH 17_ From Gene to Protein
... • Two populations of ribosomes are evident in cells: free ribsomes (in the cytosol) and bound ribosomes (attached to the ER) • Free ribosomes mostly synthesize proteins that function in the cytosol • Bound ribosomes make proteins of the endomembrane system and proteins that are secreted from the cel ...
... • Two populations of ribosomes are evident in cells: free ribsomes (in the cytosol) and bound ribosomes (attached to the ER) • Free ribosomes mostly synthesize proteins that function in the cytosol • Bound ribosomes make proteins of the endomembrane system and proteins that are secreted from the cel ...
ch20
... This procedure was used in a 2000 trial involving ten young children with SCID (severe combined immunodeficiency disease), a genetic disease in which bone marrow cells do not produce a vital enzyme because of a single defective gene. Nine of the children showed significant improvement after two ye ...
... This procedure was used in a 2000 trial involving ten young children with SCID (severe combined immunodeficiency disease), a genetic disease in which bone marrow cells do not produce a vital enzyme because of a single defective gene. Nine of the children showed significant improvement after two ye ...
polymerase chain reaction (pcr)
... PRIMERS: DNA strands--not more than fifty (usually 18-25 bp) ...
... PRIMERS: DNA strands--not more than fifty (usually 18-25 bp) ...
Protein Synthesis 06-07
... From PowerPoint® Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... From PowerPoint® Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.