Population Dynamics, Carrying Capacity
... • If the number of individuals added are balanced by those lost then there is zero population growth (ZPG) • Populations vary in their capacity for growth, also known as biotic potential. • Intrinsic rate of growth (r)- is the rate at which a population will grow if it had unlimited resources. • Car ...
... • If the number of individuals added are balanced by those lost then there is zero population growth (ZPG) • Populations vary in their capacity for growth, also known as biotic potential. • Intrinsic rate of growth (r)- is the rate at which a population will grow if it had unlimited resources. • Car ...
Carrying Capacity
... As discussed earlier, populations with a proper environment and sufficient food and space tend to grow exponentially. This is a generalization that is made for simple systems. The generalization implies that the birth rate is higher than the death rate. Birth rate is defined as the ratio of births ...
... As discussed earlier, populations with a proper environment and sufficient food and space tend to grow exponentially. This is a generalization that is made for simple systems. The generalization implies that the birth rate is higher than the death rate. Birth rate is defined as the ratio of births ...
File - Rust Science
... Brief History of Human Population Growth • Grew slowly at first but has grown rapidly recently because of the expansion of agriculture and industrial production (Industrial Revolution) AND lower death rates from improvements in hygiene and medicine. • In 2006, the population of developed countries ...
... Brief History of Human Population Growth • Grew slowly at first but has grown rapidly recently because of the expansion of agriculture and industrial production (Industrial Revolution) AND lower death rates from improvements in hygiene and medicine. • In 2006, the population of developed countries ...
- Orangefield ISD
... (r) Rate—This is the rate of growth; the number of individuals which can be produced per unit of time under ideal conditions (with no limits to the population’s growth). (t) Time—This is the unit of time upon which the rate is ...
... (r) Rate—This is the rate of growth; the number of individuals which can be produced per unit of time under ideal conditions (with no limits to the population’s growth). (t) Time—This is the unit of time upon which the rate is ...
Population and Growth Patterns
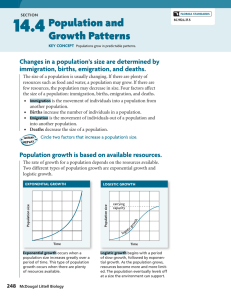
... Changes in a population’s size are determined by immigration, births, emigration, and deaths. The size of a population is usually changing. If there are plenty of resources such as food and water, a population may grow. If there are few resources, the population may decrease in size. Four factors af ...
... Changes in a population’s size are determined by immigration, births, emigration, and deaths. The size of a population is usually changing. If there are plenty of resources such as food and water, a population may grow. If there are few resources, the population may decrease in size. Four factors af ...
1. populations
... The J-shaped curve indicates that the population is undergoing exponential growth Exponential growth occurs when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate At first, the number of individuals in an exponentially growing population increases slowly Over time, however, the population ...
... The J-shaped curve indicates that the population is undergoing exponential growth Exponential growth occurs when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate At first, the number of individuals in an exponentially growing population increases slowly Over time, however, the population ...
Populations - OnMyCalendar
... many people of different ages make up a given population We can predict future growth using models called age-structure diagrams ...
... many people of different ages make up a given population We can predict future growth using models called age-structure diagrams ...
Environmental Science
... – What does it mean for an ecosystem to be in balance? – What happens after a major natural disturbance such as a fire? – Changes are the only constant in ecosystems – The notion of balance must be carefully defined ...
... – What does it mean for an ecosystem to be in balance? – What happens after a major natural disturbance such as a fire? – Changes are the only constant in ecosystems – The notion of balance must be carefully defined ...
Unit6 StudyGuide
... and live in the same area - Community – all the different living populations in the same area - Ecosystem – all the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) factors in an area - Biome – environment defined by it’s climate and the biological communities - Biosphere – the Earth - Producers – organisms ...
... and live in the same area - Community – all the different living populations in the same area - Ecosystem – all the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) factors in an area - Biome – environment defined by it’s climate and the biological communities - Biosphere – the Earth - Producers – organisms ...
Human overpopulation
Human overpopulation occurs if the number of people in a group exceeds the carrying capacity of the region occupied by that group. Overpopulation can further be viewed, in a long term perspective, as existing when a population cannot be maintained given the rapid depletion of non-renewable resources or given the degradation of the capacity of the environment to give support to the population.The term human overpopulation often refers to the relationship between the entire human population and its environment: the Earth, or to smaller geographical areas such as countries. Overpopulation can result from an increase in births, a decline in mortality rates, an increase in immigration, or an unsustainable biome and depletion of resources. It is possible for very sparsely populated areas to be overpopulated if the area has a meager or non-existent capability to sustain life (e.g. a desert). Advocates of population moderation cite issues like quality of life, carrying capacity and risk of starvation as a basis to argue against continuing high human population growth and for population decline.