Date: October 27, 2016
... “construction of buildings and roadways and the creation of wastelands” and “relentless search for more food” have reduced other animals’ life. In the fifth paragraph, Wilson mainly uses ethos to support his argument that human is destroying the environment. By discussing the “Juggernaut Theory of ...
... “construction of buildings and roadways and the creation of wastelands” and “relentless search for more food” have reduced other animals’ life. In the fifth paragraph, Wilson mainly uses ethos to support his argument that human is destroying the environment. By discussing the “Juggernaut Theory of ...
Ecology `15 Notes
... to some oxygen in a gas called ______________ ______________________. 2. Plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight to make their own food and grow. The carbon becomes part of the plant. 3. Animals consume plants. The carbon becomes part of the ______________________. 4. Plants that die and are buried m ...
... to some oxygen in a gas called ______________ ______________________. 2. Plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight to make their own food and grow. The carbon becomes part of the plant. 3. Animals consume plants. The carbon becomes part of the ______________________. 4. Plants that die and are buried m ...
chapter 8 wiki questions and answers 2014
... are easily affected by environmental changes such as loss of habitat and introduction of chemicals effect the types and abundance of many pollination - insects and birds for flowers and other species in a community more so flowering plants than their numbers would suggest they top predators regulati ...
... are easily affected by environmental changes such as loss of habitat and introduction of chemicals effect the types and abundance of many pollination - insects and birds for flowers and other species in a community more so flowering plants than their numbers would suggest they top predators regulati ...
full syllabus - University of Vermont
... attention has been given by hydrologists to ‘rainfall-runoff’ models and by physiological ecologists to ‘plant-water relations’ models. In comparison, relatively few ecosystem level models exist for in-stream biogeochemical processes. Typically in engineering models, for example, water is ‘routed’ t ...
... attention has been given by hydrologists to ‘rainfall-runoff’ models and by physiological ecologists to ‘plant-water relations’ models. In comparison, relatively few ecosystem level models exist for in-stream biogeochemical processes. Typically in engineering models, for example, water is ‘routed’ t ...
What is meant by the “Circle of Life”?
... Aim: How does biodiversity increase the stability in an ecosystem? ...
... Aim: How does biodiversity increase the stability in an ecosystem? ...
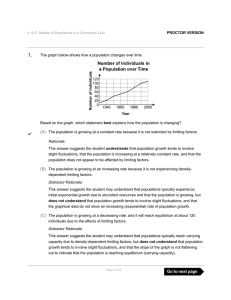
The graph below shows how a population changes over time. Based
... This answer suggests the student understands that the population experienced logistical growth due to density-dependent factors that prevented the population from being stable beyond a certain size, and that once the population exceeded the certain size (carrying capacity), the population declined d ...
... This answer suggests the student understands that the population experienced logistical growth due to density-dependent factors that prevented the population from being stable beyond a certain size, and that once the population exceeded the certain size (carrying capacity), the population declined d ...
biology 201 fall semester 2015 ecology and evolution
... the course will finish with macroevolution which is an examination of patterns of evolution above the species level. Here we will consider speciation (the process of one species splitting into two species) which is the engine the drives the diversification of life. We will also consider adaptive rad ...
... the course will finish with macroevolution which is an examination of patterns of evolution above the species level. Here we will consider speciation (the process of one species splitting into two species) which is the engine the drives the diversification of life. We will also consider adaptive rad ...
environment test
... b) species localised in a specific region c) cosmopolitan in distribution d) critically endangered species 76. What is the animal symbol of W. W. F (World Wildlife Fund) ? a) Red Panda b) Giant Panda c) Tiger d) Kangaroo 77. The most important human activity, leading to the extinction of wildlife, i ...
... b) species localised in a specific region c) cosmopolitan in distribution d) critically endangered species 76. What is the animal symbol of W. W. F (World Wildlife Fund) ? a) Red Panda b) Giant Panda c) Tiger d) Kangaroo 77. The most important human activity, leading to the extinction of wildlife, i ...
Habitat, a biological definition - Oregon State University Extension
... Your District Bio and Wildlife Control Operators • Call ODFW HQ with your address to get District Biologist contact info: 800-720-6339 or 503-947-6000 • WCOs are trained and licensed by OR Dept. of Fish and ...
... Your District Bio and Wildlife Control Operators • Call ODFW HQ with your address to get District Biologist contact info: 800-720-6339 or 503-947-6000 • WCOs are trained and licensed by OR Dept. of Fish and ...
the earth in the universe
... Ecosystems are functional units composed of all the living things in a place, their biotic components, and the physical and chemical factors which make up its non-living things, which are their abiotic components. There are different interactions between the biotic and abiotic factors as well as bet ...
... Ecosystems are functional units composed of all the living things in a place, their biotic components, and the physical and chemical factors which make up its non-living things, which are their abiotic components. There are different interactions between the biotic and abiotic factors as well as bet ...
Adaptation
... Species in 1859 it was widely (if not uni versally) held that species had evolved from one another, but no plausible mechanism for such evolution had been proposed. Darwin's solution to the problem was that small heritable varia tions among individuals within a species become the basis of large di ...
... Species in 1859 it was widely (if not uni versally) held that species had evolved from one another, but no plausible mechanism for such evolution had been proposed. Darwin's solution to the problem was that small heritable varia tions among individuals within a species become the basis of large di ...
New Title - cloudfront.net
... effects of a prolonged drought, a killing frost, or a flood. 20. Human population began growing more rapidly 500 years ago due to favorable growth conditions. ...
... effects of a prolonged drought, a killing frost, or a flood. 20. Human population began growing more rapidly 500 years ago due to favorable growth conditions. ...
Ecology_Project
... Target Audience : This lesson was developed for the ecology unit of biology and sheltered-English biology courses. It may also be suitable for life science, integrated science, environmental science courses. Background Information: Teacher notes: 1. Students create a simple, imaginary ecosystem. The ...
... Target Audience : This lesson was developed for the ecology unit of biology and sheltered-English biology courses. It may also be suitable for life science, integrated science, environmental science courses. Background Information: Teacher notes: 1. Students create a simple, imaginary ecosystem. The ...
agents of evolutionary change
... location, but each reproduces at a different time of year, and so they do not attempt to mate Behavioral isolation results from differences in mating behavior between two species Mechanical isolation is the result of differences between two species in reproductive structures or other body parts, so ...
... location, but each reproduces at a different time of year, and so they do not attempt to mate Behavioral isolation results from differences in mating behavior between two species Mechanical isolation is the result of differences between two species in reproductive structures or other body parts, so ...
Population - Ms. Farrell`s Science Center
... – Population will experience a Die-off or population crash ...
... – Population will experience a Die-off or population crash ...
The information in this document covers the IB syllabus for topic 5
... Introduction to Ecology First, a few definitions: • ecology = the study of relationships between living organisms and between organisms and their environment • ecosystem = a community and its abiotic environment • population = a group of organisms of the same species who live in the same area at the ...
... Introduction to Ecology First, a few definitions: • ecology = the study of relationships between living organisms and between organisms and their environment • ecosystem = a community and its abiotic environment • population = a group of organisms of the same species who live in the same area at the ...
Bio07_TR__U02_CH3.QXD
... • Where does the energy for life processes come from? • How does energy flow through living systems? • How efficient is the transfer of energy among organisms in an ecosystem? Producers (pages 67-68) ...
... • Where does the energy for life processes come from? • How does energy flow through living systems? • How efficient is the transfer of energy among organisms in an ecosystem? Producers (pages 67-68) ...
Restoration Ecology
... • Global declines in genetic diversity of wildlife seen; leads to inbreeding depression • Global declines in genetic diversity of ...
... • Global declines in genetic diversity of wildlife seen; leads to inbreeding depression • Global declines in genetic diversity of ...
Three Kings Vine / Native Bignonia
... which create shelter for the spiders. Other threats come from introduced spider species that attempt to establish themselves in the same habitat thereby displacing the native species. Katipos lose their ecological niche to foreign spiders such as the Australian red-back, which is more aggressive and ...
... which create shelter for the spiders. Other threats come from introduced spider species that attempt to establish themselves in the same habitat thereby displacing the native species. Katipos lose their ecological niche to foreign spiders such as the Australian red-back, which is more aggressive and ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.