vocab - Cellular Respiration
... Mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of a hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work such as the synthesis of ATP. Most ATP synthesis in cells occurs by ...
... Mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of a hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work such as the synthesis of ATP. Most ATP synthesis in cells occurs by ...
DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source of heritable
... number of different proteins an organism can produce is much greater than its number of genes. Check out the mRNA processing activity in your online textbook. It will help you understand this process. ...
... number of different proteins an organism can produce is much greater than its number of genes. Check out the mRNA processing activity in your online textbook. It will help you understand this process. ...
Elementary my dear Watson review
... Protons are found in the nucleus The number under the chemical symbol is the atomic mass (the mass of one atom of that element) ...
... Protons are found in the nucleus The number under the chemical symbol is the atomic mass (the mass of one atom of that element) ...
Energy Systems - Mrs N Benedict
... re-synthesise three molecules of ATP but the process of glycolysis itself requires energy (one molecule) The lactic acid system provides energy for high-intensity activities lasting up to 3 minutes but peaking at 1 minute, for example the 400m ...
... re-synthesise three molecules of ATP but the process of glycolysis itself requires energy (one molecule) The lactic acid system provides energy for high-intensity activities lasting up to 3 minutes but peaking at 1 minute, for example the 400m ...
Urea cycle
... The activity of urea cycle is regulated at two levels: • Dietary intake is primarily proteins much urea (amino acids are used for fuel) • Prolonged starvation breaks down of muscle proteins much urea also • The rate of synthesis of four urea cycle enzymes and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I ( ...
... The activity of urea cycle is regulated at two levels: • Dietary intake is primarily proteins much urea (amino acids are used for fuel) • Prolonged starvation breaks down of muscle proteins much urea also • The rate of synthesis of four urea cycle enzymes and carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I ( ...
Protein Synthesis
... stop • Start codon (AUG) codes for methionine • Stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) causes translation to stop ...
... stop • Start codon (AUG) codes for methionine • Stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) causes translation to stop ...
20141104103322
... Active site (and R groups of its amino acids) can lower EA and speed up a reaction by • acting as a template for substrate orientation, • stressing the substrates and stabilizing the ...
... Active site (and R groups of its amino acids) can lower EA and speed up a reaction by • acting as a template for substrate orientation, • stressing the substrates and stabilizing the ...
proteins
... The figure was adopted from http://stallion.abac.peachnet.edu/sm/kmccrae/BIOL2050/Ch1-13/JpegArt113/05jpeg/05-06_denaturation_1.jpg (October 2007) ...
... The figure was adopted from http://stallion.abac.peachnet.edu/sm/kmccrae/BIOL2050/Ch1-13/JpegArt113/05jpeg/05-06_denaturation_1.jpg (October 2007) ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... The sum of all the chemical processes occurring in an organism at one time Management of material and energy resources within the cell Catabolic – break down big molecules into smaller ones ...
... The sum of all the chemical processes occurring in an organism at one time Management of material and energy resources within the cell Catabolic – break down big molecules into smaller ones ...
Energy Transformation — Cellular Respiration
... 3. How many reduced NADH molecules are produced after the glucose has been completely broken down to ATP? And at what stage of the aerobic respiration is glucose completely broken down into carbon dioxide? 4. As glucose is split in the cytosol of the cell, is there a release of carbon dioxide as by- ...
... 3. How many reduced NADH molecules are produced after the glucose has been completely broken down to ATP? And at what stage of the aerobic respiration is glucose completely broken down into carbon dioxide? 4. As glucose is split in the cytosol of the cell, is there a release of carbon dioxide as by- ...
10 CODON ANTI- CODON CYTOPLASM RIBOSOME tRNA AMINO
... Coded amino acids in correct order: MET (start) PHE ASP LEU 8. Define the term “mutation” in relation to DNA. A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. This may result in a change to the mRNA sequence, which could cause a change in the protein and trait. 9. Describe a point mutation. Does it alway ...
... Coded amino acids in correct order: MET (start) PHE ASP LEU 8. Define the term “mutation” in relation to DNA. A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. This may result in a change to the mRNA sequence, which could cause a change in the protein and trait. 9. Describe a point mutation. Does it alway ...
Alpha-Lipoic Acid The Universal Antioxidant
... Alpha-lipoic acid is a nutritional coenzyme that is involved in energy metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and fats, has physiological functions in blood glucose disposal, and is able to scavenge a number of free radicals. Alpha-lipoic acid is a fat- and water-soluble, sulfur-containing coenzyme. ...
... Alpha-lipoic acid is a nutritional coenzyme that is involved in energy metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and fats, has physiological functions in blood glucose disposal, and is able to scavenge a number of free radicals. Alpha-lipoic acid is a fat- and water-soluble, sulfur-containing coenzyme. ...
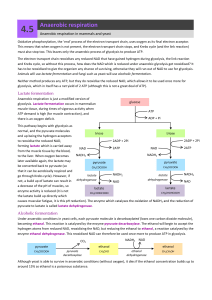
Anaerobic respiration
... Oxidative phosphorylation, the ‘end’ process of the electron transport chain, uses oxygen as its final electron acceptor. This means that when oxygen is not present, the electron transport chain stops, and Krebs cycle (and the link reaction) must also stop too. This leaves only the anaerobic process ...
... Oxidative phosphorylation, the ‘end’ process of the electron transport chain, uses oxygen as its final electron acceptor. This means that when oxygen is not present, the electron transport chain stops, and Krebs cycle (and the link reaction) must also stop too. This leaves only the anaerobic process ...
03-131 Genes, Drugs, and Disease ... 1. (10 pts, 10 min) The diagram on the left...
... a) Why is this state low in energy [Hint – where are the non-polar residues]? b) Draw the lowest energy form for the following protein. Does its “structure” differ from the first protein? 2. (6 pts, 15 min) Rituximab is a drug that is used to treat certain types of cancer (you should use web resourc ...
... a) Why is this state low in energy [Hint – where are the non-polar residues]? b) Draw the lowest energy form for the following protein. Does its “structure” differ from the first protein? 2. (6 pts, 15 min) Rituximab is a drug that is used to treat certain types of cancer (you should use web resourc ...
Vragen voor tentamen Protein Engineering (8S080)
... specificity for M. furfur. What directed-evolution method would you advise them to use in this case and why? Explain in detail how this methods works and one would apply this method in this case. (10 points). Question 4 ...
... specificity for M. furfur. What directed-evolution method would you advise them to use in this case and why? Explain in detail how this methods works and one would apply this method in this case. (10 points). Question 4 ...
II. Pre-test to identify student misconceptions prior to addressing the
... carbon dioxide in the production of organic molecules. b. Students may think that respiration occurs only in green plants when there is no light energy for photosynthesis. ...
... carbon dioxide in the production of organic molecules. b. Students may think that respiration occurs only in green plants when there is no light energy for photosynthesis. ...
Gene Duplication in the Mo-Fe Protein of Nitrogenase
... • Constructed a phylogenetic tree of the Mo-Fe protein of nitrogenase from published nucleic acid data. • Tried to get a more coherent tree by eliminating some of the sequences. • Tree still not revealing. • Mistake: using nucleotides, switched to amino acid sequences for the alpha and beta chains. ...
... • Constructed a phylogenetic tree of the Mo-Fe protein of nitrogenase from published nucleic acid data. • Tried to get a more coherent tree by eliminating some of the sequences. • Tree still not revealing. • Mistake: using nucleotides, switched to amino acid sequences for the alpha and beta chains. ...
coenzymes and cofactors
... coenzymes are organic molecules that are required by certain enzymes to carry out catalysis. They bind to the active site of the enzyme and participate in catalysis but are not considered substrates of the reaction. coenzymes often function as intermediate carriers of electrons, specific atoms o ...
... coenzymes are organic molecules that are required by certain enzymes to carry out catalysis. They bind to the active site of the enzyme and participate in catalysis but are not considered substrates of the reaction. coenzymes often function as intermediate carriers of electrons, specific atoms o ...
Work and Energy in Muscles
... proteins. Furthermore, both glycogen and proteins are hydrophilic, that is, they bind water. The result is that stored glycogen and protein have a much lower "energy density" than the hydrophobic lipids. While fat stores have 9 kcalories per gram wet weight, carbohydrates and proteins have only 1-1. ...
... proteins. Furthermore, both glycogen and proteins are hydrophilic, that is, they bind water. The result is that stored glycogen and protein have a much lower "energy density" than the hydrophobic lipids. While fat stores have 9 kcalories per gram wet weight, carbohydrates and proteins have only 1-1. ...
Translation PPT
... • GENE- a sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait • GENETIC CODE - language of the mRNA instructions as determined by the N-bases • CODON- sequence of 3 nucleotides (or just the N-bases) on mRNA that code for one amino acid • POLYLPEPTIDES- proteins made by joining any c ...
... • GENE- a sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait • GENETIC CODE - language of the mRNA instructions as determined by the N-bases • CODON- sequence of 3 nucleotides (or just the N-bases) on mRNA that code for one amino acid • POLYLPEPTIDES- proteins made by joining any c ...
Document
... subjected to high salt conditions, it transforms into A-DNA which is transiently observed in DNA transcription when DNA/RNA hybrids exist. The latter as well as double helical RNA can adopt only the A-form for reasons not yet fully understood. If DNA has a certain alternating sequence poly(dG-dC), i ...
... subjected to high salt conditions, it transforms into A-DNA which is transiently observed in DNA transcription when DNA/RNA hybrids exist. The latter as well as double helical RNA can adopt only the A-form for reasons not yet fully understood. If DNA has a certain alternating sequence poly(dG-dC), i ...
For the following mix equal volumes of one solution from Group I
... For the following, mix equal volumes of one solution from Group I with one solution from Group II to achieve the indicated general pH. Then calculate the actual pH of the mixed solution (this requires setting up an I.C.E. table). a. b. c. ...
... For the following, mix equal volumes of one solution from Group I with one solution from Group II to achieve the indicated general pH. Then calculate the actual pH of the mixed solution (this requires setting up an I.C.E. table). a. b. c. ...
Plankton Biomass and Food Web Structure
... Note: this is a static depiction-it does not provide information on how fast biomass turns over within each trophic level. ...
... Note: this is a static depiction-it does not provide information on how fast biomass turns over within each trophic level. ...
Chapter 5
... • Molecules of life are formed through reductive pathway that requires: • Source of electrons and protons • Source of energy • A carbon source at oxidized state • Process: • energy is used to release electrons from an inroganic/organic source ...
... • Molecules of life are formed through reductive pathway that requires: • Source of electrons and protons • Source of energy • A carbon source at oxidized state • Process: • energy is used to release electrons from an inroganic/organic source ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.