Nitrogen lectures (Part 2)
... – Balance of amino acids in a diet is as important as the amounts of individual amino acids • Amino acids can only be used to the extent of the least abundant amino acid relative to the animal’s requirement – Remainder of amino acids will be deaminated and N will be ...
... – Balance of amino acids in a diet is as important as the amounts of individual amino acids • Amino acids can only be used to the extent of the least abundant amino acid relative to the animal’s requirement – Remainder of amino acids will be deaminated and N will be ...
Document
... • Different tRNAs are processed in different ways, so a generic processing pathway is not possible. • Some eukaryotic and archeal tRNA genes possess introns of variable length that must be removed in processing. ...
... • Different tRNAs are processed in different ways, so a generic processing pathway is not possible. • Some eukaryotic and archeal tRNA genes possess introns of variable length that must be removed in processing. ...
APB Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... In prokaryotes, these processes take place in the __________________________________________________. ...
... In prokaryotes, these processes take place in the __________________________________________________. ...
09_DetailLectOut_jkAR
... There are three reasons that we cannot state an exact number of ATP molecules generated by one molecule of glucose. 1. Phosphorylation and the redox reactions are not directly coupled to each other, so the ratio of number of NADH to number of ATP is not a whole number. One NADH results in 10 H+ be ...
... There are three reasons that we cannot state an exact number of ATP molecules generated by one molecule of glucose. 1. Phosphorylation and the redox reactions are not directly coupled to each other, so the ratio of number of NADH to number of ATP is not a whole number. One NADH results in 10 H+ be ...
chapt05_lecture
... a. Fat stored in adipose tissue as triglycerides b. Great way to store energy: 1 gram fat = 9 kcal energy. 1) In a nonobese 155-pound man, 80-85% of his stored energy is in fat. (140,000 calories) c. Lipolysis: breaking triglycerides down into fatty acids and glycerol using the enzyme lipase. 1) Fat ...
... a. Fat stored in adipose tissue as triglycerides b. Great way to store energy: 1 gram fat = 9 kcal energy. 1) In a nonobese 155-pound man, 80-85% of his stored energy is in fat. (140,000 calories) c. Lipolysis: breaking triglycerides down into fatty acids and glycerol using the enzyme lipase. 1) Fat ...
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... The anti-codon UAC will be an exact fit for that. (Remember U and A are complementary to each other and so are G and C.) b) Tyrosine (Tyr) will be coded by either UAU or UAC on the mRNA. The anti-codon will be complementary to those – either AUA or AUG. c) Tryptophan (Trp) is coded by UGG. The anti- ...
... The anti-codon UAC will be an exact fit for that. (Remember U and A are complementary to each other and so are G and C.) b) Tyrosine (Tyr) will be coded by either UAU or UAC on the mRNA. The anti-codon will be complementary to those – either AUA or AUG. c) Tryptophan (Trp) is coded by UGG. The anti- ...
Document
... (A) increases, increases (B) decreases, decreases (C) increases, decreases (D) decreases, increases (E) More information is needed to answer this question 43. Which of the following is an acid-base neutralization reaction? (A) 2Al(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g) (B) SO2(g) + H2O(l) H2SO3( ...
... (A) increases, increases (B) decreases, decreases (C) increases, decreases (D) decreases, increases (E) More information is needed to answer this question 43. Which of the following is an acid-base neutralization reaction? (A) 2Al(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g) (B) SO2(g) + H2O(l) H2SO3( ...
Biotechnology - Jamaica Clearing
... known living organisms and some viruses. • The main role of DNA molecules is the long-term storage of information. DNA is often compared to a set of blueprints or a recipe, since it contains the instructions needed to construct other components of cells, such as proteins and RNA molecules. • The DNA ...
... known living organisms and some viruses. • The main role of DNA molecules is the long-term storage of information. DNA is often compared to a set of blueprints or a recipe, since it contains the instructions needed to construct other components of cells, such as proteins and RNA molecules. • The DNA ...
Glycolysis 1
... A deficiency in the hexokinase-related enzyme, glucokinase, leads to a rare form of diabetes, which is caused by the inability of liver and pancreatic cells to phosphorylate glucose inside cells when blood glucose levels are elevated. ...
... A deficiency in the hexokinase-related enzyme, glucokinase, leads to a rare form of diabetes, which is caused by the inability of liver and pancreatic cells to phosphorylate glucose inside cells when blood glucose levels are elevated. ...
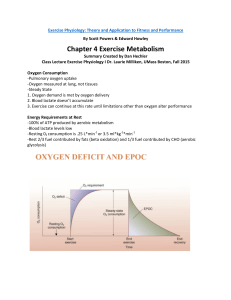
Chapter 4 Exercise Metabolism
... -Trained individuals have a lower oxygen deficit due to their higher aerobic capacity (increased cardiac output, large percentage of blood directed to active muscle, reach steady state more rapidly aka smaller oxygen deficit, less production of lactic acid.) Reason for Lag of Oxygen -Inadequate ...
... -Trained individuals have a lower oxygen deficit due to their higher aerobic capacity (increased cardiac output, large percentage of blood directed to active muscle, reach steady state more rapidly aka smaller oxygen deficit, less production of lactic acid.) Reason for Lag of Oxygen -Inadequate ...
Regulating the Internal Environment
... dry environment need to conserve water may also need to conserve salt ...
... dry environment need to conserve water may also need to conserve salt ...
Spring 2001 Key
... -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------By definition of symbols, this ion has 15 protons, its mass is 31 amu, and therefore, it must have (31 - 15 = 16) neutrons. Since it is an anion with a charge of -3, it must have three extra el ...
... -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------By definition of symbols, this ion has 15 protons, its mass is 31 amu, and therefore, it must have (31 - 15 = 16) neutrons. Since it is an anion with a charge of -3, it must have three extra el ...
SCIENCE STUDY GUIDE
... The role of the respiratory system is Oxygen to bring what substance into the body Where gas exchange occurs in the respiratory system The throat, where air enters after going through the nasal cavities ...
... The role of the respiratory system is Oxygen to bring what substance into the body Where gas exchange occurs in the respiratory system The throat, where air enters after going through the nasal cavities ...
CHE 312 - UB`s Department of Chemistry
... monosaccharides • Classify monosaccharides as L/D, aldose/ketose, triose/tetrose/pentose/hexose, furanose/pyranose, reducing/nonreducing • Define stereoisomer, enantiomer, diastereomer, epimer, anomer • Know the structures of ribose, glucose, mannose, galactose, fructose • Draw and interconvert betw ...
... monosaccharides • Classify monosaccharides as L/D, aldose/ketose, triose/tetrose/pentose/hexose, furanose/pyranose, reducing/nonreducing • Define stereoisomer, enantiomer, diastereomer, epimer, anomer • Know the structures of ribose, glucose, mannose, galactose, fructose • Draw and interconvert betw ...
General Chemistry 110 Quiz 1
... COMPLETE THE SCANTRON PORTION OF THE TEST BEFORE PROCEEDING TO THE SHORT ANSWER SECTION. Number 1 through 15 are worth 6 points each. ...
... COMPLETE THE SCANTRON PORTION OF THE TEST BEFORE PROCEEDING TO THE SHORT ANSWER SECTION. Number 1 through 15 are worth 6 points each. ...
1 - marric.us
... 30. What is the function of each of the following organelles? a. Cell membrane (pg 187) d. Ribosomes (pg 193) b. Endoplasmic Reticulum (pg 194) e. Chloroplasts (pg 197) c. Golgi apparatus (pg 195) 31. What are the differences between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? (pg 185-186) 32. Make a sketch ...
... 30. What is the function of each of the following organelles? a. Cell membrane (pg 187) d. Ribosomes (pg 193) b. Endoplasmic Reticulum (pg 194) e. Chloroplasts (pg 197) c. Golgi apparatus (pg 195) 31. What are the differences between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? (pg 185-186) 32. Make a sketch ...
Lecture 22 - Introduction to Metabolism: Regulation Key Concepts
... between citrulline and asparagine is the addition of a single amino group obtained from aspartate, however in order for this to occur, argininosuccinate has to function both as a product and a reactant. 1 of 8 pages ...
... between citrulline and asparagine is the addition of a single amino group obtained from aspartate, however in order for this to occur, argininosuccinate has to function both as a product and a reactant. 1 of 8 pages ...
Biology End-of-Course Test: Heritage High School 2013
... 1) Prokaryotic cells do NOT contain any membrane-bound organelles. These very simple cells typically contain only 4 parts (Remember NONE of these are membrane-bound organelles!): (1) DNA, (2) Cytoplasm, (3) Ribosomes, (4) Cell Membrane 2) Bacteria are the only organisms that have are prokaryotic cel ...
... 1) Prokaryotic cells do NOT contain any membrane-bound organelles. These very simple cells typically contain only 4 parts (Remember NONE of these are membrane-bound organelles!): (1) DNA, (2) Cytoplasm, (3) Ribosomes, (4) Cell Membrane 2) Bacteria are the only organisms that have are prokaryotic cel ...
Practice Bypass Answers
... h) At room temperature (72 oF) propane is a gas and water is a liquid. This means that 72 oF must be higher than the boiling point for propane, but lower than the boiling point for water. Explain why propane has a lower boiling point than water. Provide an analysis of the interparticle forces betwee ...
... h) At room temperature (72 oF) propane is a gas and water is a liquid. This means that 72 oF must be higher than the boiling point for propane, but lower than the boiling point for water. Explain why propane has a lower boiling point than water. Provide an analysis of the interparticle forces betwee ...
Nucleotide drug targets
... cell; you don’t get much more important that. ATP is adenine attached to ribose with 3 phosphates attached. One or two of these phosphates may be cleaved in a reaction to yield energy (the phosphodiester bond is a quite high energy bond). Likewise GTP is used in protein synthesis as an energy source ...
... cell; you don’t get much more important that. ATP is adenine attached to ribose with 3 phosphates attached. One or two of these phosphates may be cleaved in a reaction to yield energy (the phosphodiester bond is a quite high energy bond). Likewise GTP is used in protein synthesis as an energy source ...
Nucleotide drug targets.
... cell; you don’t get much more important that. ATP is adenine attached to ribose with 3 phosphates attached. One or two of these phosphates may be cleaved in a reaction to yield energy (the phosphodiester bond is a quite high energy bond). Likewise GTP is used in protein synthesis as an energy source ...
... cell; you don’t get much more important that. ATP is adenine attached to ribose with 3 phosphates attached. One or two of these phosphates may be cleaved in a reaction to yield energy (the phosphodiester bond is a quite high energy bond). Likewise GTP is used in protein synthesis as an energy source ...
Chapter 12
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory: The hypotheses about the nature of matter on which Dalton’s Atomic Theory is based can be summarized as: Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atom ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory: The hypotheses about the nature of matter on which Dalton’s Atomic Theory is based can be summarized as: Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atom ...
File
... - huge organic molecs composed of smaller organic molecs - made up of smaller molecs called monomers - made via a process called polymerization • there are 4 groups of organic cmpds found in living things: (in no particular order) #1 carbs #2 lipids #3 nucleic acids #4 proteins ...
... - huge organic molecs composed of smaller organic molecs - made up of smaller molecs called monomers - made via a process called polymerization • there are 4 groups of organic cmpds found in living things: (in no particular order) #1 carbs #2 lipids #3 nucleic acids #4 proteins ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.