Functional and Biochemical Analysis of Glucose-6
... This enzymopathy is usually diagnosed and classified through hematological studies and classified based on the level of G6PD enzymatic activity in red blood cells. The G6PD deficiency causes several abnormalities that ranges clinically from asymptomatic individuals through to patients showing neonat ...
... This enzymopathy is usually diagnosed and classified through hematological studies and classified based on the level of G6PD enzymatic activity in red blood cells. The G6PD deficiency causes several abnormalities that ranges clinically from asymptomatic individuals through to patients showing neonat ...
Ryoji Noyori - Nobel Lecture
... simplest but most powerful way to produce a wide array of important compounds in large quantities using inexpensive, clean hydrogen gas without forming any waste. Hydrogenation was initiated at the end of the 19th century by P. Sabatier (1912 Nobel laureate) who used fine metal particles as heterog ...
... simplest but most powerful way to produce a wide array of important compounds in large quantities using inexpensive, clean hydrogen gas without forming any waste. Hydrogenation was initiated at the end of the 19th century by P. Sabatier (1912 Nobel laureate) who used fine metal particles as heterog ...
Moles 1 - pedagogics.ca
... and stoichiometry is the study of the ratios in which chemical substances combine. In order to know the exact quantity of each substance that is required to react we need to know the number of atoms, molecules or ions present in a specific amount of that substance. However, the mass of an individual ...
... and stoichiometry is the study of the ratios in which chemical substances combine. In order to know the exact quantity of each substance that is required to react we need to know the number of atoms, molecules or ions present in a specific amount of that substance. However, the mass of an individual ...
Preview Sample 3
... List the four major classes of biological macromolecules. Describe each biological macromolecule, and how monomers of each class are brought together to form the macromolecules. Describe the relationship between functional groups and macromolecules. Appreciate the variety and chemical characteri ...
... List the four major classes of biological macromolecules. Describe each biological macromolecule, and how monomers of each class are brought together to form the macromolecules. Describe the relationship between functional groups and macromolecules. Appreciate the variety and chemical characteri ...
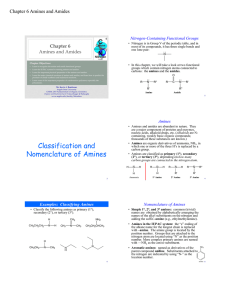
Classification and Nomenclature of Amines
... CHEM 2353 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Organic and Biochemistry for Today (Seager & Slabaugh) www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea ...
... CHEM 2353 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry Organic and Biochemistry for Today (Seager & Slabaugh) www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea ...
Mitochondria as a Pharmacological Target
... calcium handling. These events may initiate peroxidation of mitochondrial DNA, proteins, and lipids, and opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, an event linked to apoptotic cell death. Mitochondria are also targets for drugs such as antidiabetic sulfonylureas, immunosupressants, ...
... calcium handling. These events may initiate peroxidation of mitochondrial DNA, proteins, and lipids, and opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, an event linked to apoptotic cell death. Mitochondria are also targets for drugs such as antidiabetic sulfonylureas, immunosupressants, ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) molecules in the gas phase have more potential energy than in solids. C) molecules in the gas phase have more kinetic energy than in solids. D) gaseous molecules have less mass. E) molecules in the gas phase have more space between them than in solids. Ans: E Difficulty: M ...
... B) molecules in the gas phase have more potential energy than in solids. C) molecules in the gas phase have more kinetic energy than in solids. D) gaseous molecules have less mass. E) molecules in the gas phase have more space between them than in solids. Ans: E Difficulty: M ...
Engineering the pentose phosphate pathway of
... it is unable to utilise the 5-carbon sugars D-xylose and L-arabinose present in plant biomass. In this study, one key metabolic step of the catabolic D-xylose pathway in recombinant D-xylose-utilising S. cerevisiae strains was studied. This step, carried out by xylulokinase (XK), was shown to be rat ...
... it is unable to utilise the 5-carbon sugars D-xylose and L-arabinose present in plant biomass. In this study, one key metabolic step of the catabolic D-xylose pathway in recombinant D-xylose-utilising S. cerevisiae strains was studied. This step, carried out by xylulokinase (XK), was shown to be rat ...
Chapter 3: Ionic and Covalent Compounds Chapter 3: Ionic and
... 80. Anions are formed when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons. A) True B) False Ans: A Difficulty: Easy 81. The (II) in the name of the ionic compound lead (II) acetate specifically indicates that there are two lead ions present in the compound. A) True B) False Ans: B Difficulty: Medium 82. ...
... 80. Anions are formed when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons. A) True B) False Ans: A Difficulty: Easy 81. The (II) in the name of the ionic compound lead (II) acetate specifically indicates that there are two lead ions present in the compound. A) True B) False Ans: B Difficulty: Medium 82. ...
Advanced Stochastic Protein Sequence Analysis
... In the last decade(s), bioinformatics has become an impressive success story. Compared to traditional research in molecular biology, i.e. explorations in the so-called wet labs, insilico investigations are mostly cheaper and faster by some orders of magnitude. Here, the term in-silico stands for exp ...
... In the last decade(s), bioinformatics has become an impressive success story. Compared to traditional research in molecular biology, i.e. explorations in the so-called wet labs, insilico investigations are mostly cheaper and faster by some orders of magnitude. Here, the term in-silico stands for exp ...
Free radical scavenging and antioxidant effects of lactate ion: an in
... HPLC procedure. MDA quantification was performed according to a method described previously (11). The HPLC system (LDC-Milton Roy) was equipped with a spherogelTSK G1000 PW size exclusion column (7.5 mm ID ⫻ 30 cm; Cluzeau, France). The eluant was composed of 0.1 M disodium phosphate buffer, pH 8, a ...
... HPLC procedure. MDA quantification was performed according to a method described previously (11). The HPLC system (LDC-Milton Roy) was equipped with a spherogelTSK G1000 PW size exclusion column (7.5 mm ID ⫻ 30 cm; Cluzeau, France). The eluant was composed of 0.1 M disodium phosphate buffer, pH 8, a ...
Recent Development in Optical Fiber Biosensors
... Keywords: Optical fiber, biosensor, applications, review ...
... Keywords: Optical fiber, biosensor, applications, review ...
2.1 CHARACTERISATION OF ACID SOLUBLE COLLAGEN (Lates niloticus) 2 RESEARCH
... and adult fish skins. SDS PAGE showed the collagens to contain two alpha components (a1 and (2). ASC from Nile perch was found to contain more imino acids (19.3 and 20.0%, respectively for young and adult fish) than most fish species. The denaturation temperature for the collagens from the skins of ...
... and adult fish skins. SDS PAGE showed the collagens to contain two alpha components (a1 and (2). ASC from Nile perch was found to contain more imino acids (19.3 and 20.0%, respectively for young and adult fish) than most fish species. The denaturation temperature for the collagens from the skins of ...
Rate at which glutamine enters TCA cycle influences carbon atom
... ments. The Lineweaver-Burk equation was used to calculate values for maximal rate (Vmax ) and the glutamine concentration needed to achieve the half-maximal rate of CO2 production from either [U-14C]glutamine or [1-14C]glutamine (Kox ). The objective of experiment 4 was to determine whether reducing ...
... ments. The Lineweaver-Burk equation was used to calculate values for maximal rate (Vmax ) and the glutamine concentration needed to achieve the half-maximal rate of CO2 production from either [U-14C]glutamine or [1-14C]glutamine (Kox ). The objective of experiment 4 was to determine whether reducing ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... • compounds that dissolve in a solvent are said to be soluble, while those that do not are said to be insoluble – NaCl is soluble in water, AgCl is insoluble in water – the degree of solubility depends on the temperature – even insoluble compounds dissolve, just not enough to be ...
... • compounds that dissolve in a solvent are said to be soluble, while those that do not are said to be insoluble – NaCl is soluble in water, AgCl is insoluble in water – the degree of solubility depends on the temperature – even insoluble compounds dissolve, just not enough to be ...
The Bacterial Toxin RelE Displays Codon
... of protein synthesis by RelE in vivo. We have found that although RelE does not degrade free RNA, it cleaves mRNA in the ribosomal A site with high codon specificity. Among stop codons UAG is cleaved with fast, UAA intermediate and UGA slow rate, while UCG and CAG are cleaved most rapidly among sens ...
... of protein synthesis by RelE in vivo. We have found that although RelE does not degrade free RNA, it cleaves mRNA in the ribosomal A site with high codon specificity. Among stop codons UAG is cleaved with fast, UAA intermediate and UGA slow rate, while UCG and CAG are cleaved most rapidly among sens ...
Week 1 -- Schedule
... Exp. 1.2 – tall glass, paper towel, sink full of water, safety goggles* *It is believe you could go without these in these particular experiments. Vocabulary The number in parenthesis after the word is the page number the word’s definition can be found on. Additionally, there are other words in bold ...
... Exp. 1.2 – tall glass, paper towel, sink full of water, safety goggles* *It is believe you could go without these in these particular experiments. Vocabulary The number in parenthesis after the word is the page number the word’s definition can be found on. Additionally, there are other words in bold ...
Support Material
... Ans. The energy gap between the valence band and conduction band in an insulator is very large while in a conductor, the energy gap is very small or there is overlapping between valence band and conduction band. Q.30. CaCl2 will introduce Schottky defect if added to AgCl crystal. Explain. Ans. Two A ...
... Ans. The energy gap between the valence band and conduction band in an insulator is very large while in a conductor, the energy gap is very small or there is overlapping between valence band and conduction band. Q.30. CaCl2 will introduce Schottky defect if added to AgCl crystal. Explain. Ans. Two A ...
Nutrition for sport and exercise
... Permissions Editor: Mardell Schultz © 2008 Thomson Wadsworth, a part of The Thomson Corporation. Thomson, the Star logo, and Wadsworth are trademarks used herein under license. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this work covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any m ...
... Permissions Editor: Mardell Schultz © 2008 Thomson Wadsworth, a part of The Thomson Corporation. Thomson, the Star logo, and Wadsworth are trademarks used herein under license. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this work covered by the copyright hereon may be reproduced or used in any form or by any m ...
The Protein Cevalently Linked to the 5'... of Poliovirus RNA by Victor Robert Ambros
... be recovered from poliovirus RNA chains varying in length from 7,50C nucleotides (full-sized RNA) to about 500 nucleotides. ...
... be recovered from poliovirus RNA chains varying in length from 7,50C nucleotides (full-sized RNA) to about 500 nucleotides. ...
Glycerol transport and phosphoenolpyruvate
... play an important role in the regulation of glycerol metabolism in numerous bacteria. The mechanisms involved in this regulation are different in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, but they are both mediated via glycerol kinase. In Gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli or Salmonella ...
... play an important role in the regulation of glycerol metabolism in numerous bacteria. The mechanisms involved in this regulation are different in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, but they are both mediated via glycerol kinase. In Gram-negative bacteria such as Escherichia coli or Salmonella ...
Rh(acac)(CO)(PR1R2R3) - University of the Free State
... The rates of the reactions seem to be both sterically and electronically dependent, while the activation parameters indicated an associative mechanism for the oxidative addition step. This is consistent with low, positive enthalpies and large, negative entropies which is typical for iodomethane oxid ...
... The rates of the reactions seem to be both sterically and electronically dependent, while the activation parameters indicated an associative mechanism for the oxidative addition step. This is consistent with low, positive enthalpies and large, negative entropies which is typical for iodomethane oxid ...
Molecular Mechanisms of Inhibition of Streptococcus Species by
... be able to adhere to the tissue surface and compete with the normal microbiota present on that surface [5,34,35]. Subsequently, for sustainable attachment, biofilms are developed and this may lead to invasion of the host tissue [6]. To establish biofilm, planktonic bacteria attaches to either inert ...
... be able to adhere to the tissue surface and compete with the normal microbiota present on that surface [5,34,35]. Subsequently, for sustainable attachment, biofilms are developed and this may lead to invasion of the host tissue [6]. To establish biofilm, planktonic bacteria attaches to either inert ...
METABOLIC CUES AND REGULATORY PROTEINS
... establish an intracellular niche protected from digestion. Moreover, if humans inhale bacteria-laden aerosols, L. pneumophila can survive and replicate within alveolar macrophages to cause the severe pneumonia, Legionnaires’ disease. To persist within these diverse niches, L. pneumophila alternates ...
... establish an intracellular niche protected from digestion. Moreover, if humans inhale bacteria-laden aerosols, L. pneumophila can survive and replicate within alveolar macrophages to cause the severe pneumonia, Legionnaires’ disease. To persist within these diverse niches, L. pneumophila alternates ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.