Chromatography - Union College
... The goal of affinity chromatography is to separate all the molecules of a particular specificity from the whole gamut of molecules in a mixture such as a blood serum. For example, the antibodies in a serum sample specific for a particular antigenic determinant can be isolated by the use of affinity ...
... The goal of affinity chromatography is to separate all the molecules of a particular specificity from the whole gamut of molecules in a mixture such as a blood serum. For example, the antibodies in a serum sample specific for a particular antigenic determinant can be isolated by the use of affinity ...
protein - Warren County Schools
... The DNA in each chromosome makes up many genes (as well as vast stretches of noncoding DNA(introns), the function of which is unknown). A gene is any given segment along the DNA that encodes instructions that allow a cell to produce a specific product typically, a protein such as an enzyme - that in ...
... The DNA in each chromosome makes up many genes (as well as vast stretches of noncoding DNA(introns), the function of which is unknown). A gene is any given segment along the DNA that encodes instructions that allow a cell to produce a specific product typically, a protein such as an enzyme - that in ...
Document
... Food and Drug Administration. Food Standards: amendment of standards of identity for enriched grain products to require addition of folic acid. Federal Register. 1996;61(44):8781-97. Riddell, LJ, Chisholm A, et.al. Dietary strategies for lowering HCY concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000; 71(6): 1448 ...
... Food and Drug Administration. Food Standards: amendment of standards of identity for enriched grain products to require addition of folic acid. Federal Register. 1996;61(44):8781-97. Riddell, LJ, Chisholm A, et.al. Dietary strategies for lowering HCY concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000; 71(6): 1448 ...
Reactions
... • 4: Several enzymes of the Calvin Cycle are activated by the breaking of disulphide bridges of enzymes involved in the working of the cycle. – the activity of the light reactions is communicated to the dark reactions by an ...
... • 4: Several enzymes of the Calvin Cycle are activated by the breaking of disulphide bridges of enzymes involved in the working of the cycle. – the activity of the light reactions is communicated to the dark reactions by an ...
Paper
... 7. A chemical equilibrium is established when eleven moles of hydrogen and eleven moles of iodine are mixed at a temperature of 764 K. Initially the colour of the mixture is deep purple due to the high concentration of iodine vapour. The purple colour fades and when equilibrium is established the co ...
... 7. A chemical equilibrium is established when eleven moles of hydrogen and eleven moles of iodine are mixed at a temperature of 764 K. Initially the colour of the mixture is deep purple due to the high concentration of iodine vapour. The purple colour fades and when equilibrium is established the co ...
Solution
... Sample Problem 20.1 The Enzyme Active Site What is the function of the active site in an enzyme? ...
... Sample Problem 20.1 The Enzyme Active Site What is the function of the active site in an enzyme? ...
What does glycolysis make and why is it important?
... sources assert that glycolysis produces pyruvic acid (i.e., pyruvate and protons), and that under anaerobic conditions, glycolysis produces lactic acid. In their thorough review of the stoichiometry of glycolysis, Robergs et al. (10), among others, including authors of papers in the Journal of Appli ...
... sources assert that glycolysis produces pyruvic acid (i.e., pyruvate and protons), and that under anaerobic conditions, glycolysis produces lactic acid. In their thorough review of the stoichiometry of glycolysis, Robergs et al. (10), among others, including authors of papers in the Journal of Appli ...
Energy Systems
... exercise. Anaerobic Glycolysis refers to the breakdown of glucose (glycolysis) to pyruvate, which in the absence of O2, is converted to lactic acid. In muscle fibers, glucose is made available through the breakdown of muscle glycogen stores. Anaerobic glycolysis is not limited by the availability of ...
... exercise. Anaerobic Glycolysis refers to the breakdown of glucose (glycolysis) to pyruvate, which in the absence of O2, is converted to lactic acid. In muscle fibers, glucose is made available through the breakdown of muscle glycogen stores. Anaerobic glycolysis is not limited by the availability of ...
Questions - Vanier College
... d. origins of replication always give rise to single replication forks. e. two replication forks diverge from each origin but one always lags behind the other. 20. The energy necessary for making a DNA molecule comes directly from a. sugar. d. NADPH. b. ATP. e. NADH. c. the release of phosphates. 21 ...
... d. origins of replication always give rise to single replication forks. e. two replication forks diverge from each origin but one always lags behind the other. 20. The energy necessary for making a DNA molecule comes directly from a. sugar. d. NADPH. b. ATP. e. NADH. c. the release of phosphates. 21 ...
Normal Protein Trafficking and the Unfolded Protein Response
... Normal trafficking of proteins through the cell involves: 1) Production of proteins along the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) ...
... Normal trafficking of proteins through the cell involves: 1) Production of proteins along the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) ...
experiment six
... Boiling and immediately display yellow precipitation and turn to be brick-red precipitation (sugar about >20g/L) ...
... Boiling and immediately display yellow precipitation and turn to be brick-red precipitation (sugar about >20g/L) ...
Topic: Exchange and functions of carbohydrates
... Digestion and absorption of carbohydrates in gastrointestinal tract. The source of carbohydrates in the human body is food carbohydrates, the main of which is starch. Also, there is glucose, sucrose, lactose and fructose in food. Starch is the form of glucose depositing in the cells of plants. Lacto ...
... Digestion and absorption of carbohydrates in gastrointestinal tract. The source of carbohydrates in the human body is food carbohydrates, the main of which is starch. Also, there is glucose, sucrose, lactose and fructose in food. Starch is the form of glucose depositing in the cells of plants. Lacto ...
L3-RS_Aerobic & Anaerobic Metabolism in
... systems have “caught up with” the working muscles. ◦ Prior to this, some aerobic respiration will occur thanks to the muscle protein, myoglobin, which binds and stores oxygen. ...
... systems have “caught up with” the working muscles. ◦ Prior to this, some aerobic respiration will occur thanks to the muscle protein, myoglobin, which binds and stores oxygen. ...
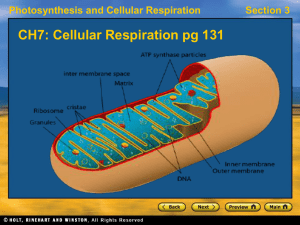
CH7Cellular-Respiration
... Efficiency of Cellular Respiration • In the first stage of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis, an anaerobic process. • Glycolysis results in 2 ATP molecules for each glucose molecule that is broken down. • In the 2nd stage, pyruvate EITHER passes through the ...
... Efficiency of Cellular Respiration • In the first stage of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to pyruvate during glycolysis, an anaerobic process. • Glycolysis results in 2 ATP molecules for each glucose molecule that is broken down. • In the 2nd stage, pyruvate EITHER passes through the ...
Biogeochemical Cycles PPT
... things. The cycles might limit the organisms of Earth or they might happen along side, changing the environment. GEO: Earth. Rocks. Land. This refers to the non-living processes at work. Oxygen cycles through many systems. It's in you and plants for the 'bio' part of the cycle. Oxygen might also win ...
... things. The cycles might limit the organisms of Earth or they might happen along side, changing the environment. GEO: Earth. Rocks. Land. This refers to the non-living processes at work. Oxygen cycles through many systems. It's in you and plants for the 'bio' part of the cycle. Oxygen might also win ...
ppt - Carnegie Mellon University
... Carnegie Mellon University, *University of Pittsburgh Medical School, Pittsburgh, PA ...
... Carnegie Mellon University, *University of Pittsburgh Medical School, Pittsburgh, PA ...
5lb (2270 g) - BioTech USA
... ITS BIOLOGICAL VALUE (BV) IS 104, WHICH MEANS THAT THE PROTEIN OF MUSCLE ON IS UTILIZED BY THIS PERCENTAGE. THIS IS REMARKABLE, ESPECIALLY WHEN COMPARED TO OTHER FORMS OF PROTEIN, FOR EXAMPLE: EGG PROTEIN (100) AND ...
... ITS BIOLOGICAL VALUE (BV) IS 104, WHICH MEANS THAT THE PROTEIN OF MUSCLE ON IS UTILIZED BY THIS PERCENTAGE. THIS IS REMARKABLE, ESPECIALLY WHEN COMPARED TO OTHER FORMS OF PROTEIN, FOR EXAMPLE: EGG PROTEIN (100) AND ...
Analysis of the LacI family of repressor proteins in non
... It is a cogent depiction of how a set of 'structural' genes may be coordinately transcribed in response to environmental conditions and regulates metabolic events in the cell (Lewis, 2005). Binding of the lacO operator region by the LacI repressor protein in E. coli is well studied. Blast analysis o ...
... It is a cogent depiction of how a set of 'structural' genes may be coordinately transcribed in response to environmental conditions and regulates metabolic events in the cell (Lewis, 2005). Binding of the lacO operator region by the LacI repressor protein in E. coli is well studied. Blast analysis o ...
No Slide Title
... Consider the double mutant, AB, composed of mutation A and mutation B. In general (but not always -- see below), the binding free energy perturbations caused by single mutations are additive, in other words DDG°wt-mutAB = DDG°wt-mutA + DDG°wt-mutB + DDG°i where DDG°i ≈ 0. DDG°i has been termed the “ ...
... Consider the double mutant, AB, composed of mutation A and mutation B. In general (but not always -- see below), the binding free energy perturbations caused by single mutations are additive, in other words DDG°wt-mutAB = DDG°wt-mutA + DDG°wt-mutB + DDG°i where DDG°i ≈ 0. DDG°i has been termed the “ ...
NAME: Chemistry 232 Analytical Chemistry
... protonated form of Histidine being titrated with 0.1M NaOH. Include the following points: 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 mL titrant. ...
... protonated form of Histidine being titrated with 0.1M NaOH. Include the following points: 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, and 35 mL titrant. ...
The protein quality of raw leaf, seed and root of Moringa oleifera
... of M.oleifera. Leucine is responsible for regulating blood sugar concentrations, growth and repairs of muscles/tissues, hormone production, wound healing and energy production. Its deficiency causes dizziness, headaches, fatigue, depression, confusion, irritability and hypoglycemia in infants [24] R ...
... of M.oleifera. Leucine is responsible for regulating blood sugar concentrations, growth and repairs of muscles/tissues, hormone production, wound healing and energy production. Its deficiency causes dizziness, headaches, fatigue, depression, confusion, irritability and hypoglycemia in infants [24] R ...
Biology 230 Genetics, Spring semester 2005
... tel. 721-7107, email: [email protected]. Lecturer: Dr. John Taylor, Petch Building Rm 011, tel. 472-4079, email: [email protected] Senior Lab Instructor: Ms. Dawna Brand, Cunningham Rm. 110, Tel.721-7096, email: [email protected] Textbook: Genetics Analysis and Principles by Brooker, 4th (2012) edition, McG ...
... tel. 721-7107, email: [email protected]. Lecturer: Dr. John Taylor, Petch Building Rm 011, tel. 472-4079, email: [email protected] Senior Lab Instructor: Ms. Dawna Brand, Cunningham Rm. 110, Tel.721-7096, email: [email protected] Textbook: Genetics Analysis and Principles by Brooker, 4th (2012) edition, McG ...
1 Light Microscopes Electron Microscopes • The simplest form of
... Uses a beam of electrons to magnify the object. These microscopes have 250 times more resolution power than light microscopes so therefore have more accurate clarity on the image. The magnification in electron microscopes is also significantly more than in light microscopes allowing cells to be view ...
... Uses a beam of electrons to magnify the object. These microscopes have 250 times more resolution power than light microscopes so therefore have more accurate clarity on the image. The magnification in electron microscopes is also significantly more than in light microscopes allowing cells to be view ...
Lecture 19
... Allosteric control: by substrates, products, or coenzymes of the pathway (e.g. CTP in ATCase) Covalent modification: (de)phosphorylation by (phosphatases)kinases which are themselves regulated Substrate cycles: Fluxes through r and f can be separately regulated Genetic control: up or down regulated ...
... Allosteric control: by substrates, products, or coenzymes of the pathway (e.g. CTP in ATCase) Covalent modification: (de)phosphorylation by (phosphatases)kinases which are themselves regulated Substrate cycles: Fluxes through r and f can be separately regulated Genetic control: up or down regulated ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.