View Essential-4 Data Sheet
... eicosapentaenoic acid(EPA) per serving. As the most abundant fatty acid in the brain, adequate amounts of DHA are needed throughout infancy and adulthood for ongoing optimal function. Low levels of DHA may adversely influence behavior and mental performance, and have been correlated with changes in ...
... eicosapentaenoic acid(EPA) per serving. As the most abundant fatty acid in the brain, adequate amounts of DHA are needed throughout infancy and adulthood for ongoing optimal function. Low levels of DHA may adversely influence behavior and mental performance, and have been correlated with changes in ...
Gen Chem Final--review problems Fall 2006
... In a solution calorimeter, 50.0 mL of 0.100 M AgNO3 solution and 50.0 mL of 0.100 M HCl are mixed. The following reaction occurs: Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Î AgCl(s) If the two solutions were initially at 22.6°C and the final temperature is 23.4°C, calculate qrxn and ΔHrxn. Assume that the surroundings are ...
... In a solution calorimeter, 50.0 mL of 0.100 M AgNO3 solution and 50.0 mL of 0.100 M HCl are mixed. The following reaction occurs: Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Î AgCl(s) If the two solutions were initially at 22.6°C and the final temperature is 23.4°C, calculate qrxn and ΔHrxn. Assume that the surroundings are ...
PowerPoint
... All one kind of atom. Compounds are substances that can be broken down by chemical methods • When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. • Made of molecules- two or more atoms ...
... All one kind of atom. Compounds are substances that can be broken down by chemical methods • When they are broken down, the pieces have completely different properties than the compound. • Made of molecules- two or more atoms ...
Energy Boost: The Warburg Effect Returns in a New Theory of Cancer
... shift to glycolysis.” Such transformed cells take up glucose continuously, generating energy in the cell—energy used to drive cell division and growth. Glycolysis produces only two ATP molecules per glucose molecule, compared with 38 for complete oxidation. But for a cancer cell, “It’s actually high ...
... shift to glycolysis.” Such transformed cells take up glucose continuously, generating energy in the cell—energy used to drive cell division and growth. Glycolysis produces only two ATP molecules per glucose molecule, compared with 38 for complete oxidation. But for a cancer cell, “It’s actually high ...
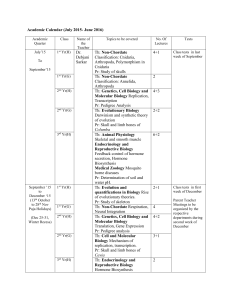
Academic Calendar (July 2015- June 2016) Debjani Sarkar Th: Non
... Class tests in first week of December Parent Teacher Meetings to be organized by the respective departments during second week of December ...
... Class tests in first week of December Parent Teacher Meetings to be organized by the respective departments during second week of December ...
9.4 DNA-Binding Proteins
... 9.2 trp Repressor and role of Tryptophan • trp repressor uses helix-turn-helix (HTH) DNA binding motif to contact operator • Aporepressor is not active in binding DNA • Tryptophan forces recognition helices of trp repressor dimer into proper position to bind trp operator Fig. 12 ...
... 9.2 trp Repressor and role of Tryptophan • trp repressor uses helix-turn-helix (HTH) DNA binding motif to contact operator • Aporepressor is not active in binding DNA • Tryptophan forces recognition helices of trp repressor dimer into proper position to bind trp operator Fig. 12 ...
Chapter One
... All of the statements about the nature of the hydrogen bond are true EXCEPT: a. The donor is a hydrogen atom bonded to a carbon. b. The more linear the bond, the stronger the interaction. c. The acceptor is a weakly electronegative atom containing a nonbonding pair of electrons. d. It is a type of n ...
... All of the statements about the nature of the hydrogen bond are true EXCEPT: a. The donor is a hydrogen atom bonded to a carbon. b. The more linear the bond, the stronger the interaction. c. The acceptor is a weakly electronegative atom containing a nonbonding pair of electrons. d. It is a type of n ...
Final a
... 4. (10 pts) List the environmental conditions/small molecules that activate rubisco and/or enzymes of the Calvin cycle. ...
... 4. (10 pts) List the environmental conditions/small molecules that activate rubisco and/or enzymes of the Calvin cycle. ...
Background reading from Campbell et al
... meiosis and mitosis; how do we get from DNA to proteins. I don’t expect you to know the messy details – e.g., every last step of meiosis or mitosis. In most cases, I just want you to take a look at the introductory sections of the listed chapters. This will be particularly important if you did not t ...
... meiosis and mitosis; how do we get from DNA to proteins. I don’t expect you to know the messy details – e.g., every last step of meiosis or mitosis. In most cases, I just want you to take a look at the introductory sections of the listed chapters. This will be particularly important if you did not t ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... – Isotopes = atoms of the same element with different atomic masses ...
... – Isotopes = atoms of the same element with different atomic masses ...
Endocrine Vivas
... (irreversible, the enzyme for acetoacetate => acetyl-CoA is not found in liver cells) - These products are water soluble (unlike fatty acids and triglycerides) and are exported from the liver to extraheaptic tissues (esp. brain, skeletal and cardiac muscle) for ultilisation - They convert the β-HB = ...
... (irreversible, the enzyme for acetoacetate => acetyl-CoA is not found in liver cells) - These products are water soluble (unlike fatty acids and triglycerides) and are exported from the liver to extraheaptic tissues (esp. brain, skeletal and cardiac muscle) for ultilisation - They convert the β-HB = ...
Chemistry Content Standards
... SC3 Students will use the modern atomic theory to explain the characteristics of atoms. a. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, and position of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. b. Use the orbital configuration of neutral atoms to explain its effect on the atom’s chemical prop ...
... SC3 Students will use the modern atomic theory to explain the characteristics of atoms. a. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, and position of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. b. Use the orbital configuration of neutral atoms to explain its effect on the atom’s chemical prop ...
C nuclear magnetic resonance studies of anaerobic
... respectively. The now generally accepted mechanism of glucose catabolism in the bloodstream form of these eukaryotes is the Embden-Meyerhof scheme, first proposed by Grant and Fulton (1$). Under anaerobic conditions however, when equimolar quantities of pyruvate and glycerol are produced (12,14), re ...
... respectively. The now generally accepted mechanism of glucose catabolism in the bloodstream form of these eukaryotes is the Embden-Meyerhof scheme, first proposed by Grant and Fulton (1$). Under anaerobic conditions however, when equimolar quantities of pyruvate and glycerol are produced (12,14), re ...
Protein Metabolism
... 4- Amines: dietary or body monomine by the action of amine oxidase, NH3 is generated. 5- Purines/Pyrimidines: Catabolism of Pu./Py., NH2 attached to the rings is released as NH3. 6- Non-Oxidative deamination of A.As.: Asn, Cys, Gln, His, Ser and Thr. The reaction starts with removal of H2O (dehydrat ...
... 4- Amines: dietary or body monomine by the action of amine oxidase, NH3 is generated. 5- Purines/Pyrimidines: Catabolism of Pu./Py., NH2 attached to the rings is released as NH3. 6- Non-Oxidative deamination of A.As.: Asn, Cys, Gln, His, Ser and Thr. The reaction starts with removal of H2O (dehydrat ...
CHEMISTRY FINAL EXAM REVIEW SHEET
... Hydrogen is usually +1. Oxygen is usually –2. In a compound, the more electronegative element is given an oxidation number equal to its usual ionic charge. The sum of the oxidation numbers must equal the overall charge on the compound or ion. ...
... Hydrogen is usually +1. Oxygen is usually –2. In a compound, the more electronegative element is given an oxidation number equal to its usual ionic charge. The sum of the oxidation numbers must equal the overall charge on the compound or ion. ...
respiration_how cell..
... Amino acids that will be catabolized must have their amino groups removed via deamination. The carbon skeletons are modified by enzymes and enter as intermediaries into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle, depending on their structure. ...
... Amino acids that will be catabolized must have their amino groups removed via deamination. The carbon skeletons are modified by enzymes and enter as intermediaries into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle, depending on their structure. ...
Inborn Errors of Amino Acid Metabolism
... If a pregnant mother is affected, the fetus is affected but the opposite will not affect the mother because the mother’s system will clear it. dopamine ...
... If a pregnant mother is affected, the fetus is affected but the opposite will not affect the mother because the mother’s system will clear it. dopamine ...
Ars Pharmaceutica - Facultad de Farmacia
... determination of the amino acid profile of the earthworm flour in order to be used as a non-conventional ingredient in the formulation and preparation of diets for fish is very important. The traditional method for the amino acid composition analysis of proteins is separation by ion-exchange chromat ...
... determination of the amino acid profile of the earthworm flour in order to be used as a non-conventional ingredient in the formulation and preparation of diets for fish is very important. The traditional method for the amino acid composition analysis of proteins is separation by ion-exchange chromat ...
PP - Columbia University
... Exception #1: • 1) Water: 55 M (pure water) is considered the “unit” concentration in this case instead of 1M The concentration of water rarely changes during the course of an aqueous reaction, since water is at such a high concentration. • So when calulating Go, instead of writing in “55” when wat ...
... Exception #1: • 1) Water: 55 M (pure water) is considered the “unit” concentration in this case instead of 1M The concentration of water rarely changes during the course of an aqueous reaction, since water is at such a high concentration. • So when calulating Go, instead of writing in “55” when wat ...
Slides - Pages
... prior biochemical knowledge Goal: Investigate the empirical support for biochemical ...
... prior biochemical knowledge Goal: Investigate the empirical support for biochemical ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.