
Chapter 9
... Figure 5.4 (a) Linear and ring forms. Chemical equilibrium between the linear and ring structures greatly favors the formation of rings. To form the glucose ring, carbon 1 bonds to the oxygen attached to carbon 5. ...
... Figure 5.4 (a) Linear and ring forms. Chemical equilibrium between the linear and ring structures greatly favors the formation of rings. To form the glucose ring, carbon 1 bonds to the oxygen attached to carbon 5. ...
Reactive Oxygen Species
... (red), so that they would now contain a new mixture of molecules, such as crosslinkers and enzymes. Clustering could occur either extracellularly, within the membrane, or in the cytosol (a–c, respectively). Raft clustering could also occur through GPI-anchored proteins (yellow), either as a primary ...
... (red), so that they would now contain a new mixture of molecules, such as crosslinkers and enzymes. Clustering could occur either extracellularly, within the membrane, or in the cytosol (a–c, respectively). Raft clustering could also occur through GPI-anchored proteins (yellow), either as a primary ...
Structure and physical-chemical properties of enzymes
... double bond in a nonhydrolytic, nonoxidative elimination ...
... double bond in a nonhydrolytic, nonoxidative elimination ...
Chapters 14
... 7. What is the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 9.1 g of H3PO4 in enough water to make 22.3 L of solution? Assume that H3PO4 ionizes completely in water to H+ and PO43ions. What is the pH of the solution? Find the concentration of OH-? ...
... 7. What is the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 9.1 g of H3PO4 in enough water to make 22.3 L of solution? Assume that H3PO4 ionizes completely in water to H+ and PO43ions. What is the pH of the solution? Find the concentration of OH-? ...
• Sources of glucose • Phases of glucose homeostasis • Hormones
... oxidaCon for energy producCon q High KB conc. and glucose levels inhibit proteolysis in muscle (conservaCon of muscle) q When all fat and KBs are used up => Body uses muscle protein to maintain ...
... oxidaCon for energy producCon q High KB conc. and glucose levels inhibit proteolysis in muscle (conservaCon of muscle) q When all fat and KBs are used up => Body uses muscle protein to maintain ...
APenzymes
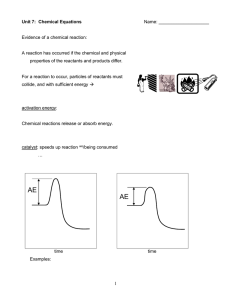
... increase rate of reaction without being consumed reduce activation energy don’t change free energy (G) released or required ...
... increase rate of reaction without being consumed reduce activation energy don’t change free energy (G) released or required ...
Influence of the Side Chain in the Structure and Fragmentation of
... for the radical cation. This is not surprising considering that structures A and B differ on the relative orientation the carboxylic group with respect to the CH3 side chain. For example, the OCCN dihedral angles for structures IIA and IIB are 169° and -167°, respectively. However, ionization introd ...
... for the radical cation. This is not surprising considering that structures A and B differ on the relative orientation the carboxylic group with respect to the CH3 side chain. For example, the OCCN dihedral angles for structures IIA and IIB are 169° and -167°, respectively. However, ionization introd ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... (12%) 5.60 g of solid carbon is placed in a rigid evacuated 2.5 L container. Carbon dioxide is added to the container to a final pressure of 1.50 atm at 298 K. a. Calculate the number of moles of each reactant in the container originally. 2 CO(g) ∆H˚ = 173 kJ b. The container is heated to 1100 K and ...
... (12%) 5.60 g of solid carbon is placed in a rigid evacuated 2.5 L container. Carbon dioxide is added to the container to a final pressure of 1.50 atm at 298 K. a. Calculate the number of moles of each reactant in the container originally. 2 CO(g) ∆H˚ = 173 kJ b. The container is heated to 1100 K and ...
Environmentally Induced Changes in Amino Acid Composition in the
... Amino acid composition is an important feature in determining the nutritional value of wheat grain for human and animal diets. Environmental conditions are known to influence protein quantity as well as grain production and, in turn, amino acid composition. In this study, grain yield, protein conten ...
... Amino acid composition is an important feature in determining the nutritional value of wheat grain for human and animal diets. Environmental conditions are known to influence protein quantity as well as grain production and, in turn, amino acid composition. In this study, grain yield, protein conten ...
Poster
... A particular heme-containing enzyme, known as CYP17, converts cholesterol-derived hormones into androgens including testosterone. Fe(III) is a key part as all reactions occur within this heme group. Pharmacological efforts, such as the drug abiraterone, decrease the efficiency of CYP17 catalysis and ...
... A particular heme-containing enzyme, known as CYP17, converts cholesterol-derived hormones into androgens including testosterone. Fe(III) is a key part as all reactions occur within this heme group. Pharmacological efforts, such as the drug abiraterone, decrease the efficiency of CYP17 catalysis and ...
students - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... polymer: a large molecule (often a chain) made of many smaller molecules called monomers Polymers can be made more rigid if the chains are linked together by way of a crosslinking agent. ...
... polymer: a large molecule (often a chain) made of many smaller molecules called monomers Polymers can be made more rigid if the chains are linked together by way of a crosslinking agent. ...
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
... Catalytic Domain of Human Phenylalanine Hydroxylase in its Catalytically Active Fe(II) Form and Binary Complex with Tetrahydrobiopterin. J.Mol.Biol. 314; 266 H.Erlandsen, E.Bjorgo, T.Flatmark, R.C.Stevens(2000). Crystal Structure and SiteSpecific Mutagenesis of Pterin-Bound Human Phenylalanine Hydro ...
... Catalytic Domain of Human Phenylalanine Hydroxylase in its Catalytically Active Fe(II) Form and Binary Complex with Tetrahydrobiopterin. J.Mol.Biol. 314; 266 H.Erlandsen, E.Bjorgo, T.Flatmark, R.C.Stevens(2000). Crystal Structure and SiteSpecific Mutagenesis of Pterin-Bound Human Phenylalanine Hydro ...
Microbiology bio 123
... 1. used in surgery, 2. can be used on living tissue, 3. can be used to purify water, Alcohols, 1. antiseptics, 2. work by denaturing proteins, 3. they are dehydrating agents, they dissolve lipids, 4. The more carbons in the alcohol the better, 1. CH3OH, methanol, very weak alcohol, 2. C2H5OH, ethano ...
... 1. used in surgery, 2. can be used on living tissue, 3. can be used to purify water, Alcohols, 1. antiseptics, 2. work by denaturing proteins, 3. they are dehydrating agents, they dissolve lipids, 4. The more carbons in the alcohol the better, 1. CH3OH, methanol, very weak alcohol, 2. C2H5OH, ethano ...
Page 1 - csfcbiology
... Name the monomers that make up the active site of the enzyme (lines 6 – 7). ...
... Name the monomers that make up the active site of the enzyme (lines 6 – 7). ...
Lecture #4 - Dr. Ames - Molecular and Cell Biology
... scores and modeled as a quadratic function of the ln-liver nonheme iron as the independent variable. The equation for the RCR ratio's Z score was obtained from inverted RCR values (1/RCR) so that normal rats had the lower instead of the higher values. For presentation purposes each model line was ob ...
... scores and modeled as a quadratic function of the ln-liver nonheme iron as the independent variable. The equation for the RCR ratio's Z score was obtained from inverted RCR values (1/RCR) so that normal rats had the lower instead of the higher values. For presentation purposes each model line was ob ...
Computational method on biochemistry
... acids. Only experimental data were used in parameterization. • However, AMBER has been widely used not only for proteins and DNA, but also for many other classes of models, such as polymers and small molecules. For the latter classes of models, various authors have added parameters and extended AMBE ...
... acids. Only experimental data were used in parameterization. • However, AMBER has been widely used not only for proteins and DNA, but also for many other classes of models, such as polymers and small molecules. For the latter classes of models, various authors have added parameters and extended AMBE ...
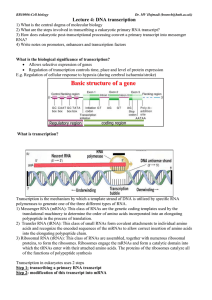
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Performed by spliceosomes (large RNA-protein complex made of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) Recognise exon-intron boundaries and splice exons together by transesterification reactions Cell type-specific splicing ...
... Performed by spliceosomes (large RNA-protein complex made of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins) Recognise exon-intron boundaries and splice exons together by transesterification reactions Cell type-specific splicing ...
Chapter 14 Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, and the Pentose
... an acyl arsenate, which spontaneously hydrolyzes. This prevents formation of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and ATP but allows formation of 3-phosphoglycerate, which continues through the pathway. 16. Role of the Vitamin Niacin Adults engaged in strenuous physical activity require an intake of about 160 ...
... an acyl arsenate, which spontaneously hydrolyzes. This prevents formation of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and ATP but allows formation of 3-phosphoglycerate, which continues through the pathway. 16. Role of the Vitamin Niacin Adults engaged in strenuous physical activity require an intake of about 160 ...
MMP-10 catalytic domain, human, recombinant
... MW = 18.5kDa. Recombinant matrix metalloproteinase-10 (MMP-10, stromelysin-2, transin 2) cloned from human cDNA, expressed in E. coli. The enzyme consists of the catalytic domain of human MMP-10 (residues 99-263 swissprot accession P09238) with the mutation F170N. The protein has been mutated to inc ...
... MW = 18.5kDa. Recombinant matrix metalloproteinase-10 (MMP-10, stromelysin-2, transin 2) cloned from human cDNA, expressed in E. coli. The enzyme consists of the catalytic domain of human MMP-10 (residues 99-263 swissprot accession P09238) with the mutation F170N. The protein has been mutated to inc ...
Synergistic Effects of Branched
... Key words: wine fermentation, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, branched-chain amino acids, phenylalanine, aroma compounds The effects of adding branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs, including L-valine, L-leucine and L-isoleucine), L-phenylalanine and a mixture of them (BCAAs + Phe) on the fermentation profile ...
... Key words: wine fermentation, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, branched-chain amino acids, phenylalanine, aroma compounds The effects of adding branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs, including L-valine, L-leucine and L-isoleucine), L-phenylalanine and a mixture of them (BCAAs + Phe) on the fermentation profile ...
Pseudo-Replication of [GADV]-Proteins and Origin of Life
... means that the nucleotides are far more complex than the four amino acids. The nucleotides would never be synthesized under pre-biotic conditions through a random combinatory process [4]. Moreover, it must be quite difficult to synthesize even ribose (fructofuranose: a component of nucleotide) havin ...
... means that the nucleotides are far more complex than the four amino acids. The nucleotides would never be synthesized under pre-biotic conditions through a random combinatory process [4]. Moreover, it must be quite difficult to synthesize even ribose (fructofuranose: a component of nucleotide) havin ...
Cellular Respiration
... (ATP) from macromolecules (glucose). Catabolic: Rxn that breaks molecules down Makes CO2 and H2O as well as energy (ATP) ...
... (ATP) from macromolecules (glucose). Catabolic: Rxn that breaks molecules down Makes CO2 and H2O as well as energy (ATP) ...
Biology CST framework
... functions. For example, all organisms require an outside source of energy to sustain life processes; all organisms demonstrate patterns of growth and, in many cases, senescence, the process of becoming old; and the continuity of all species requires reproduction. All organisms are constructed from t ...
... functions. For example, all organisms require an outside source of energy to sustain life processes; all organisms demonstrate patterns of growth and, in many cases, senescence, the process of becoming old; and the continuity of all species requires reproduction. All organisms are constructed from t ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.



















![Pseudo-Replication of [GADV]-Proteins and Origin of Life](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015397345_1-c189eb37b7232bb5a87b48dfe8b0c10b-300x300.png)

