Problem 1: A brief history of life in the universe
... atoms escape more readily than nitrogen molecules even though the escape velocity is independent of the mass of the escaping object. The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, inter ...
... atoms escape more readily than nitrogen molecules even though the escape velocity is independent of the mass of the escaping object. The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, inter ...
DNA Review Worksheet
... 9. If a strand of mRNA contain the sequence, U-A-G-C-U-A-U-C-A-A-A-U, what tRNA anticodons would be needed to translate the sequence?_____________________________ 10. How does mRNA get out of the nucleus? _______________________________________________ 11. What is the difference between an amino aci ...
... 9. If a strand of mRNA contain the sequence, U-A-G-C-U-A-U-C-A-A-A-U, what tRNA anticodons would be needed to translate the sequence?_____________________________ 10. How does mRNA get out of the nucleus? _______________________________________________ 11. What is the difference between an amino aci ...
Problem 1: “A brief history” of life in the universe
... atoms escape more readily than nitrogen molecules even though the escape velocity is independent of the mass of the escaping object. The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, inter ...
... atoms escape more readily than nitrogen molecules even though the escape velocity is independent of the mass of the escaping object. The chemical composition of the atmosphere of a planet depends on the temperature of the planet’s atmosphere (which in turn depends on the distance from the sun, inter ...
biochemical tests and their use for identification purposes
... keep the cell in oxidation-reduction balance. Fermentation of glucose begins with glycolysis to generate energy, reduced coenzyme, and an electron acceptor. Regeneration of oxidized coenzyme needed for continued energy production is coupled to the reduction of a break-down product of glucose. Lactic ...
... keep the cell in oxidation-reduction balance. Fermentation of glucose begins with glycolysis to generate energy, reduced coenzyme, and an electron acceptor. Regeneration of oxidized coenzyme needed for continued energy production is coupled to the reduction of a break-down product of glucose. Lactic ...
CH1710 PrEX#2 Sp2013 answers
... _____ 19. Which of the following is an acid base reaction? A) C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) B) 2 HClO4(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + Ca(ClO4)2(aq) C) Fe(s) + 2 AgNO3(aq) → 2 Ag(s) + Fe(NO3)2(aq) D) MgSO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Mg(NO3)2(aq) + BaSO4(s) ...
... _____ 19. Which of the following is an acid base reaction? A) C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) B) 2 HClO4(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + Ca(ClO4)2(aq) C) Fe(s) + 2 AgNO3(aq) → 2 Ag(s) + Fe(NO3)2(aq) D) MgSO4(aq) + Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Mg(NO3)2(aq) + BaSO4(s) ...
I. DNA, Chromosomes, Chromatin, and Genes II. DNA
... 9. If a strand of mRNA contain the sequence, U-A-G-C-U-A-U-C-A-A-A-U, what tRNA anticodons would be needed to translate the sequence?_____________________________ 10. How does mRNA get out of the nucleus? ______________________________________________ 11. What is the difference between an amino acid ...
... 9. If a strand of mRNA contain the sequence, U-A-G-C-U-A-U-C-A-A-A-U, what tRNA anticodons would be needed to translate the sequence?_____________________________ 10. How does mRNA get out of the nucleus? ______________________________________________ 11. What is the difference between an amino acid ...
Chapter 8
... • Biologists want to know which reactions occur spontaneously and which require input of energy • To do so, they need to determine energy changes that occur in chemical reactions ...
... • Biologists want to know which reactions occur spontaneously and which require input of energy • To do so, they need to determine energy changes that occur in chemical reactions ...
But when you consider that problems with energy production are a
... of six carbon atoms, is broken down to smaller chains of three carbon atoms. The breaking of the bond from six carbon atoms to three atoms is just like releasing a compressed spring. A compressed spring has stored energy and if you cut the string binding it, it releases its energy and springs outwar ...
... of six carbon atoms, is broken down to smaller chains of three carbon atoms. The breaking of the bond from six carbon atoms to three atoms is just like releasing a compressed spring. A compressed spring has stored energy and if you cut the string binding it, it releases its energy and springs outwar ...
Chemical Calculations, Chemical Equations
... Atoms forming negative ions always generate one, predictable kind (gaining all electrons to bring the s&p orbital sum to 8). However, some atoms can form more than one positively charged ion, having the ability to lose different amount of electrons each time. This behavior is difficult to predict, a ...
... Atoms forming negative ions always generate one, predictable kind (gaining all electrons to bring the s&p orbital sum to 8). However, some atoms can form more than one positively charged ion, having the ability to lose different amount of electrons each time. This behavior is difficult to predict, a ...
nutrition h
... Protein is necessary for the growth, repair, and maintenance of every cell in the body. It is present in various forms in the body as part of enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and tissues. Proteins help maintain the proper acid/base balance in the body, and if needed they can be broken down by the body ...
... Protein is necessary for the growth, repair, and maintenance of every cell in the body. It is present in various forms in the body as part of enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and tissues. Proteins help maintain the proper acid/base balance in the body, and if needed they can be broken down by the body ...
Slide ()
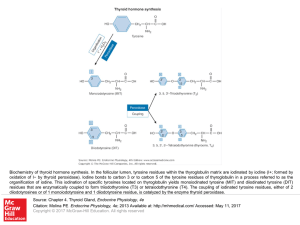
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles
... By bacteria: Plants and animals cannot take nitrogen directly out of the atmosphere. Therefore, it must be fixed, or taken out of the atmosphere, by bacteria. These bacteria live in symbiosis with legumes, a simple nut like dried fruit within the soil. By lightning, forest fires and hot lava flows: ...
... By bacteria: Plants and animals cannot take nitrogen directly out of the atmosphere. Therefore, it must be fixed, or taken out of the atmosphere, by bacteria. These bacteria live in symbiosis with legumes, a simple nut like dried fruit within the soil. By lightning, forest fires and hot lava flows: ...
PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY AND FRUCTOSE METABOLISM
... • Glycogen is less readily depleted in muscle and there is more total glycogen in muscle than in any other tissue of the body. • Brain has a very low glycogen concentration. The brain is largely dependent upon circulating glucose for the carbohydrate that it requires. ...
... • Glycogen is less readily depleted in muscle and there is more total glycogen in muscle than in any other tissue of the body. • Brain has a very low glycogen concentration. The brain is largely dependent upon circulating glucose for the carbohydrate that it requires. ...
Chap 4. Growth and Metabolism
... Glycolysis – Conversion of C6 sugars to CO2 and pyruvic acid Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb Cycle) – Oxydation of pyruvic acid to H+, eand CO2 (occurs in mitochondria) 3. The Q10 - The rate of respiration doubles when temperature rises 10 oC (18 oF) - Respiration can be reduced by lowering O2 and increasin ...
... Glycolysis – Conversion of C6 sugars to CO2 and pyruvic acid Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb Cycle) – Oxydation of pyruvic acid to H+, eand CO2 (occurs in mitochondria) 3. The Q10 - The rate of respiration doubles when temperature rises 10 oC (18 oF) - Respiration can be reduced by lowering O2 and increasin ...
Lipid-binding proteins in rat and human kidney
... In the present study, we showed for the first time that mRNA for H-FABP, SCP2, ACBP, CRBP, and PITP is expressed variably in rat glomeruli or RCM. Because lipophilic molecules, such as retinoic acid, and phosphatidylinositol are known to be elements of several cell-tocell signaling pathways, these L ...
... In the present study, we showed for the first time that mRNA for H-FABP, SCP2, ACBP, CRBP, and PITP is expressed variably in rat glomeruli or RCM. Because lipophilic molecules, such as retinoic acid, and phosphatidylinositol are known to be elements of several cell-tocell signaling pathways, these L ...
Meaning of Life Packet
... Regulation involves a number of coordinated activities that serve to maintain homeostasis, a stable internal environment. This is important because an organism’s internal and external environments are constantly changing. The two major organ systems involved in regulation are the nervous system and ...
... Regulation involves a number of coordinated activities that serve to maintain homeostasis, a stable internal environment. This is important because an organism’s internal and external environments are constantly changing. The two major organ systems involved in regulation are the nervous system and ...
unit3_lesson10_translation1_markscheme
... POD Mark Scheme Explain the translation of a protein from DNA [8]. ...
... POD Mark Scheme Explain the translation of a protein from DNA [8]. ...
chap18 oxidative phosphorylation
... Oxidative pphosphorylation produces 30 of the 32 molecules of ATP that are formed when glucose is oxidized to CO2 and H2O. The process is conceptually easy but mechanistically very difficult. The electron flow from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen through protein complexes leads to pumping of protons outsid ...
... Oxidative pphosphorylation produces 30 of the 32 molecules of ATP that are formed when glucose is oxidized to CO2 and H2O. The process is conceptually easy but mechanistically very difficult. The electron flow from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen through protein complexes leads to pumping of protons outsid ...
Testing Methylation Pathways
... Methylation is a process where certain nutrients called ‘methyl donors’ are added to specific elements of DNA, our gene markers and proteins that keep them physiologically active. Methylation is a major pathway to focus on in understanding autoimmune and neurological diseases such as multiple sclero ...
... Methylation is a process where certain nutrients called ‘methyl donors’ are added to specific elements of DNA, our gene markers and proteins that keep them physiologically active. Methylation is a major pathway to focus on in understanding autoimmune and neurological diseases such as multiple sclero ...
Lipid Oxidation - anslab.iastate.edu
... • Ground state oxygen has its outermost pair of electrons parallel spins: does not allow them to react with most molecules • Ground-state or triplet oxygen is not very reactive • Can be activated by the addition of energy, and transformed into reactive ...
... • Ground state oxygen has its outermost pair of electrons parallel spins: does not allow them to react with most molecules • Ground-state or triplet oxygen is not very reactive • Can be activated by the addition of energy, and transformed into reactive ...
Oxidation of Carbohydrate
... – High net ATP yield but slow ATP production – Must be broken down into free fatty acids (FFAs) and glycerol – Only FFAs are used to make ATP ...
... – High net ATP yield but slow ATP production – Must be broken down into free fatty acids (FFAs) and glycerol – Only FFAs are used to make ATP ...
Enzyme Activity
... all enzymes have active site engaged enzyme is saturated maximum rate of reaction ...
... all enzymes have active site engaged enzyme is saturated maximum rate of reaction ...
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA), Krebs Cycle
... multienzyme complex. pyr dehydrogenase complex is not part of TCA cycle proper, but is a mojor source of acetyl CoA. The irreversibility of the reaction explains why glucose can not be formed from acetyl CoA in gluconeogenesis. ...
... multienzyme complex. pyr dehydrogenase complex is not part of TCA cycle proper, but is a mojor source of acetyl CoA. The irreversibility of the reaction explains why glucose can not be formed from acetyl CoA in gluconeogenesis. ...
Lesson 12. Hormones
... Insulin is a polypeptide hormone synthesized in the pancreas by β-cells, which construct a single chain molecule called proinsulin. Enzymes excise a portion of the proinsulin molecule called the C peptide, producing the actual insulin molecule. When in demand, the β-cells will release insulin togeth ...
... Insulin is a polypeptide hormone synthesized in the pancreas by β-cells, which construct a single chain molecule called proinsulin. Enzymes excise a portion of the proinsulin molecule called the C peptide, producing the actual insulin molecule. When in demand, the β-cells will release insulin togeth ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.