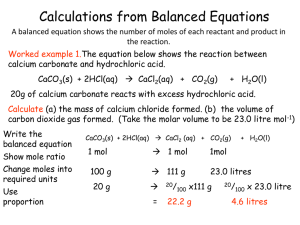
Calculations from Balanced Equations
... Any other reactant which is left over is said to be ‘in excess’. The reactant which is used up determines the mass of product formed. ...
... Any other reactant which is left over is said to be ‘in excess’. The reactant which is used up determines the mass of product formed. ...
Novel regulatory roles of cAMP receptor proteins in
... available in the online Supplementary Material). M. smegmatis mc2155 (Snapper et al., 1990) and derived strains (Table S1) were grown in LB supplemented with 0.05 % (w/v) Tween 80 (Sigma ...
... available in the online Supplementary Material). M. smegmatis mc2155 (Snapper et al., 1990) and derived strains (Table S1) were grown in LB supplemented with 0.05 % (w/v) Tween 80 (Sigma ...
HIGHLY VISCOUS DOUGH FORMING PROPERTIES OF MARAMA PROTEIN
... defined as the ratio of G" over G', reflects the balance between the viscous and the elastic character of a viscoelastic material (Mezger, 2006). As small dynamic deformation analysis is non-destructive, it can provide some information on the types of molecular bonding that may be responsible for th ...
... defined as the ratio of G" over G', reflects the balance between the viscous and the elastic character of a viscoelastic material (Mezger, 2006). As small dynamic deformation analysis is non-destructive, it can provide some information on the types of molecular bonding that may be responsible for th ...
Crystal structure of mouse coronavirus receptor
... fusion protein (17). During maturation, the spike protein is often cleaved into a receptor-binding subunit S1 and a membranefusion subunit S2 that associate together through noncovalent interactions (Fig. 1A). S1 sequences are relatively well conserved within each coronavirus group, but differ marke ...
... fusion protein (17). During maturation, the spike protein is often cleaved into a receptor-binding subunit S1 and a membranefusion subunit S2 that associate together through noncovalent interactions (Fig. 1A). S1 sequences are relatively well conserved within each coronavirus group, but differ marke ...
Does Lactic Acid Cause Muscular Fatigue?
... Aerobic metabolism. As indicated, pyruvate and NADH, (and, perhaps, lactic acid), must be absorbed from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria of muscle fibers in order to continue being metabolized. Mitochondria are rod-shaped structures found in the cytoplasm of cells (see figure 4). They have been l ...
... Aerobic metabolism. As indicated, pyruvate and NADH, (and, perhaps, lactic acid), must be absorbed from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria of muscle fibers in order to continue being metabolized. Mitochondria are rod-shaped structures found in the cytoplasm of cells (see figure 4). They have been l ...
Neural Marker Antibodies Epitope Tag Antibodies
... tend to self-aggregate into distinctive extracellular “plaques.” These plaques are evident in brains from patients with Alzheimer’s disease, as well as in brains from individuals with a history of traumatic head injuries. In the case of Alzheimer’s disease, it has been suggested that these extracell ...
... tend to self-aggregate into distinctive extracellular “plaques.” These plaques are evident in brains from patients with Alzheimer’s disease, as well as in brains from individuals with a history of traumatic head injuries. In the case of Alzheimer’s disease, it has been suggested that these extracell ...
BIO205 - National Open University of Nigeria
... duplicated genetic material, creating two identical daughter cells. The meiosis session makes you to understand the events that occur in the process of meiosis that takes place to produce gametes during sexual reproduction. You will get to know more on prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that make up a ...
... duplicated genetic material, creating two identical daughter cells. The meiosis session makes you to understand the events that occur in the process of meiosis that takes place to produce gametes during sexual reproduction. You will get to know more on prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that make up a ...
Role of Dietary Soy Protein in Obesity
... humans [14]. Among the three macronutrients (carbohydrate, fat, and protein), protein has the most suppressing effect on food intake. In addition, dietary protein has been shown to induce higher satiating and thermogenic effects and greater weight loss than carbohydrates [15-17]. In a randomized tri ...
... humans [14]. Among the three macronutrients (carbohydrate, fat, and protein), protein has the most suppressing effect on food intake. In addition, dietary protein has been shown to induce higher satiating and thermogenic effects and greater weight loss than carbohydrates [15-17]. In a randomized tri ...
chemistry - My Study materials – Kumar
... as the smallest particles of matter are called atoms. Characteristics of atoms: Atom is the smallest particle of matter. All elements are made of tiny particles called atom. Atoms are very small in size and cannot be seen through naked eyes. Atom does not exist in free-state in nature. But atom take ...
... as the smallest particles of matter are called atoms. Characteristics of atoms: Atom is the smallest particle of matter. All elements are made of tiny particles called atom. Atoms are very small in size and cannot be seen through naked eyes. Atom does not exist in free-state in nature. But atom take ...
Significance of Intestinal Digestion of Dietary Protein
... using the MBT resulting from bag pore size were rather small and of minor importance with both concentrates and forages. Vanhatalo (1995) found that with several feeds, the free surface area (percentage of total cloth area) rather than the pore size of the bag material had a significant effect on N ...
... using the MBT resulting from bag pore size were rather small and of minor importance with both concentrates and forages. Vanhatalo (1995) found that with several feeds, the free surface area (percentage of total cloth area) rather than the pore size of the bag material had a significant effect on N ...
Micropreparation of tissue collagenase fragments of type I collagen
... the front) was excised, homogenized and the polypeptide fraction isolated according to the procedure described in Section 2, CE in bare silica capillary run in 25 mM phosphate buffer (pH 2.5) revealed the profile shown in Fig. 2A. The separation was rather fast compared to fragments of similar size ...
... the front) was excised, homogenized and the polypeptide fraction isolated according to the procedure described in Section 2, CE in bare silica capillary run in 25 mM phosphate buffer (pH 2.5) revealed the profile shown in Fig. 2A. The separation was rather fast compared to fragments of similar size ...
Powerpoint
... Provides information on disappearance of substrate only. May see very little change associated with oxidation in vivo. ...
... Provides information on disappearance of substrate only. May see very little change associated with oxidation in vivo. ...
Jon Magnuson, Glenn Fryxell, Linda Lasure, Doug Elliot (PNNL)
... Enzymes are nano-machines of cells, catalyzing thousands of useful chemical reactions. Microscopic reversibility means that outside cells, reactions A --> B and B --> A are feasible. Unlike typical chemical catalysts, enzymatic reactions occur at ambient conditions; i.e. green technology. Enzyme fra ...
... Enzymes are nano-machines of cells, catalyzing thousands of useful chemical reactions. Microscopic reversibility means that outside cells, reactions A --> B and B --> A are feasible. Unlike typical chemical catalysts, enzymatic reactions occur at ambient conditions; i.e. green technology. Enzyme fra ...
Glycogen branches out: new perspectives on the role of glycogen
... glycolytic pathway results in the generation of fructose 2,6bisphosphate, which is a potent allosteric activator of phosphofructokinase, and thus a key metabolic regulator of glycolytic rates and ATP production (53). A variety of stimuli are integrated in the regulation of glycogen phosphorylase act ...
... glycolytic pathway results in the generation of fructose 2,6bisphosphate, which is a potent allosteric activator of phosphofructokinase, and thus a key metabolic regulator of glycolytic rates and ATP production (53). A variety of stimuli are integrated in the regulation of glycogen phosphorylase act ...
Thiosulfoxide (Sulfane) Sulfur: New Chemistry and New Regulatory
... (named after the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research where they were first developed) series (e.g., WR-2721, WR-151327). These compounds are thought to act by increasing antioxidant activity such as that due to manganese superoxide dismutase [37]. There are several reports showing that MER, given ...
... (named after the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research where they were first developed) series (e.g., WR-2721, WR-151327). These compounds are thought to act by increasing antioxidant activity such as that due to manganese superoxide dismutase [37]. There are several reports showing that MER, given ...
Being right on Q: shaping eukaryotic evolution
... was reconstructed [28,29]. This ‘Lokiarchaeon’ encodes a cytoskeleton and some genes associated with endocytosis/internal membrane formation. A new exciting model posits that these genes plus some endosymbiont ones would allow LECA to develop internal control over secreted endosymbiont membranes and ...
... was reconstructed [28,29]. This ‘Lokiarchaeon’ encodes a cytoskeleton and some genes associated with endocytosis/internal membrane formation. A new exciting model posits that these genes plus some endosymbiont ones would allow LECA to develop internal control over secreted endosymbiont membranes and ...
88KB
... Abstract: Hepatitis delta virus ribozymes have been proposed to perform self-cleavage via a general acid/ base mechanism involving an active-site cytosine, based on evidence from both a crystal structure of the cleavage product and kinetic measurements. To determine whether this cytosine (C75) in th ...
... Abstract: Hepatitis delta virus ribozymes have been proposed to perform self-cleavage via a general acid/ base mechanism involving an active-site cytosine, based on evidence from both a crystal structure of the cleavage product and kinetic measurements. To determine whether this cytosine (C75) in th ...
Respiratory Basics - Nursecom Home Page
... Aerobic metabolism uses oxygen to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). When glucose is burned or oxidized, as many as 36 ATP are created. Water and carbon dioxide are the bi-products. Anaerobic metabolism creates only 2 ATP in the absence of oxygen with lactic acid a toxic by- ...
... Aerobic metabolism uses oxygen to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). When glucose is burned or oxidized, as many as 36 ATP are created. Water and carbon dioxide are the bi-products. Anaerobic metabolism creates only 2 ATP in the absence of oxygen with lactic acid a toxic by- ...
Biochemical studies of enzymes in insect cuticle hardening
... several PLP-dependent decarboxylases, such as ADC, glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) and CSADC. This study helps to understand symptoms associated with the abnormal cysteine concentrations in several neurodegenerative diseases. A mammalian enzyme, glutamate decarboxylase like-1 (GADL1), has been shown t ...
... several PLP-dependent decarboxylases, such as ADC, glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) and CSADC. This study helps to understand symptoms associated with the abnormal cysteine concentrations in several neurodegenerative diseases. A mammalian enzyme, glutamate decarboxylase like-1 (GADL1), has been shown t ...
Brucella Quorum Sensing: much more than
... methyl donor, but as provider of the homoserine lactone ring. In brief, binding of SAM by LuxI initiates the reaction. Subsequently, acyl-ACP binds to the enzyme complex, followed by amide bond formation and the release of holo-ACP. Next, lactonization of the homoserine ring occurs, and the product ...
... methyl donor, but as provider of the homoserine lactone ring. In brief, binding of SAM by LuxI initiates the reaction. Subsequently, acyl-ACP binds to the enzyme complex, followed by amide bond formation and the release of holo-ACP. Next, lactonization of the homoserine ring occurs, and the product ...
A low carbohydrate, high protein diet combined
... growth rates (Figure 1B). Of note, there was no significant difference in the weights of these mice over the course of the study (Figure 1C), thus ruling out that differences in tumor growth rates were due to caloric restriction. This is important because caloric restriction, which causes cancer cel ...
... growth rates (Figure 1B). Of note, there was no significant difference in the weights of these mice over the course of the study (Figure 1C), thus ruling out that differences in tumor growth rates were due to caloric restriction. This is important because caloric restriction, which causes cancer cel ...
Chem 33 Lab - Santa Clara University
... plates or heating mantles are available for this purpose. Never use an open flame in the organic laboratory. Some solvents such as diethyl ether, t-butyl methyl ether, and methanol have flash points so low that they can be ignited by the surface of a hot plate. 6. Be sure to handle organic chemicals ...
... plates or heating mantles are available for this purpose. Never use an open flame in the organic laboratory. Some solvents such as diethyl ether, t-butyl methyl ether, and methanol have flash points so low that they can be ignited by the surface of a hot plate. 6. Be sure to handle organic chemicals ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.























