AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... Future AP Chemistry Student, Welcome to AP Chemistry! I am eagerly anticipating a great year of Chemistry. In order to ensure the best start for everyone next fall, I have prepared a summer assignment that reviews basic chemistry concepts. There is a multitude of tremendous chemistry resources avail ...
... Future AP Chemistry Student, Welcome to AP Chemistry! I am eagerly anticipating a great year of Chemistry. In order to ensure the best start for everyone next fall, I have prepared a summer assignment that reviews basic chemistry concepts. There is a multitude of tremendous chemistry resources avail ...
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
... • Molecular Orbital Theory (more general but “complex”) – All e–’s in molecule fill up a set of molecular orbitals that are made up of linear combinations of atomic orbitals on two or more atoms ...
... • Molecular Orbital Theory (more general but “complex”) – All e–’s in molecule fill up a set of molecular orbitals that are made up of linear combinations of atomic orbitals on two or more atoms ...
General Biology I Final Exam
... A chemical compound having the same molecular formula as another but a different geometric configuration, as when atoms or groups of atoms are attached in different spatial arrangements on either side of a double bond or a ring. ...
... A chemical compound having the same molecular formula as another but a different geometric configuration, as when atoms or groups of atoms are attached in different spatial arrangements on either side of a double bond or a ring. ...
11.3 Section Summary 6.3 – pages 296
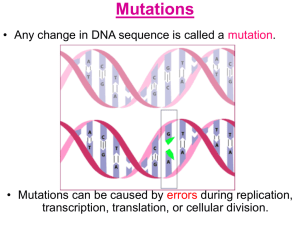
... the altered gene would become part of the genetic makeup of the offspring. ...
... the altered gene would become part of the genetic makeup of the offspring. ...
Worksheet 8 Notes - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... (Oxidation—the oxidation number of copper is increasing from 0 to 2+) NO3- (aq) → NO2 (g) (Reduction—the oxidation number of nitrogen is decreasing from 5+ to 4+) Step 3: Balance atoms (except H and O) This step is not necessary—copper and nitrogen are balanced. Step 4: Balance oxygen by adding wate ...
... (Oxidation—the oxidation number of copper is increasing from 0 to 2+) NO3- (aq) → NO2 (g) (Reduction—the oxidation number of nitrogen is decreasing from 5+ to 4+) Step 3: Balance atoms (except H and O) This step is not necessary—copper and nitrogen are balanced. Step 4: Balance oxygen by adding wate ...
Identification and Characterization of cvHsp
... cvHsp were requested and fully sequenced on both strands using an ABI automatic sequencer. 59-Rapid amplification of cDNA ends experiments were performed using the Marathon Ready human heart cDNA (CLONTECH). The following primers were used: 59-CCGCTCGGAAGGTGGAAGAGGTTCT-39 and 59-CGAGGGCTGGACAGGAGAGG ...
... cvHsp were requested and fully sequenced on both strands using an ABI automatic sequencer. 59-Rapid amplification of cDNA ends experiments were performed using the Marathon Ready human heart cDNA (CLONTECH). The following primers were used: 59-CCGCTCGGAAGGTGGAAGAGGTTCT-39 and 59-CGAGGGCTGGACAGGAGAGG ...
11111 Hhllill II III 11111 /III 11111 lihA IFU III III /MUll 110 III
... According to one aspect of the present invention there is provided a peptide having the amino acid sequence of a fragment of HIV which interacts specifically with a particular human leucocyte antigen (HLA) class I molecule, to stimulate cytotoxic T lymphocyte immunity, the peptide having the sequenc ...
... According to one aspect of the present invention there is provided a peptide having the amino acid sequence of a fragment of HIV which interacts specifically with a particular human leucocyte antigen (HLA) class I molecule, to stimulate cytotoxic T lymphocyte immunity, the peptide having the sequenc ...
Which is not a major function of the circulatory system? A) delivering
... together to digest food so that is can be used by the body. • The digestive system is a series of tubelike organs called the digestive tract. • The Digestive Tract Organs: • Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus • The liver, gall bladder, pancreas, and sa ...
... together to digest food so that is can be used by the body. • The digestive system is a series of tubelike organs called the digestive tract. • The Digestive Tract Organs: • Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus • The liver, gall bladder, pancreas, and sa ...
Central Dogma
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/si tes/dl/free/0072437316/120077/micro06.swf::Protein Synthesis ...
... http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/si tes/dl/free/0072437316/120077/micro06.swf::Protein Synthesis ...
Heterologous products from the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis
... differences, present among naturally occurring K. lactis strains and among laboratory strains deriving from mutagenesis and genetic crosses, greatly affect production [4]. In addition, specific mutant strains might be generated and selected for production efficiency. To date, mutants of the secretio ...
... differences, present among naturally occurring K. lactis strains and among laboratory strains deriving from mutagenesis and genetic crosses, greatly affect production [4]. In addition, specific mutant strains might be generated and selected for production efficiency. To date, mutants of the secretio ...
Serine Proteases
... Principle of Enzyme Catalysis • Linus Pauling (1946) formulated the first basic principle of enzyme catalysis – Enzyme increase the rate of a chemical reaction by binding tighter and stabilizing the transition state of its specific substrate more than the ground state – Therefore, higher affinity of ...
... Principle of Enzyme Catalysis • Linus Pauling (1946) formulated the first basic principle of enzyme catalysis – Enzyme increase the rate of a chemical reaction by binding tighter and stabilizing the transition state of its specific substrate more than the ground state – Therefore, higher affinity of ...
Amino Acids of the Sulfolobus solfataricus Mini-chromosome
... the wild type protein. DNA band shift assays were carried out with amounts of protein ranging from 160 to 1600 fmol on various DNA ligands, namely molecules containing a bubble of 20 T residues called Bub-20T molecules, blunt duplexes, and single-stranded oligonucleotides as indicated in Fig. 5A. Wi ...
... the wild type protein. DNA band shift assays were carried out with amounts of protein ranging from 160 to 1600 fmol on various DNA ligands, namely molecules containing a bubble of 20 T residues called Bub-20T molecules, blunt duplexes, and single-stranded oligonucleotides as indicated in Fig. 5A. Wi ...
Vitamins
... −raises blood calcium and phosphorus by increasing absorption from digestive tract −withdrawing calcium from bones −stimulating retention by kidneys deficiencies ...
... −raises blood calcium and phosphorus by increasing absorption from digestive tract −withdrawing calcium from bones −stimulating retention by kidneys deficiencies ...
Carboxypeptidase A - Chemistry Courses: About
... in the recent part of this decade have provided great insight regarding the catalytic mechanism of the prototypical zinc-requiring protease carboxypeptidase A (CPA). Importantly, some of our ideas regarding the general theory of enzyme catalysis have been inspired and developed through studies of th ...
... in the recent part of this decade have provided great insight regarding the catalytic mechanism of the prototypical zinc-requiring protease carboxypeptidase A (CPA). Importantly, some of our ideas regarding the general theory of enzyme catalysis have been inspired and developed through studies of th ...
Chapter 26
... valence bond electrons to the more electronegative atom and then counting the charge on the quasi ion. A carbon assigned four valence electrons would have an oxidation number of 0. The carbon in N5-methyl-THF (top left) is assigned six electrons from the three C-H bonds and thus has a oxidation numb ...
... valence bond electrons to the more electronegative atom and then counting the charge on the quasi ion. A carbon assigned four valence electrons would have an oxidation number of 0. The carbon in N5-methyl-THF (top left) is assigned six electrons from the three C-H bonds and thus has a oxidation numb ...
BURNERS AND FLAMES:
... called the ground (energy) state of the atom. If energy is added to an atom, some of the electrons in the atom absorb that energy and jump into an orbital of high energy and an excited (energy) state is formed. One way of viewing the energy levels in an atom is by picturing a stairway. Each stair re ...
... called the ground (energy) state of the atom. If energy is added to an atom, some of the electrons in the atom absorb that energy and jump into an orbital of high energy and an excited (energy) state is formed. One way of viewing the energy levels in an atom is by picturing a stairway. Each stair re ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 30: Ion pumps in the membrane
... Na+/K+ ATPase has two conformations The overall structure is ααββ. The α subunits (1000 amino acids) have 8 transmembrane helices each, plus a large cytoplasmic ATPase domain. Each α subunit appears to be a complete functional unit, and the purpose of the dimer and the β subunit (300 amino acids, mo ...
... Na+/K+ ATPase has two conformations The overall structure is ααββ. The α subunits (1000 amino acids) have 8 transmembrane helices each, plus a large cytoplasmic ATPase domain. Each α subunit appears to be a complete functional unit, and the purpose of the dimer and the β subunit (300 amino acids, mo ...
The Respiratory System - Mohawk Valley Community College
... 1. Chemoreceptors monitor blood chemistry 2. Main stimulus is carbon dioxide and pH 3. Carbon dioxide transport 4. Main stimulant for respiratory efforts 5. Also tied to pH 6. Oxygen concentrations are of secondary importance ...
... 1. Chemoreceptors monitor blood chemistry 2. Main stimulus is carbon dioxide and pH 3. Carbon dioxide transport 4. Main stimulant for respiratory efforts 5. Also tied to pH 6. Oxygen concentrations are of secondary importance ...
02_Lectures_Meredith
... Elements and Compounds • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio ...
... Elements and Compounds • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio ...
Nucleic Acids and DNA
... Sugar phosphate backbone is found on outside, bases inside and pair up Each base is H-bonded with a base on the opposite strand with the same number of H-bonds A complete turn takes 34 Å and has 10 bases per turn ...
... Sugar phosphate backbone is found on outside, bases inside and pair up Each base is H-bonded with a base on the opposite strand with the same number of H-bonds A complete turn takes 34 Å and has 10 bases per turn ...
chapter-2 - HCC Learning Web
... • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics different from those of its elements ...
... • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics different from those of its elements ...
Breath of Life Reading
... lungs. When you exhale, you release this carbon dioxide from your lungs into the external environment around you. Like many other homeostatic processes, breathing involves precise feedback systems. Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are “fed back” as inputs as part of a chain of cause-andeffec ...
... lungs. When you exhale, you release this carbon dioxide from your lungs into the external environment around you. Like many other homeostatic processes, breathing involves precise feedback systems. Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are “fed back” as inputs as part of a chain of cause-andeffec ...
Chapter 9
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduce ...
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduce ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.