- Wiley Online Library
... but may occur in sugar-rich plant saps which frequently fall dry, or in honey - both well-known habitats for Z. mobilis [I]. Desiccation of plant saps should lead to an increase in sucrose concentration and thence of its moieties glucose and fructose, by the action of invertase. Thus, an increasing ...
... but may occur in sugar-rich plant saps which frequently fall dry, or in honey - both well-known habitats for Z. mobilis [I]. Desiccation of plant saps should lead to an increase in sucrose concentration and thence of its moieties glucose and fructose, by the action of invertase. Thus, an increasing ...
AP Bio Wording - Biology with Radjewski
... Significance – Allows specialized cellular functions to be performed away from the rest of the cell and Allowed specialization of tissues ...
... Significance – Allows specialized cellular functions to be performed away from the rest of the cell and Allowed specialization of tissues ...
bonding and geometry
... One of the elements is more electronegative than the other and therefore has a greater desire for the shared pair The MORE electronegative element tends to pull the electrons closer and thus has a slightly negative charge The LESS electronegative element has a slightly positive charge since th ...
... One of the elements is more electronegative than the other and therefore has a greater desire for the shared pair The MORE electronegative element tends to pull the electrons closer and thus has a slightly negative charge The LESS electronegative element has a slightly positive charge since th ...
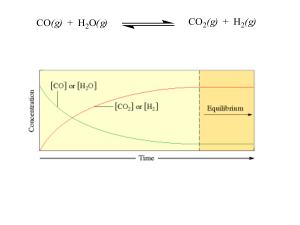
Lesson 1 Reversible reactions and equilibrium
... 2. More soluble fertiliser – bad It will dissolve in rain and wash into local drains. 3. Avoid applying it before rain is due – good This means it won’t dissolve in the rain and wash into drains. 4. Grow a quick crop of legumes – good But depends on timings of crops, etc. 5. Use fertiliser with larg ...
... 2. More soluble fertiliser – bad It will dissolve in rain and wash into local drains. 3. Avoid applying it before rain is due – good This means it won’t dissolve in the rain and wash into drains. 4. Grow a quick crop of legumes – good But depends on timings of crops, etc. 5. Use fertiliser with larg ...
Hemoglobin and the Heme Group: Metal Complexes in the Blood for
... When the concentration of protons (H+) is low (pH 9), positive charges do not form on the residues at the subunit interfaces, so the salt bridges cannot form (right image in Figure 8). However, at pH 7, histidine residues at the subunit interfaces (not the histidine residues that bind the heme group ...
... When the concentration of protons (H+) is low (pH 9), positive charges do not form on the residues at the subunit interfaces, so the salt bridges cannot form (right image in Figure 8). However, at pH 7, histidine residues at the subunit interfaces (not the histidine residues that bind the heme group ...
Ionic Bonding
... 7. Water is known for its many anomalous properties. Use your knowledge of intermolecular forces and intramolecular bonding to explain theoretically why lakes freeze from top to bottom. 8. Using Table 3 (page 85), predict whether each of the following moleculeswould be polar or nonpolar. (a) CH3OH(l ...
... 7. Water is known for its many anomalous properties. Use your knowledge of intermolecular forces and intramolecular bonding to explain theoretically why lakes freeze from top to bottom. 8. Using Table 3 (page 85), predict whether each of the following moleculeswould be polar or nonpolar. (a) CH3OH(l ...
Unit 6 – Chemical Reactions: Particles and Energy
... rearrangement process of a chemical reaction requires that all atoms from the reactant molecules MUST become part of one of the products. The conservation of mass we observed at the beginning of the course is evident during chemical reactions; coefficients describe how many whole particles of each ...
... rearrangement process of a chemical reaction requires that all atoms from the reactant molecules MUST become part of one of the products. The conservation of mass we observed at the beginning of the course is evident during chemical reactions; coefficients describe how many whole particles of each ...
THE ROLE OF NATURAL SELECTION IN THE ORIGIN OF LIFE
... Polymers checked to form double helices and to crosspair with RNA → some both properties Experiments demonstrate: ...
... Polymers checked to form double helices and to crosspair with RNA → some both properties Experiments demonstrate: ...
Dr. V. Main Powerpoint
... • The electron transport chain is in the cristae of the mitochondrion • Most of the chain’s components are proteins, which exist in multiprotein complexes • The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chai ...
... • The electron transport chain is in the cristae of the mitochondrion • Most of the chain’s components are proteins, which exist in multiprotein complexes • The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chai ...
Document
... FOODS - spoil by microbial fermentations - made by microbial fermentations (wine, cheese, pickles, bread) MUSCLE cells use fermentation if O2 is depleted ...
... FOODS - spoil by microbial fermentations - made by microbial fermentations (wine, cheese, pickles, bread) MUSCLE cells use fermentation if O2 is depleted ...
- Catalyst
... Question 2: Which one of the following statements is generally true about electronegativity when you look at the periodic table? Circle one: a) Electronegativity decreases as we move left to right and decreases as we move top to bottom. b) Electronegativity decreases as we move left to right and ...
... Question 2: Which one of the following statements is generally true about electronegativity when you look at the periodic table? Circle one: a) Electronegativity decreases as we move left to right and decreases as we move top to bottom. b) Electronegativity decreases as we move left to right and ...
Southern Blot
... and KEL2 was determined by assaying for the production of KEL1 and KEL2 antigens. The PIP1 and PIP2 alleles were studied with a Southern blot analysis of endonuclease Taq1 cut DNA where PIP1 shows a 4 kb fragment hybridizing to the probe while PIP2 shows a 6 kb fragment hybridizing to the probe. The ...
... and KEL2 was determined by assaying for the production of KEL1 and KEL2 antigens. The PIP1 and PIP2 alleles were studied with a Southern blot analysis of endonuclease Taq1 cut DNA where PIP1 shows a 4 kb fragment hybridizing to the probe while PIP2 shows a 6 kb fragment hybridizing to the probe. The ...
Protein Synthesis Card Sort
... attaches to the unzipped DNA and reads the A, T, G, C (Nitrogen base pairs) code. ...
... attaches to the unzipped DNA and reads the A, T, G, C (Nitrogen base pairs) code. ...
X1-1 - murov.info
... a factor of seven in chemical reactions. Why is it that hydrogen isotopes have such a large rate difference when intimately involved in a chemical reaction? 6. In contrast to chemical reactivity, nuclear stability is very dependent on the neutron to proton ratio. For even numbered elements, the numb ...
... a factor of seven in chemical reactions. Why is it that hydrogen isotopes have such a large rate difference when intimately involved in a chemical reaction? 6. In contrast to chemical reactivity, nuclear stability is very dependent on the neutron to proton ratio. For even numbered elements, the numb ...
Acid K a
... How to write out Ka and Kb rxns and expressions. The weaker the acid the stronger the conjugate base (and vice versa). Conjugate bases of strong acids have no basic ...
... How to write out Ka and Kb rxns and expressions. The weaker the acid the stronger the conjugate base (and vice versa). Conjugate bases of strong acids have no basic ...
Review-examII-2010
... molecule contains several short, double-helical regions. Any given tRNA will accept only one specific amino acid. The amino acid attachment is always to an A nucleotide at the 3' end of the molecule. There is at least one tRNA for each of the 20 amino acids. ...
... molecule contains several short, double-helical regions. Any given tRNA will accept only one specific amino acid. The amino acid attachment is always to an A nucleotide at the 3' end of the molecule. There is at least one tRNA for each of the 20 amino acids. ...
NMEICT PROJECT
... study the enzyme kinetics. It has many applications in enzyme kinetics. It helps in understanding the rates of reactions which assist in judging the kind of reaction that enzyme follows. (single- or multiple-substrate mechanism). Enzyme activity measures the amount of enzyme in a reaction. There are ...
... study the enzyme kinetics. It has many applications in enzyme kinetics. It helps in understanding the rates of reactions which assist in judging the kind of reaction that enzyme follows. (single- or multiple-substrate mechanism). Enzyme activity measures the amount of enzyme in a reaction. There are ...
Unit 4 ~ Learning Guide Name
... b. osmosis (2 marks) = the movement of water molecules from areas of lower concentration (note lower concentration of solution actually means greater amounts of water) to areas of higher concentrations (note higher concentration of solution actually means greater amounts of water) across a semi-perm ...
... b. osmosis (2 marks) = the movement of water molecules from areas of lower concentration (note lower concentration of solution actually means greater amounts of water) to areas of higher concentrations (note higher concentration of solution actually means greater amounts of water) across a semi-perm ...
The Respiratory System
... and smaller tubes called bronchioles. At the end of each of these tubes are small air sacs called alveoli. Capillaries, which are small blood vessels with thin walls, are wrapped around these alveoli. ...
... and smaller tubes called bronchioles. At the end of each of these tubes are small air sacs called alveoli. Capillaries, which are small blood vessels with thin walls, are wrapped around these alveoli. ...
Succinate
... - Recall that substrate-level phosphorylations involved high-energy intermediates, such as 1,3bisphosphoglycerate and succinyl CoA. Despite attempts to isolate similar high-energy intermediates involved in oxidative phosphorylation, none were ever found. Peter Mitchell proposed the chemiosmotic the ...
... - Recall that substrate-level phosphorylations involved high-energy intermediates, such as 1,3bisphosphoglycerate and succinyl CoA. Despite attempts to isolate similar high-energy intermediates involved in oxidative phosphorylation, none were ever found. Peter Mitchell proposed the chemiosmotic the ...
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 THE ARACHIDONIC ACID - diss.fu
... calcium for the translocation of the enzyme to membranes, however, the activity is calciumindependent (Watson and Doherty, 1994; Brinckmann et al., 1998; Hoffman et al., 1988). The 15-LOX activity is dependent on the hydroperoxide tone (Vanderhoek et al., 1982). The ‘threshold peroxide tone’ is depe ...
... calcium for the translocation of the enzyme to membranes, however, the activity is calciumindependent (Watson and Doherty, 1994; Brinckmann et al., 1998; Hoffman et al., 1988). The 15-LOX activity is dependent on the hydroperoxide tone (Vanderhoek et al., 1982). The ‘threshold peroxide tone’ is depe ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.