2 -1 -2 -1 1 2 K
... Protein: polymer consisting of AA’s linked by peptide bonds AA in a polymer is called a residue Folded into 3D structures Structure of protein determines its function Primary structure: linear arrangement of AA’s ...
... Protein: polymer consisting of AA’s linked by peptide bonds AA in a polymer is called a residue Folded into 3D structures Structure of protein determines its function Primary structure: linear arrangement of AA’s ...
Score A_c5_17022012
... (c) State what happens to the hydrogen produced at step 6 [2m] ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ (d) Identify compound X. _________________ [1m] (e) The reduced co-enzyme produced in step 1 will enter the ...
... (c) State what happens to the hydrogen produced at step 6 [2m] ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ (d) Identify compound X. _________________ [1m] (e) The reduced co-enzyme produced in step 1 will enter the ...
Singlet Oxygen
... compounds. However, the first excited state of an oxygen molecule is a singlet state, which can readily react with other singlet molecules. Radiative decay to the triplet ground state is a spin-forbidden transition resulting in a long-lived excited state. Excited singlet oxygen emits phosphorescence ...
... compounds. However, the first excited state of an oxygen molecule is a singlet state, which can readily react with other singlet molecules. Radiative decay to the triplet ground state is a spin-forbidden transition resulting in a long-lived excited state. Excited singlet oxygen emits phosphorescence ...
100 Pectin is a complex polysaccharide consisting mainly of
... sources, maximum enzyme production was observed with Ammonium chloride (inorganic N source) and Beef extract (organic N source), between 72 to 96 hrs. Of the two natural carbon sources tested, the banana peel powder yielded higher enzyme compared to the orange peel powder during the same period. A r ...
... sources, maximum enzyme production was observed with Ammonium chloride (inorganic N source) and Beef extract (organic N source), between 72 to 96 hrs. Of the two natural carbon sources tested, the banana peel powder yielded higher enzyme compared to the orange peel powder during the same period. A r ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... information and diagram below. A biologist prepares an analysis of the activity of the enzyme Maltase, which promotes the hydrolysis of disaccharides to monosaccharides. Three flasks containing 10 milliliters of 4 percent maltose in water are prepared with the addition of the substances described be ...
... information and diagram below. A biologist prepares an analysis of the activity of the enzyme Maltase, which promotes the hydrolysis of disaccharides to monosaccharides. Three flasks containing 10 milliliters of 4 percent maltose in water are prepared with the addition of the substances described be ...
Energy Substrate Metabolism in - Journal of Clinical Investigation
... in 24 hr and 7.5% in 48 hr. By comparison with the much greater per cent decreases in the rates of oleic acid-1-'C oxidation after storage of the platelets, the small changes in specific radioactivity of the fatty acid pool were considered negligible. Changes in the specific activity of the fatty ac ...
... in 24 hr and 7.5% in 48 hr. By comparison with the much greater per cent decreases in the rates of oleic acid-1-'C oxidation after storage of the platelets, the small changes in specific radioactivity of the fatty acid pool were considered negligible. Changes in the specific activity of the fatty ac ...
Polyamines
... Buffering of Cellular pH – The reversible protonation of multiple amino groups of PAs, serves as buffer in the cells Role in Flowering – Floral axis synthesizes large quantities of conjugate PAs de ...
... Buffering of Cellular pH – The reversible protonation of multiple amino groups of PAs, serves as buffer in the cells Role in Flowering – Floral axis synthesizes large quantities of conjugate PAs de ...
Vitamin `C
... vitamin") is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex. Its phosphate derivatives are involved in many cellular processes. The best-characterized form is thiamine pyrophosphate(TPP), a coenzyme in the catabolism of sugars and amino acids. Thiamine is used in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter a ...
... vitamin") is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex. Its phosphate derivatives are involved in many cellular processes. The best-characterized form is thiamine pyrophosphate(TPP), a coenzyme in the catabolism of sugars and amino acids. Thiamine is used in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter a ...
Enzyme - PharmaStreet
... in the loss of enzyme activity and subsequent disease (e.g. scurvy). Cofactors are either metal ions (e.g. zinc) or small organic molecules called coenzymes (e.g. NAD + , pyridoxal phosphate). • Most coenzymes are bound by ionic bonds and other non-covalent bonding interactions, but some are bound c ...
... in the loss of enzyme activity and subsequent disease (e.g. scurvy). Cofactors are either metal ions (e.g. zinc) or small organic molecules called coenzymes (e.g. NAD + , pyridoxal phosphate). • Most coenzymes are bound by ionic bonds and other non-covalent bonding interactions, but some are bound c ...
CS273_SequenceSimilarity1
... • Nucleic acids and proteins are related by molecular evolution Orthologs: two proteins in animals X and Y that evolved from one protein in immediate ancestor animal Z Paralogs: two proteins that evolved from one protein through duplication in some ancestor Homologs: orthologs or paralogs that ...
... • Nucleic acids and proteins are related by molecular evolution Orthologs: two proteins in animals X and Y that evolved from one protein in immediate ancestor animal Z Paralogs: two proteins that evolved from one protein through duplication in some ancestor Homologs: orthologs or paralogs that ...
Enzyme
... positions relative to OH and COO- groups— only one of these two CH2COO- groups can therefore undergo catalysis! ...
... positions relative to OH and COO- groups— only one of these two CH2COO- groups can therefore undergo catalysis! ...
Chemistry 21 A - El Camino College
... 9. a) endothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ b) exothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ 10. The percentage yield is _____________________________________________________________________ __________ ...
... 9. a) endothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ b) exothermic reaction is ___________________________________________________________________ 10. The percentage yield is _____________________________________________________________________ __________ ...
Document
... anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose C6H12O6 6 O2 6 CO2 6 H2O Energy (ATP heat) ...
... anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose C6H12O6 6 O2 6 CO2 6 H2O Energy (ATP heat) ...
Chapter 23
... the ability of hemoglobin to hold oxygen • The substance 2.3-bisphosphoglycerate increases the ability of hemoglobin to release oxygen • Fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen than does maternal ...
... the ability of hemoglobin to hold oxygen • The substance 2.3-bisphosphoglycerate increases the ability of hemoglobin to release oxygen • Fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen than does maternal ...
Ion Exchange Chromatography
... separation of ions and polar molecules based on the charge properties of the molecules. Dr Gihan Gawish ...
... separation of ions and polar molecules based on the charge properties of the molecules. Dr Gihan Gawish ...
01.CN_Other pages/p1-9
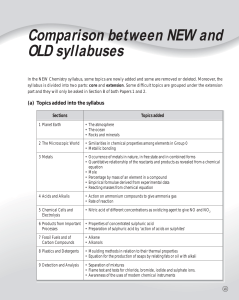
... In the NEW Chemistry syllabus, some topics are newly added and some are removed or deleted. Moreover, the syllabus is divided into two parts: core and extension. Some difficult topics are grouped under the extension part and they will only be asked in Section B of both Papers 1 and 2. ...
... In the NEW Chemistry syllabus, some topics are newly added and some are removed or deleted. Moreover, the syllabus is divided into two parts: core and extension. Some difficult topics are grouped under the extension part and they will only be asked in Section B of both Papers 1 and 2. ...
Marine alga Sargassum horneri active component
... clearance of defective proteins and organelles, differentiation, and development [3-5]. Dysfunctions in autophagy are associated with severe diseases, such as heart disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancers [4,6,7]. There are three distinct types of autophagy: macroautophagy, microautophagy, ...
... clearance of defective proteins and organelles, differentiation, and development [3-5]. Dysfunctions in autophagy are associated with severe diseases, such as heart disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancers [4,6,7]. There are three distinct types of autophagy: macroautophagy, microautophagy, ...
Separation and Purification of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme
... Tyr, Pro and Glu in F-3 gh account for 82% of total amino by gel filtration. Fraction 3 (F-3) and F-4 showed a high acids, suggesting that this fraction has a high potential as inhibition of 90% or above. In particular, F-3 showed the inhibitor of ACE activities. highest ACE-inhibition of 97.8% (Fig ...
... Tyr, Pro and Glu in F-3 gh account for 82% of total amino by gel filtration. Fraction 3 (F-3) and F-4 showed a high acids, suggesting that this fraction has a high potential as inhibition of 90% or above. In particular, F-3 showed the inhibitor of ACE activities. highest ACE-inhibition of 97.8% (Fig ...
추가7b
... Living organisms require large coding capacities for information transfer Profound complexity of functioning systems To succeed as a coding mechanism, a class of molecules must have a large capacity for variation Glycosylation is the most important posttranslational modification in terms of codi ...
... Living organisms require large coding capacities for information transfer Profound complexity of functioning systems To succeed as a coding mechanism, a class of molecules must have a large capacity for variation Glycosylation is the most important posttranslational modification in terms of codi ...
BIOLOGY EOC STUDY GUIDE with Practice Questions
... What is the name of the macromolecule that makes up the majority of the cell membrane? A. nucleotide B. lipid C. carbohydrate D. protein 22. What is the advantage of cells being so small? A. Small cells contain a greater quantity of enzymes than large cells. B. Small cells do not require energy and ...
... What is the name of the macromolecule that makes up the majority of the cell membrane? A. nucleotide B. lipid C. carbohydrate D. protein 22. What is the advantage of cells being so small? A. Small cells contain a greater quantity of enzymes than large cells. B. Small cells do not require energy and ...
Bio EOC Study Guide
... What is the name of the macromolecule that makes up the majority of the cell membrane? A. nucleotide B. lipid C. carbohydrate D. protein 22. What is the advantage of cells being so small? A. Small cells contain a greater quantity of enzymes than large cells. B. Small cells do not require energy and ...
... What is the name of the macromolecule that makes up the majority of the cell membrane? A. nucleotide B. lipid C. carbohydrate D. protein 22. What is the advantage of cells being so small? A. Small cells contain a greater quantity of enzymes than large cells. B. Small cells do not require energy and ...
7 A - Reigate School
... habitat. For example, fish are adapted to living underwater. They have gills to take oxygen out of the water, fins to swim with and streamlined bodies to help them move easily through Does not drink the water. This jack rabbit is another example. Physical environmental factors change from day to day ...
... habitat. For example, fish are adapted to living underwater. They have gills to take oxygen out of the water, fins to swim with and streamlined bodies to help them move easily through Does not drink the water. This jack rabbit is another example. Physical environmental factors change from day to day ...
Molecule of the Month: AgrA DNA Binding Domain AgrA is the
... contains both a histidine kinase (AgrC) and a response regulator (AgrA) (Figure 1). The other components of the system (AgrB and AgrD) function to generate the active form of Autoinducing Peptid (AIP). AgrD is the precursor to AIP and upon being synthesized binds to AgrB (a transmembrane protein). A ...
... contains both a histidine kinase (AgrC) and a response regulator (AgrA) (Figure 1). The other components of the system (AgrB and AgrD) function to generate the active form of Autoinducing Peptid (AIP). AgrD is the precursor to AIP and upon being synthesized binds to AgrB (a transmembrane protein). A ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.