The nucleotide sequence and derived amino acid
... et al., 1981), and what appears to be CA II cDNA from the mouse (Curtis, 1983), no extensive nucleotide or amino acid sequences are as yet available for a CA isozyme from any rodent species. In this respect, it will be very useful to determine the sequences of the CA isozyme genes of mice, not only ...
... et al., 1981), and what appears to be CA II cDNA from the mouse (Curtis, 1983), no extensive nucleotide or amino acid sequences are as yet available for a CA isozyme from any rodent species. In this respect, it will be very useful to determine the sequences of the CA isozyme genes of mice, not only ...
Biology Etymology
... Glucose - Six carbon sugar (carbohydrate) that is metabolized during glycolysis and fermentation. Glu actually translates to Sweet, so the word glucose translates to Full of Sweet. (Figure 16) Sugar Amylose Deoxyribose Fructose Glucose Lactose Maltose Ribose Sucrose Figure 16. List of various sugars ...
... Glucose - Six carbon sugar (carbohydrate) that is metabolized during glycolysis and fermentation. Glu actually translates to Sweet, so the word glucose translates to Full of Sweet. (Figure 16) Sugar Amylose Deoxyribose Fructose Glucose Lactose Maltose Ribose Sucrose Figure 16. List of various sugars ...
as PDF
... cells of Langerhance islets in the pancreas. Its secretion is stimulated by hypoglycemia. The hormone glucagon, epinephrine, norepinephrine, growth hormone, and cortisol exert the opposite effects to insulin and they belong in the counter-regulatory hormones 3. The disorders of some organs (Liver an ...
... cells of Langerhance islets in the pancreas. Its secretion is stimulated by hypoglycemia. The hormone glucagon, epinephrine, norepinephrine, growth hormone, and cortisol exert the opposite effects to insulin and they belong in the counter-regulatory hormones 3. The disorders of some organs (Liver an ...
9. Shikimates and Phenyl propanoids
... OSO3 glucose. S N • About 120 glucosinolates are known in plants, where the R group is alkyl, derived from methionine, alanine, (R group variable) leucine, or valin; aromatic, derived from phenylalanine and tyrosine; or indolic derived from tryptophan. ...
... OSO3 glucose. S N • About 120 glucosinolates are known in plants, where the R group is alkyl, derived from methionine, alanine, (R group variable) leucine, or valin; aromatic, derived from phenylalanine and tyrosine; or indolic derived from tryptophan. ...
91391 Sample Assessment Schedule
... The primary alcohol CH3– CH2– CH2 – CH2OH forms only one product as the H and OH atoms on adjacent carbon atoms are replaced with a carbonto-carbon double bond. The secondary alcohol CH3– CH2– CHOH– CH3 forms a mixture of products as OH is on the 2nd carbon atom. Either the 1st H is removed, forming ...
... The primary alcohol CH3– CH2– CH2 – CH2OH forms only one product as the H and OH atoms on adjacent carbon atoms are replaced with a carbonto-carbon double bond. The secondary alcohol CH3– CH2– CHOH– CH3 forms a mixture of products as OH is on the 2nd carbon atom. Either the 1st H is removed, forming ...
shaped and -shaped copolymers Star polymers 星形杂臂聚合物
... in 1979 as a refugee. He completed his B.Sc.(Hons) degree in 1983 and Ph.D. in 1987 from Griffith University. He joined CSIRO in 1986 as a research fellow. He then moved to ICI Australia in late 1987 to undertake the challenge of industrial research. He returned to CSIRO in late 1990, and in 1995 he ...
... in 1979 as a refugee. He completed his B.Sc.(Hons) degree in 1983 and Ph.D. in 1987 from Griffith University. He joined CSIRO in 1986 as a research fellow. He then moved to ICI Australia in late 1987 to undertake the challenge of industrial research. He returned to CSIRO in late 1990, and in 1995 he ...
C3 Revision Question Booklet
... Extra soap required to get a lather Describe how softening the hard water could save money. ...
... Extra soap required to get a lather Describe how softening the hard water could save money. ...
Homology Modeling via Protein Threading - lmm
... interactions are fundamental to cellular function and are associated with processes such as enzymatic activity, immunological recognition, DNA repair and replication, and cell signaling. Function can be inferred from the nature of the protein with its interactants ...
... interactions are fundamental to cellular function and are associated with processes such as enzymatic activity, immunological recognition, DNA repair and replication, and cell signaling. Function can be inferred from the nature of the protein with its interactants ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Dalton’s Postulates Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. (As far as Dalton knew, they couldn’t be changed at all). ...
... Dalton’s Postulates Atoms of an element are not changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions; atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. (As far as Dalton knew, they couldn’t be changed at all). ...
File
... nicotinic acid 1/3 of nicotinic acid (plasma) bound to plasma proteins bloodnicotinamide and acidcell membrane by simple diffusion Nicotinic acid transport kidney tubules and red blood cells require carrier ...
... nicotinic acid 1/3 of nicotinic acid (plasma) bound to plasma proteins bloodnicotinamide and acidcell membrane by simple diffusion Nicotinic acid transport kidney tubules and red blood cells require carrier ...
Powerpoint - Master Brewers Association
... • The uptake of wort sugars is an important property of brewer’s yeast strains. • The formation of esters and diacetyl by yeast significantly contributes to beer flavour. • Yeast species such as Brettanomyces and yeast strains producing 4-vinyl guaiacol are important cultures in the production of ...
... • The uptake of wort sugars is an important property of brewer’s yeast strains. • The formation of esters and diacetyl by yeast significantly contributes to beer flavour. • Yeast species such as Brettanomyces and yeast strains producing 4-vinyl guaiacol are important cultures in the production of ...
unit 4: chemical reaction rates
... Scientists discovered that by simply determining the mass of the substance, it was possible to count particles or atoms. A mole (mol) is the amount of a pure substance that contains the same amount of chemical units as there are atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon, namely 12. In order to avoid confu ...
... Scientists discovered that by simply determining the mass of the substance, it was possible to count particles or atoms. A mole (mol) is the amount of a pure substance that contains the same amount of chemical units as there are atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon, namely 12. In order to avoid confu ...
Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 5052-5058
... Results and discussion Recognizing the potential of the thiazolidine method for orthogonal Cys bioconjugation, we initiated a study to improve the prole of this reaction. Recently we showed that 2-acetyl benzeno boronic acids (2ABBA) reversibly functionalize protein exposed lysine residues via the ...
... Results and discussion Recognizing the potential of the thiazolidine method for orthogonal Cys bioconjugation, we initiated a study to improve the prole of this reaction. Recently we showed that 2-acetyl benzeno boronic acids (2ABBA) reversibly functionalize protein exposed lysine residues via the ...
Honey
... diabetics than sugar and other sweeteners. This is because • Honey has a lower glycaemic Index (GI) i.e. it does not raise blood sugar levels as quickly as sugar. • Additionally, it also requires lower levels of insulin compared to regular white sugar to metabolize. The trouble is, fructose is absor ...
... diabetics than sugar and other sweeteners. This is because • Honey has a lower glycaemic Index (GI) i.e. it does not raise blood sugar levels as quickly as sugar. • Additionally, it also requires lower levels of insulin compared to regular white sugar to metabolize. The trouble is, fructose is absor ...
Powerpoint slides - School of Engineering and Applied Science
... Many of these bonds are very week and easy to break, but hundreds or thousands working together give the protein structure great stability ...
... Many of these bonds are very week and easy to break, but hundreds or thousands working together give the protein structure great stability ...
Connection of Propionyl-CoA Metabolism to Polyketide
... the vector pBluescript SK (Stratagene) sequentially to construct the disruption vector pYQ8.4. Plasmid pYQ8.4 was transformed into RRAW7 to delete pcsA by homologous recombination. The fungal transformation technique followed that of Miller et al. (1985) with the modification of embedding the protop ...
... the vector pBluescript SK (Stratagene) sequentially to construct the disruption vector pYQ8.4. Plasmid pYQ8.4 was transformed into RRAW7 to delete pcsA by homologous recombination. The fungal transformation technique followed that of Miller et al. (1985) with the modification of embedding the protop ...
CMESCC 4 Physiology of the Combined and Multievents
... conduction, and neurons operate on an on or off basis. If the neural signal received is sufficient, the neuron will conduct the received impulse. If a motor neuron is sufficiently stimulated, all muscle fibers affected by that motor neuron will be stimulated into contraction. For these reasons contr ...
... conduction, and neurons operate on an on or off basis. If the neural signal received is sufficient, the neuron will conduct the received impulse. If a motor neuron is sufficiently stimulated, all muscle fibers affected by that motor neuron will be stimulated into contraction. For these reasons contr ...
Trafficking of phosphatidylinositol by phosphatidylinositol transfer
... of 271 amino acids, which showed no sequence similarity with other known proteins. Previously, a PITP that facilitates the transfer of PtdIns and PtdCho in vitro has been isolated from the cytosol of yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisae [3]. This protein is encoded by the SEC14 gene and is required for tr ...
... of 271 amino acids, which showed no sequence similarity with other known proteins. Previously, a PITP that facilitates the transfer of PtdIns and PtdCho in vitro has been isolated from the cytosol of yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisae [3]. This protein is encoded by the SEC14 gene and is required for tr ...
Protocol for RiboShredder™ RNase Blend
... Storage Buffer: RiboShredder RNase Blend is supplied in a 50% glycerol solution containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 100 mM NaCl, and 0.1 mM EDTA. Dilution Buffer: RiboShredder RNase Blend may be diluted to a lower working concentration in the indicated Storage Buffer. Dilutions may be stored up to t ...
... Storage Buffer: RiboShredder RNase Blend is supplied in a 50% glycerol solution containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 100 mM NaCl, and 0.1 mM EDTA. Dilution Buffer: RiboShredder RNase Blend may be diluted to a lower working concentration in the indicated Storage Buffer. Dilutions may be stored up to t ...
Document
... Plant Nutrients • Plants absorb many elements, some of which they do not need. • An element is considered an essential nutrient if it meets three criteria: • It is necessary for complete, normal plant development through a full life cycle. • It itself is necessary; no substitute can be effective. • ...
... Plant Nutrients • Plants absorb many elements, some of which they do not need. • An element is considered an essential nutrient if it meets three criteria: • It is necessary for complete, normal plant development through a full life cycle. • It itself is necessary; no substitute can be effective. • ...
File - Ms. Richards IB Biology HL
... respiration and nitrogen containing compounds that result from the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acids. • When these macromolecules are broken apart for energy or converted to carbohydrates or fats, enzymes remove nitrogen in the form of ammonia, a small and very toxic molecule • How animals exc ...
... respiration and nitrogen containing compounds that result from the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acids. • When these macromolecules are broken apart for energy or converted to carbohydrates or fats, enzymes remove nitrogen in the form of ammonia, a small and very toxic molecule • How animals exc ...
DESIGN AND SYNTHESIS OF TRIPHENYL-1H-PYRAZOLE DERIVATIVES AS ANTICANCER AGENTS
... potent anticancer agents but their undesirable side effects delineates the urgent need for the development of NCEs as effective anticancer agents. In addition, the design, development, and commercialization of a drug is a tedious, time consuming and costintensive process. For these reasons, any tool ...
... potent anticancer agents but their undesirable side effects delineates the urgent need for the development of NCEs as effective anticancer agents. In addition, the design, development, and commercialization of a drug is a tedious, time consuming and costintensive process. For these reasons, any tool ...
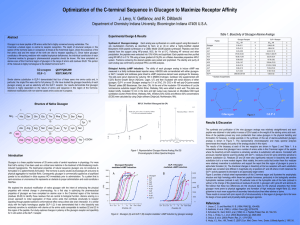
Levy APS - Indiana University Bloomington
... C-terminal -helical region is central to receptor recognition. The depth of structural analysis in this section of the hormone pales in comparison to those at the N-terminal region, where the presence of the first amino acid and the nature of the ninth are vital to receptor signaling (1). Since nat ...
... C-terminal -helical region is central to receptor recognition. The depth of structural analysis in this section of the hormone pales in comparison to those at the N-terminal region, where the presence of the first amino acid and the nature of the ninth are vital to receptor signaling (1). Since nat ...
Lesson 8. Enzymes
... reactions. Enzymes are biological catalysts responsible for supporting almost all of the chemical reactions that maintain animal homeostasis. Enzyme reactions are always reversible. The substance, upon which an enzyme acts, is called as substrate. Enzymes are involved in conversion of substrate into ...
... reactions. Enzymes are biological catalysts responsible for supporting almost all of the chemical reactions that maintain animal homeostasis. Enzyme reactions are always reversible. The substance, upon which an enzyme acts, is called as substrate. Enzymes are involved in conversion of substrate into ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.