Carbohydrates and Lipids - Washington State University
... • Chitin (present in the arthropod exoskeleton and also in cell walls of lower plants) is a β(1-4) bond polymer of glucosamine residues ...
... • Chitin (present in the arthropod exoskeleton and also in cell walls of lower plants) is a β(1-4) bond polymer of glucosamine residues ...
Sample exam 1
... For this problem, you can ignore the effects of the transmembrane electrical potential difference. b. At these physiological conditions, ATP hydrolysis has a free energy change of – 58 kJ/mol. How many moles of ATP must be hydrolyzed to generate the gastric juice in part a? 8. Even though acetate un ...
... For this problem, you can ignore the effects of the transmembrane electrical potential difference. b. At these physiological conditions, ATP hydrolysis has a free energy change of – 58 kJ/mol. How many moles of ATP must be hydrolyzed to generate the gastric juice in part a? 8. Even though acetate un ...
The ATP-PCr energy system can operate with or without oxygen but
... The aerobic system, which is dependent on oxygen, is the most complex of the three energy systems. The metabolic reactions that take place in the presence of oxygen are responsible for most of the cellular energy produced by the body. However, aerobic metabolism is the slowest way to resynthesize AT ...
... The aerobic system, which is dependent on oxygen, is the most complex of the three energy systems. The metabolic reactions that take place in the presence of oxygen are responsible for most of the cellular energy produced by the body. However, aerobic metabolism is the slowest way to resynthesize AT ...
Concepts in Biochemistry 3/e
... G6P can be converted to glucose by glucose-6phosphatase (transport via bloodstream to the peripheral organs) G6P can be converted to glycogen – when body’s demand for glucose is low G6P can be converted to acetyl-CoA via glycolysis and action of pyruvate dehydrogenase (this glucosederived acetyl-CoA ...
... G6P can be converted to glucose by glucose-6phosphatase (transport via bloodstream to the peripheral organs) G6P can be converted to glycogen – when body’s demand for glucose is low G6P can be converted to acetyl-CoA via glycolysis and action of pyruvate dehydrogenase (this glucosederived acetyl-CoA ...
Chapter 2 - Chemical Basis of Life 2.1 Introduction(p. 32) A
... Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are unsaturated fats. c. Phospholipids contain glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group, and are important in cell structures. d. Steroids are complex ring structures, and in ...
... Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are unsaturated fats. c. Phospholipids contain glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group, and are important in cell structures. d. Steroids are complex ring structures, and in ...
Old Exam 1 Questions KEY
... Secondary structure refers to the common structural motifs, such as α-helixes and β-pleated sheets, which result from interactions between adjacent amino acid side chains. What type of bond maintains the secondary structure of a protein? a. b. c. d. e. ...
... Secondary structure refers to the common structural motifs, such as α-helixes and β-pleated sheets, which result from interactions between adjacent amino acid side chains. What type of bond maintains the secondary structure of a protein? a. b. c. d. e. ...
Topic 2: Molecular biology (21 hours)
... • Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds allowing a Topic 4 Chemical bonding and structure diversity of stable compounds to exist. Option B Biochemistry • Life is based on carbon compounds including Aims: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. • Aim 7: ICT can be used for molecular vi ...
... • Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds allowing a Topic 4 Chemical bonding and structure diversity of stable compounds to exist. Option B Biochemistry • Life is based on carbon compounds including Aims: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. • Aim 7: ICT can be used for molecular vi ...
Homework1
... Identify whether each of the following covalent bonds, C-O, C-H, N-H and O-H is polar or nonpolar, and explain how these different characteristics relate to the electronegativity of each atom involved in the bond. ...
... Identify whether each of the following covalent bonds, C-O, C-H, N-H and O-H is polar or nonpolar, and explain how these different characteristics relate to the electronegativity of each atom involved in the bond. ...
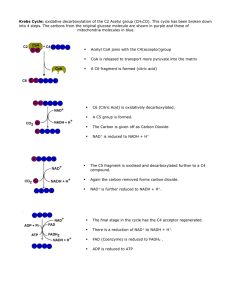
The Kreb`s Cycle - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • The products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (as was shown on the previous slide.) • Oxygen is needed for aerobic respiration because it is the final acceptor in the electron transport chain; without it the process ...
... • The products of aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (as was shown on the previous slide.) • Oxygen is needed for aerobic respiration because it is the final acceptor in the electron transport chain; without it the process ...
Krebs Cycle
... The krebs cycle is an example of the metabolic cycles mentioned in section 7.6.1 . Each step in the cycle requires enzymes to reduce the activation energy. The reactions all take place in the matrix of the mitochondria and are usually represented as a circular diagram. Try to overcome the idea that ...
... The krebs cycle is an example of the metabolic cycles mentioned in section 7.6.1 . Each step in the cycle requires enzymes to reduce the activation energy. The reactions all take place in the matrix of the mitochondria and are usually represented as a circular diagram. Try to overcome the idea that ...
Chirality in Chemistry
... Examples of secondary structures can be found here. Why does the shape of this secondary structure matter? As enzymes, the biological catalysts which allow our cells to work, are made of proteins, the shape of the secondary structure is important in how they can function. Enzymes work through a “lo ...
... Examples of secondary structures can be found here. Why does the shape of this secondary structure matter? As enzymes, the biological catalysts which allow our cells to work, are made of proteins, the shape of the secondary structure is important in how they can function. Enzymes work through a “lo ...
Protein Synthesis Poster
... Contains the information for a specific protein. Made up of codons (sequence of three bases) Each codon is specific for one amino acid. transfer RNA (tRNA) Picks up the appropriate amino acid floating in the ...
... Contains the information for a specific protein. Made up of codons (sequence of three bases) Each codon is specific for one amino acid. transfer RNA (tRNA) Picks up the appropriate amino acid floating in the ...
Revision - Mr C Biology
... Contains the information for a specific protein. Made up of codons (sequence of three bases) Each codon is specific for one amino acid. transfer RNA (tRNA) Picks up the appropriate amino acid floating in the ...
... Contains the information for a specific protein. Made up of codons (sequence of three bases) Each codon is specific for one amino acid. transfer RNA (tRNA) Picks up the appropriate amino acid floating in the ...
CHEMISTRY Answer ALL questions of the on
... (ii) describe with a reason what pH value would be suitable to use in an electrophoresis experiment designed to separate these two amino acids in solution. ...
... (ii) describe with a reason what pH value would be suitable to use in an electrophoresis experiment designed to separate these two amino acids in solution. ...
Page 1 - csfcbiology
... The skin prevents poisonous substances entering and harming the body (line 3). Explain why these substances are unable to pass through the outer layer of skin cells by active ...
... The skin prevents poisonous substances entering and harming the body (line 3). Explain why these substances are unable to pass through the outer layer of skin cells by active ...
碩命題橫式 - 國立彰化師範大學圖書館
... 10. The direct sources of nitrogen that are used to make urea via the Urea Cycle are: (a). citrulline and ornithine (b). arginine and aspartate (c). arginine and citrulline (d). ammonia and arginine (e). aspartate and ammonia 11. Which product in glycolysis also involve in serine synthesis? (a) G6P. ...
... 10. The direct sources of nitrogen that are used to make urea via the Urea Cycle are: (a). citrulline and ornithine (b). arginine and aspartate (c). arginine and citrulline (d). ammonia and arginine (e). aspartate and ammonia 11. Which product in glycolysis also involve in serine synthesis? (a) G6P. ...
Biochemistry
... Explain the role of condensation and hydrolysis reactions in the formation and break down of organic compounds (notes and figure 6.18 on pg 159 of your book) **Know the different kinds of organic compounds (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids) and functions and properties of each (Stu ...
... Explain the role of condensation and hydrolysis reactions in the formation and break down of organic compounds (notes and figure 6.18 on pg 159 of your book) **Know the different kinds of organic compounds (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids) and functions and properties of each (Stu ...
CHEM 470 - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Make-up exams: No individual make-up exams will be offered. Your final grade, however, will be based only on the three highest scores; that is, if you miss one exam or score poorly in one of the four hourly exams, this grade will be dropped. Grades: Letter grades will be based on the total points ob ...
... Make-up exams: No individual make-up exams will be offered. Your final grade, however, will be based only on the three highest scores; that is, if you miss one exam or score poorly in one of the four hourly exams, this grade will be dropped. Grades: Letter grades will be based on the total points ob ...
BOTANY DEPARTMENT - university of nairobi staff profiles
... Define homeostatis, differentiate between Homoeotherms and Poikilotherms Distinguish different modes autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition Understand anaerobic and aerobic metabolism and its importance A good understanding of biological reductive and oxidative reactions. Evaluate the function of A ...
... Define homeostatis, differentiate between Homoeotherms and Poikilotherms Distinguish different modes autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition Understand anaerobic and aerobic metabolism and its importance A good understanding of biological reductive and oxidative reactions. Evaluate the function of A ...
PP-Protein Synthesis
... Identify the genetic code and explain how it is read. Summarize the process of translation. ...
... Identify the genetic code and explain how it is read. Summarize the process of translation. ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules 1. Polymers What are Polymers?
... (single subunit of transthyretin) ...
... (single subunit of transthyretin) ...
Topic 2: Molecular biology (21 hours)
... Guidance: • Only the ring forms of D-ribose, alpha–D-glucose and beta-D-glucose are expected in drawings. • Sugars include monosaccharides and disaccharides. • Only one saturated fat is expected and its specific name is not necessary. • The variable radical of amino acids can be shown as R. The stru ...
... Guidance: • Only the ring forms of D-ribose, alpha–D-glucose and beta-D-glucose are expected in drawings. • Sugars include monosaccharides and disaccharides. • Only one saturated fat is expected and its specific name is not necessary. • The variable radical of amino acids can be shown as R. The stru ...
Slide 1
... Metabolism = sum total of chemical reactions occurring in an organism Catabolism = Chemical reactions that break down molecules (energy releasing) – Ex: cellular respiration, hydrolysis of complex molecules ...
... Metabolism = sum total of chemical reactions occurring in an organism Catabolism = Chemical reactions that break down molecules (energy releasing) – Ex: cellular respiration, hydrolysis of complex molecules ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.