Section 5 - anabolism. the process by which molecules are
... 3. NADH inhibits pyruvate decarboxylase and reduces the amount of acetyl-CoA fed into the Kreb’s cycle, reducing the amount of NADH produced. ...
... 3. NADH inhibits pyruvate decarboxylase and reduces the amount of acetyl-CoA fed into the Kreb’s cycle, reducing the amount of NADH produced. ...
Introduction - Assets - Cambridge University Press
... very dilute water vapor. Liquid water is a fleeting substance that can persist only above 0 °C and under an atmospheric pressure higher than 6 mbars. Therefore, the size of a planet and its distance from the star are two basic characteristics that will determine the presence of liquid water. If a bo ...
... very dilute water vapor. Liquid water is a fleeting substance that can persist only above 0 °C and under an atmospheric pressure higher than 6 mbars. Therefore, the size of a planet and its distance from the star are two basic characteristics that will determine the presence of liquid water. If a bo ...
From Gene to Protein
... • proteins are composed of a unique sequence of amino acids. • mRNA carries the code for the order and type of amino acids to be included in the protein. The “genetic code” is the unique order of triplet codons located on the mRNA strand. (back) ...
... • proteins are composed of a unique sequence of amino acids. • mRNA carries the code for the order and type of amino acids to be included in the protein. The “genetic code” is the unique order of triplet codons located on the mRNA strand. (back) ...
here - VCU
... A nucleotide consists of a base (one of four chemicals: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) plus a molecule of sugar and one of phosphoric acid. Dinucleotide: A sequence of 2 base pairs. Oligonucleotides are short sequences of nucleotides (RNA or DNA), typically with twenty or fewer bases. Auto ...
... A nucleotide consists of a base (one of four chemicals: adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) plus a molecule of sugar and one of phosphoric acid. Dinucleotide: A sequence of 2 base pairs. Oligonucleotides are short sequences of nucleotides (RNA or DNA), typically with twenty or fewer bases. Auto ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
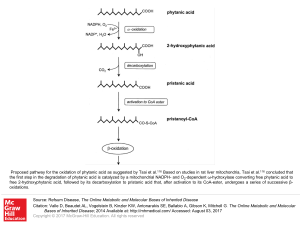
... Proposed pathway for the oxidation of phytanic acid as suggested by Tsai et al.116 Based on studies in rat liver mitochondria, Tsai et al.116 concluded that the first step in the degradation of phytanic acid is catalyzed by a mitochondrial NADPH- and O2-dependent ω-hydroxylase converting free phytan ...
... Proposed pathway for the oxidation of phytanic acid as suggested by Tsai et al.116 Based on studies in rat liver mitochondria, Tsai et al.116 concluded that the first step in the degradation of phytanic acid is catalyzed by a mitochondrial NADPH- and O2-dependent ω-hydroxylase converting free phytan ...
Weathering and Erosion - School District 67 Okanagan Skaha
... Rate of Weathering Several factors determine the rate at which rock weathers: • Wet vs. dry climates • The composition of the rock (what minerals it contains) • The amount of surface area exposed ...
... Rate of Weathering Several factors determine the rate at which rock weathers: • Wet vs. dry climates • The composition of the rock (what minerals it contains) • The amount of surface area exposed ...
Glucose-6-P to Fructose-6-P
... Substrates for Gluconeogenesis Pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, amino acids and all TCA intermediates can be utilized • Fatty acids cannot! • Most fatty acids yield only acetyl-CoA • Acetyl-CoA (through TCA cycle) cannot provide for net synthesis of sugars ...
... Substrates for Gluconeogenesis Pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, amino acids and all TCA intermediates can be utilized • Fatty acids cannot! • Most fatty acids yield only acetyl-CoA • Acetyl-CoA (through TCA cycle) cannot provide for net synthesis of sugars ...
Electron Transport Chain (1)
... into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate or acetyl CoA - Carbohydrates: break down the glycosidiclinkages and we get sugars which goes straight into glycolysis - Proteins: becomes amino acids and can be turned into pyruvate, acetyl CoA or it can go straight into the citric acid cycle - Then everything that g ...
... into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate or acetyl CoA - Carbohydrates: break down the glycosidiclinkages and we get sugars which goes straight into glycolysis - Proteins: becomes amino acids and can be turned into pyruvate, acetyl CoA or it can go straight into the citric acid cycle - Then everything that g ...
Name Date Period 1. What are the end products of aerobic cell
... How many ATP molecules (net yield) are produced per molecule of glucose as a direct result of glycolysis? A. ...
... How many ATP molecules (net yield) are produced per molecule of glucose as a direct result of glycolysis? A. ...
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is
... (C) carbon dioxide only (D) water only (E) carbon dioxide and water 56.The concentration of bacteria is greater around an algal filament exposed to red light than around the same filament exposed to green light because (A) green light affects enzyme action in bacteria (B) photosynthesis proceeds mor ...
... (C) carbon dioxide only (D) water only (E) carbon dioxide and water 56.The concentration of bacteria is greater around an algal filament exposed to red light than around the same filament exposed to green light because (A) green light affects enzyme action in bacteria (B) photosynthesis proceeds mor ...
chapt 6
... Cells will use the energy in carbohydrates first. – Complex carbohydrates are metabolized into simple sugars. Cells can use the energy in fats and proteins as well. – Fats are digested into fatty acids and glycerol. – Proteins are digested into amino acids. Cells must convert fats and proteins into ...
... Cells will use the energy in carbohydrates first. – Complex carbohydrates are metabolized into simple sugars. Cells can use the energy in fats and proteins as well. – Fats are digested into fatty acids and glycerol. – Proteins are digested into amino acids. Cells must convert fats and proteins into ...
Dried blood spot analysis on the Biochrom 30 Amino Acid Analyser
... A number of tests are then carried out on these blood spots for the purposes of newborn screening. Typically the Biochrom 30 Amino Acid Analyser is used for the amino acid analysis of plasma and urine. However it can also be used for analysis of other types of samples such as dried blood spots follo ...
... A number of tests are then carried out on these blood spots for the purposes of newborn screening. Typically the Biochrom 30 Amino Acid Analyser is used for the amino acid analysis of plasma and urine. However it can also be used for analysis of other types of samples such as dried blood spots follo ...
BIO 101 Blinderman Mercer County Community College Division of
... 10. Examine cellular respiration, C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O as an exergonic reaction 11. Examine photosynthesis , 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ light energy) C6H12O6 + 6O2 as endergonic reaction 12. Describe the cell as a system not in equilibrium as an open system 13. Analyze the ability of cells to couple ...
... 10. Examine cellular respiration, C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O as an exergonic reaction 11. Examine photosynthesis , 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ light energy) C6H12O6 + 6O2 as endergonic reaction 12. Describe the cell as a system not in equilibrium as an open system 13. Analyze the ability of cells to couple ...
Macromolecules of Life – Lecture 1
... f. Guard Cells g. Vein i. Xylem ii. Phloem h. Chloroplasts i. Chlorophyll ...
... f. Guard Cells g. Vein i. Xylem ii. Phloem h. Chloroplasts i. Chlorophyll ...
Activity 2.2.3 The Biochemistry of Food
... these molecules are used to build our body parts, some are used to drive chemical reactions necessary for life, and others are used as sources of energy. Many of the molecules in our bodies are very large and are made by combining smaller molecules. These very large molecules are called macromolecul ...
... these molecules are used to build our body parts, some are used to drive chemical reactions necessary for life, and others are used as sources of energy. Many of the molecules in our bodies are very large and are made by combining smaller molecules. These very large molecules are called macromolecul ...
Nutrition: How to obtain food: This is descriptive
... Bulk feeders - humans, lions, buffalo. Eat large pieces of food. Some animals, like corals might be hard to put into one of these categories. Corals are mostly suspension feeders, but they also photosynthesize (with the help of algae living in their tissues) What kind of food does an animal eat? Her ...
... Bulk feeders - humans, lions, buffalo. Eat large pieces of food. Some animals, like corals might be hard to put into one of these categories. Corals are mostly suspension feeders, but they also photosynthesize (with the help of algae living in their tissues) What kind of food does an animal eat? Her ...
UC Irvine FOCUS! 5 E Lesson Plan Title: Genetics Scavenger Hunt
... called A, T, C, and G for short) that are strung in patterns on extremely thin, coiled strands in the cell. How thin? Cells are tiny — invisible to the naked eye — and each cell in your body contains about 6 feet of DNA thread, for a total of about 3 billion miles (if all your DNA threads were stret ...
... called A, T, C, and G for short) that are strung in patterns on extremely thin, coiled strands in the cell. How thin? Cells are tiny — invisible to the naked eye — and each cell in your body contains about 6 feet of DNA thread, for a total of about 3 billion miles (if all your DNA threads were stret ...
Cell Metabolism - Cathkin High School
... 10. The following diagram represents stages in the complete breakdown of glucose in aerobic respiration. Glucose Stage X Pyruvic acid Stage Y ...
... 10. The following diagram represents stages in the complete breakdown of glucose in aerobic respiration. Glucose Stage X Pyruvic acid Stage Y ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.