Outline of this course:
... Output is determined by the supply side: – supplies of capital, labor – technology Changes in demand for goods & services (C, I, G ) only affect prices, not quantities. Complete price flexibility is a crucial assumption, so classical theory applies in the long run. ...
... Output is determined by the supply side: – supplies of capital, labor – technology Changes in demand for goods & services (C, I, G ) only affect prices, not quantities. Complete price flexibility is a crucial assumption, so classical theory applies in the long run. ...
Ch10.pps
... Now that we’ve derived the IS part of AD, it’s now time to complete the model of AD by adding a money market equilibrium schedule, the LM curve. To develop this theory, we begin with the supply of real money balances (M/P); both of these variables are taken to be exogenously given. This yields a ve ...
... Now that we’ve derived the IS part of AD, it’s now time to complete the model of AD by adding a money market equilibrium schedule, the LM curve. To develop this theory, we begin with the supply of real money balances (M/P); both of these variables are taken to be exogenously given. This yields a ve ...
Lecture 7. Classical monetary theory
... Original logic of identity of supply and demand for all goods: “A product is no sooner created, than it, from that instant, affords a market for other products to the full extent of its own value.”2 Failures of validity are rather obvious: Say’s law asserts that the aggregate demand for commodities ...
... Original logic of identity of supply and demand for all goods: “A product is no sooner created, than it, from that instant, affords a market for other products to the full extent of its own value.”2 Failures of validity are rather obvious: Say’s law asserts that the aggregate demand for commodities ...
The market economy: theory, ideology and reality
... salt, dried chillies and molasses. What was done to secure these was to take some of its own produce, a bunch of raw bananas or some eggs, to a location about a mile away on a Wednesday or Saturday and where on those days the required goods would be available. Seldom was there direct barter. The act ...
... salt, dried chillies and molasses. What was done to secure these was to take some of its own produce, a bunch of raw bananas or some eggs, to a location about a mile away on a Wednesday or Saturday and where on those days the required goods would be available. Seldom was there direct barter. The act ...
Honours Finance (Advanced Concepts in Finance)
... economic cycle – Higher return necessarily paired with higher volatility • Investors simply chose risk/return trade-off that suited their preferences ...
... economic cycle – Higher return necessarily paired with higher volatility • Investors simply chose risk/return trade-off that suited their preferences ...
The Federal Reserve System is the central bank of the United States
... The discount rate is the interest rate banks are charged when they borrow from the Federal Reserve. The discount rate can be altered by the Federal Reserve either to encourage or discourage borrowing from financial institutions. A change in the discount rate has a more pronounced affect on the money ...
... The discount rate is the interest rate banks are charged when they borrow from the Federal Reserve. The discount rate can be altered by the Federal Reserve either to encourage or discourage borrowing from financial institutions. A change in the discount rate has a more pronounced affect on the money ...
How Macroeconomics Affects our Everyday Lives Productivity growth
... When unemployment rate is high, it is going to be harder for individuals who want to work to find a job. Unemployed people will not be able to pay their bills. Crime, mental illness and suicide will increase. Many economists consider unemployment as the single most important macroeconomic issue. ...
... When unemployment rate is high, it is going to be harder for individuals who want to work to find a job. Unemployed people will not be able to pay their bills. Crime, mental illness and suicide will increase. Many economists consider unemployment as the single most important macroeconomic issue. ...
Classical and Neoclassical Theory of Money and
... - Investment => the purchase of “the right to the series of prospective net returns” expected from “the output” “during the life of the capital asset” - Marginal Efficiency of Capital - defined as the relation between the prospective yield of one more unit of capital asset and the cost of producing ...
... - Investment => the purchase of “the right to the series of prospective net returns” expected from “the output” “during the life of the capital asset” - Marginal Efficiency of Capital - defined as the relation between the prospective yield of one more unit of capital asset and the cost of producing ...
Factor Price Equalization and Stolper
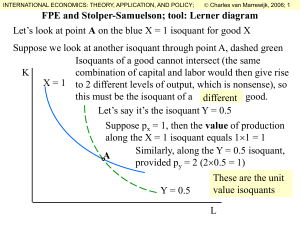
... Let’s look at point A on the blue X = 1 isoquant for good X Suppose we look at another isoquant through point A, dashed green Isoquants of a good cannot intersect (the same combination of capital and labor would then give rise K X = 1 to 2 different levels of output, which is nonsense), so this must ...
... Let’s look at point A on the blue X = 1 isoquant for good X Suppose we look at another isoquant through point A, dashed green Isoquants of a good cannot intersect (the same combination of capital and labor would then give rise K X = 1 to 2 different levels of output, which is nonsense), so this must ...
MACRO ECONOMICS I UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
... 19. In the Fisher’s extended equation of exchange MI VI represents: (A) Credit money (B) Primary money (C) Both primary and credit money (D) General price level 20. In Fisher’s transaction velocity model, one of the following is not an assumption: (A) Velocity of circulation of money is constant (B) ...
... 19. In the Fisher’s extended equation of exchange MI VI represents: (A) Credit money (B) Primary money (C) Both primary and credit money (D) General price level 20. In Fisher’s transaction velocity model, one of the following is not an assumption: (A) Velocity of circulation of money is constant (B) ...
EcoNZ - University of Otago
... jobs, causing an increase in the supply of labour, the demand for labour was minimal due to low business confidence. In hard economic times, employers are reluctant to invest resources in training young people when older unemployed experienced workers are available. Therefore, employers are more lik ...
... jobs, causing an increase in the supply of labour, the demand for labour was minimal due to low business confidence. In hard economic times, employers are reluctant to invest resources in training young people when older unemployed experienced workers are available. Therefore, employers are more lik ...
The State of the MOnetarist Debate
... and rapid force on aggregate demand. Most monetarists, but not all, contend that the influence of such actions is transitory. Post-Keynesians advance three main arguments for the primacy of fiscal actions. Increases in Government spending add directly to aggregate demand, and reductions in tax rates ...
... and rapid force on aggregate demand. Most monetarists, but not all, contend that the influence of such actions is transitory. Post-Keynesians advance three main arguments for the primacy of fiscal actions. Increases in Government spending add directly to aggregate demand, and reductions in tax rates ...
I. What Is a Business Cycle?
... bad after World War II as they were before 2. The average contraction before 1929 lasted 21 months compared to 11 months after 1945 3. The average expansion before 1929 lasted 25 months compared to 50 months after 1945 4. Romer’s 1986 article sparked a strong debate, as it argued that pre-1929 data ...
... bad after World War II as they were before 2. The average contraction before 1929 lasted 21 months compared to 11 months after 1945 3. The average expansion before 1929 lasted 25 months compared to 50 months after 1945 4. Romer’s 1986 article sparked a strong debate, as it argued that pre-1929 data ...
The demand for loanable funds
... is called the par value. The two of these determine how much you will receive if you purchase the instrument. If you buy this thing, you will receive coupon rate times the par value or 0.05*$5000 = $250 each year that you own the bond. If you own a bond, you can either hold it or you can sell it if ...
... is called the par value. The two of these determine how much you will receive if you purchase the instrument. If you buy this thing, you will receive coupon rate times the par value or 0.05*$5000 = $250 each year that you own the bond. If you own a bond, you can either hold it or you can sell it if ...
The Quantity Theory of Money in a Developing Economy: Empirical
... monetary stability through the management of debt and foreign exchange rate. In essence, appropriate demand and supply management policies by the CBN necessary for economic development requires money to be stable and functional. As such, since early 1990s, the CBN has employed a market-oriented mone ...
... monetary stability through the management of debt and foreign exchange rate. In essence, appropriate demand and supply management policies by the CBN necessary for economic development requires money to be stable and functional. As such, since early 1990s, the CBN has employed a market-oriented mone ...
The Problem of Full Employment by Parvez Hasan
... application of the credit policy presupposes many conditions including the existence of an organized money market, fullest, cooperation of the commercial and financial institutions etc. This however does not imply that monetary policy as an instrument of regulating investment is to completely dispen ...
... application of the credit policy presupposes many conditions including the existence of an organized money market, fullest, cooperation of the commercial and financial institutions etc. This however does not imply that monetary policy as an instrument of regulating investment is to completely dispen ...
not in the textbook? - Lancaster University
... The Keynesian income-expenditure model demonstrates this formally: G (fiscal deficit spending) is the amount by which previously unemployed labour and unused capital are remunerated for raising output/income. That output/income is direcet in part to taxation (T = tG; 0 < t < 1), in part to saving (S ...
... The Keynesian income-expenditure model demonstrates this formally: G (fiscal deficit spending) is the amount by which previously unemployed labour and unused capital are remunerated for raising output/income. That output/income is direcet in part to taxation (T = tG; 0 < t < 1), in part to saving (S ...
Aggregate Demand File
... then they are likely to spend more now. • If they think that they are likely to get a promotion in the future due to a booming economy and strong sales, then they will feel more confident about taking a loan or using up savings. • High consumer confidence is likely to lead to increased ...
... then they are likely to spend more now. • If they think that they are likely to get a promotion in the future due to a booming economy and strong sales, then they will feel more confident about taking a loan or using up savings. • High consumer confidence is likely to lead to increased ...
© Worth Publishers, Do Not Duplicate
... by a small but significant minority of economists. According to this theory, shortrun economic fluctuations should be explained while maintaining the assumptions of the classical model, which we have used to study the long run. Most important, real business cycle theory assumes that prices are fully ...
... by a small but significant minority of economists. According to this theory, shortrun economic fluctuations should be explained while maintaining the assumptions of the classical model, which we have used to study the long run. Most important, real business cycle theory assumes that prices are fully ...
Secular stagnation or financial cycle drag?
... operates at full employment and to avoid a costly deflationary spiral. Such a spiral would arise because, with nominal interest rates stuck at the zero lower bound, falling prices would raise real interest rates, which would cut spending further, which, in turn, would depress output and employment a ...
... operates at full employment and to avoid a costly deflationary spiral. Such a spiral would arise because, with nominal interest rates stuck at the zero lower bound, falling prices would raise real interest rates, which would cut spending further, which, in turn, would depress output and employment a ...
Scylla and Charybdis: Navigating a Liquidity Trap
... The Great Japanese Recession of 1995-2005 was less severe than our country’s Great Depression. Average Japanese inflation was -0.2% and real GDP remained relatively steady compared to the steep evisceration of household and corporate balance sheets. The Japanese learned painfully that traditional mo ...
... The Great Japanese Recession of 1995-2005 was less severe than our country’s Great Depression. Average Japanese inflation was -0.2% and real GDP remained relatively steady compared to the steep evisceration of household and corporate balance sheets. The Japanese learned painfully that traditional mo ...
69. Adina Dornean - Danubius Proceedings
... the interest. At the same time, the entrepreneur does not ignore the acceleration effect according to which an increase of the consumption can determine an increase more than proportional of the investments in the area in which these goods are manufactured for which the demand has increased, in the ...
... the interest. At the same time, the entrepreneur does not ignore the acceleration effect according to which an increase of the consumption can determine an increase more than proportional of the investments in the area in which these goods are manufactured for which the demand has increased, in the ...
krugman ir macro module 38(74).indd
... Students have already been exposed to the idea that changes in fiscal policy will shift the AD curve. The extension to monetary policy is fairly straightforward, but make sure students understand the process. Any shift in aggregate demand is based on the change in the interest rate causing a change ...
... Students have already been exposed to the idea that changes in fiscal policy will shift the AD curve. The extension to monetary policy is fairly straightforward, but make sure students understand the process. Any shift in aggregate demand is based on the change in the interest rate causing a change ...
unit description
... prohibited. For the purposes of this fair dealing exception, students should be aware that the rule allowing copying, for fair dealing purposes, of 10% of the work, or one chapter/article, applies to the original work from which the excerpt in this course material was taken, and not to the course ma ...
... prohibited. For the purposes of this fair dealing exception, students should be aware that the rule allowing copying, for fair dealing purposes, of 10% of the work, or one chapter/article, applies to the original work from which the excerpt in this course material was taken, and not to the course ma ...