Roseobacter gallaeciensis sp. nov., a new marine - HAL
... to prepare genomic DNA for PCR. Bacteria grown in MB were centrifuged at 3000 g at 4 °C for 10 min. The pellet obtained was resuspended in 200 µl lysis mixture (10 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8 -0, 1 mM EDTA, 1% Triton X-100) and boiled for 5 min. After a single chloroform extraction, 5 µl supernatant was used ...
... to prepare genomic DNA for PCR. Bacteria grown in MB were centrifuged at 3000 g at 4 °C for 10 min. The pellet obtained was resuspended in 200 µl lysis mixture (10 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8 -0, 1 mM EDTA, 1% Triton X-100) and boiled for 5 min. After a single chloroform extraction, 5 µl supernatant was used ...
The quest for the entrepreneurial gene
... These SNPs and other types of genomic variation are what make humans different from each other. The total number and locations of SNP markers that need to be genotyped to detect an association between common genetic variants and an outcome of interest (a phenotype of an individual) were identified b ...
... These SNPs and other types of genomic variation are what make humans different from each other. The total number and locations of SNP markers that need to be genotyped to detect an association between common genetic variants and an outcome of interest (a phenotype of an individual) were identified b ...
A Recipe for Traits.indd
... (T) and Cytosine (C). These bases, G, A, T, C are commonly referred to as the “DNA alphabet.” This DNA alphabet encodes a detailed set of instructions for building an organism’s physical traits. The DNA instructions are divided into segments called genes. Differences in the DNA sequence of each gene ...
... (T) and Cytosine (C). These bases, G, A, T, C are commonly referred to as the “DNA alphabet.” This DNA alphabet encodes a detailed set of instructions for building an organism’s physical traits. The DNA instructions are divided into segments called genes. Differences in the DNA sequence of each gene ...
Solutions for Recombinant DNA Unit Exam
... DNA template – the thing we want to amplify dNTPs – nucleotides used in the reaction (Optional) Buffer – keeps the reaction conditions constant over the long time b) Circle the set of primers from the options below, which you would use for PCR reaction in part (a)? Set 1: 5’TACACTTATACTTTC3’ and 3’G ...
... DNA template – the thing we want to amplify dNTPs – nucleotides used in the reaction (Optional) Buffer – keeps the reaction conditions constant over the long time b) Circle the set of primers from the options below, which you would use for PCR reaction in part (a)? Set 1: 5’TACACTTATACTTTC3’ and 3’G ...
overview - El Paso High School
... DNA replication begins with the binding of a large protein complex—the pre-replication complex—to a specific site on the DNA molecule. The complex contains DNA polymerase, which catalyzes addition of nucleotides. The complex binds to a region on the chromosome called the origin of replication (ori). ...
... DNA replication begins with the binding of a large protein complex—the pre-replication complex—to a specific site on the DNA molecule. The complex contains DNA polymerase, which catalyzes addition of nucleotides. The complex binds to a region on the chromosome called the origin of replication (ori). ...
Supporting Information
... ScNCE103Δ complementation was possible by introduction of plasmid pScNCE103-GFP. This ...
... ScNCE103Δ complementation was possible by introduction of plasmid pScNCE103-GFP. This ...
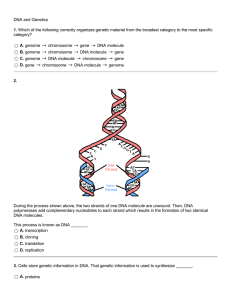
DNA and Genetics 1. Which of the following correctly organizes
... their functions. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a type of nucleic acid that carries all the instructions for the characteristics of an organism. Genes are specific segments of DNA that influence a particular trait or group of traits. 2. The process of DNA replication begins with one double-stranded ...
... their functions. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a type of nucleic acid that carries all the instructions for the characteristics of an organism. Genes are specific segments of DNA that influence a particular trait or group of traits. 2. The process of DNA replication begins with one double-stranded ...
Hydrogen autotrophy of Nocardia opaca strains is
... method of Marmur (1961) these linear plasmids were not detectable; this may be due to their sensitivity to shearing forces. On conventional agarose gel electrophoresis the linear plasmids formed a broad band located slightly above the largest A HindIII fragment (Fig. 2). In lysates of N . opaca obta ...
... method of Marmur (1961) these linear plasmids were not detectable; this may be due to their sensitivity to shearing forces. On conventional agarose gel electrophoresis the linear plasmids formed a broad band located slightly above the largest A HindIII fragment (Fig. 2). In lysates of N . opaca obta ...
Characterization of two rice DNA methyltransferases
... recommended by the manufacturer. First strand cDNA was synthesized at 42EC for 1 h using the adapter supplied with the kit (5'-(A)12CCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTAATTCTGTGCTCGC) and RNA (2 Fg) from mature leaves as the template. A 1 Fl of reverse transcription reaction was subsequently used in 35 cycles of PCR ...
... recommended by the manufacturer. First strand cDNA was synthesized at 42EC for 1 h using the adapter supplied with the kit (5'-(A)12CCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTAATTCTGTGCTCGC) and RNA (2 Fg) from mature leaves as the template. A 1 Fl of reverse transcription reaction was subsequently used in 35 cycles of PCR ...
PCR - AREA
... Dot-blot and Northern-blot, molecular cloning, qRT-PCR MICRODIAG, dr Ivana Stanković and dr Ana Vučurović, Department of Biology and Plant Pathology, Faculty of Sciences and Biotechnology, University of Bari, Italy ...
... Dot-blot and Northern-blot, molecular cloning, qRT-PCR MICRODIAG, dr Ivana Stanković and dr Ana Vučurović, Department of Biology and Plant Pathology, Faculty of Sciences and Biotechnology, University of Bari, Italy ...
DNA Replication, Repair, and Recombination
... via cointegrate 1. Pair of staggered ss cuts 2. Ligation of both ends at integration site forms replication fork 3. Replication forms cointegrate 4. Site-specific recombination cointegrate resolved ...
... via cointegrate 1. Pair of staggered ss cuts 2. Ligation of both ends at integration site forms replication fork 3. Replication forms cointegrate 4. Site-specific recombination cointegrate resolved ...
DNA Extraction - Utah Agriculture in the Classroom
... 18.What can be done with my extracted DNA? This sample could be used for gel electrophoresis, for example, but all you will see is a smear. The DNA you have extracted is genomic, meaning that you have the entire collection of DNA from each cell. Unless you cut the DNA with restriction enzymes, it ...
... 18.What can be done with my extracted DNA? This sample could be used for gel electrophoresis, for example, but all you will see is a smear. The DNA you have extracted is genomic, meaning that you have the entire collection of DNA from each cell. Unless you cut the DNA with restriction enzymes, it ...
Presentation
... Transgenes for a protein are inserted into the egg of a domestic animal, next to the promoter for lactoglobulin—a protein in milk. The transgenic animal then produces large quantities of the protein in its milk. ...
... Transgenes for a protein are inserted into the egg of a domestic animal, next to the promoter for lactoglobulin—a protein in milk. The transgenic animal then produces large quantities of the protein in its milk. ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 8e
... Transgenes for a protein are inserted into the egg of a domestic animal, next to the promoter for lactoglobulin—a protein in milk. The transgenic animal then produces large quantities of the protein in its milk. ...
... Transgenes for a protein are inserted into the egg of a domestic animal, next to the promoter for lactoglobulin—a protein in milk. The transgenic animal then produces large quantities of the protein in its milk. ...
PDF
... thus heterologous D N A transformed into L. planmrum must be stably maintained, in the absence of selection pressure, and not transferred to other microorganisms in the ecosystems. One approach to achieving this objective is to insert foreign D N A into the Lactobaeillas ger~ome. Shcirlinock et al. ...
... thus heterologous D N A transformed into L. planmrum must be stably maintained, in the absence of selection pressure, and not transferred to other microorganisms in the ecosystems. One approach to achieving this objective is to insert foreign D N A into the Lactobaeillas ger~ome. Shcirlinock et al. ...
Reveal—visual eQTL analytics
... number of traits, problems arise with a fully genome-wide screen where millions of SNPs, for example in the human genome, are tested for association with hundreds or thousands of traits. Many applications in this area combine the (visual) detection of significant SNPs with the genomic context, mainl ...
... number of traits, problems arise with a fully genome-wide screen where millions of SNPs, for example in the human genome, are tested for association with hundreds or thousands of traits. Many applications in this area combine the (visual) detection of significant SNPs with the genomic context, mainl ...
Subset-Based Ant Colony Optimisation for the Discovery of Gene
... Many examples of GWAS data analysis exist in the literature that demonstrate the association between a single SNP and disease. There are known single associations for Type II diabetes and traits such as height for instance. However, there is a considerable amount of missing heritability, for example ...
... Many examples of GWAS data analysis exist in the literature that demonstrate the association between a single SNP and disease. There are known single associations for Type II diabetes and traits such as height for instance. However, there is a considerable amount of missing heritability, for example ...
A physical map of the genome of Hmmophilus
... Digestion of DNA in agarose blocks. Usually digests were carried out on the DNA contained in one-third of a complete plug. Restriction einzyme buffers were diffused into the agarose blocks as outlined below. Plugs or portions of plugs were washed in Eppendorf tubes with 500 1.11 vlolumesof buffer (u ...
... Digestion of DNA in agarose blocks. Usually digests were carried out on the DNA contained in one-third of a complete plug. Restriction einzyme buffers were diffused into the agarose blocks as outlined below. Plugs or portions of plugs were washed in Eppendorf tubes with 500 1.11 vlolumesof buffer (u ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.