DNA Sequence Capture and Enrichment by Microarray Followed by
... DNA was nebulized to yield fragments from 250 bp to approximately 1 kb in size, and a 22mer linker was added to both ends. The DNA fragments were then hybridized to the NF1 sequence-capture array for 3 days. After hybridization and stringent washing, the DNA fragments remaining on the array (mostly ...
... DNA was nebulized to yield fragments from 250 bp to approximately 1 kb in size, and a 22mer linker was added to both ends. The DNA fragments were then hybridized to the NF1 sequence-capture array for 3 days. After hybridization and stringent washing, the DNA fragments remaining on the array (mostly ...
Kernel Approaches for Nonlinear Genetic Association Regression
... Kangar00: Kernel Approaches for Nonlinear Genetic Association Regression Stefanie Friedrichs ...
... Kangar00: Kernel Approaches for Nonlinear Genetic Association Regression Stefanie Friedrichs ...
Simultaneous mutation scanning for gross deletions
... Primers were designed to amplify all 79 exons of the DMD gene (the entire 30 UTR is not covered), two alternative promoters (purkinje and cortical) and two exons of the myelin protein zero gene (MPZ) located at 1q22 to control for whole gene deletions or duplications. In all cases, primers were desi ...
... Primers were designed to amplify all 79 exons of the DMD gene (the entire 30 UTR is not covered), two alternative promoters (purkinje and cortical) and two exons of the myelin protein zero gene (MPZ) located at 1q22 to control for whole gene deletions or duplications. In all cases, primers were desi ...
DNA Self-assembly Model for Matrix Addition Problem
... DNA computing is a new kind of information processing pattern, which is based on biochemical reaction with DNA molecules, bio-enzyme and so on being the most basic materials. DNA computing was first put forward by Adlema[1,2] in 1994. He solved the problem of a seven vertices Hamilton road with DNA ...
... DNA computing is a new kind of information processing pattern, which is based on biochemical reaction with DNA molecules, bio-enzyme and so on being the most basic materials. DNA computing was first put forward by Adlema[1,2] in 1994. He solved the problem of a seven vertices Hamilton road with DNA ...
Phenotypic and Genotypic Comparisons among Strains of the
... molecular weight of the bacterial genome was calculated by the equation: M = (70.03 - 0.35 x mol% G+C) x 107/k’ (9), where k’ represents the reaction rate constant. DNA-DNA hybridization. Determination of the genetic relationship between two bacterial strains was based on initial renaturation rates ...
... molecular weight of the bacterial genome was calculated by the equation: M = (70.03 - 0.35 x mol% G+C) x 107/k’ (9), where k’ represents the reaction rate constant. DNA-DNA hybridization. Determination of the genetic relationship between two bacterial strains was based on initial renaturation rates ...
Lesson Plan, GeneChip® Microarrays: Teacher`s Guide
... may decide to use this module and the activities in it to supplement a unit on DNA, genetics, or even one on the Human Genome Project. The entire module is organized to go from a basic introduction of the GeneChip microarray and then build from there. After the basic introduction, the module moves o ...
... may decide to use this module and the activities in it to supplement a unit on DNA, genetics, or even one on the Human Genome Project. The entire module is organized to go from a basic introduction of the GeneChip microarray and then build from there. After the basic introduction, the module moves o ...
Title Heterochromatin Blocks Constituting the Entire
... Briefly, bacterial cells containing recombinant DNA were plated on agar media, individual colonies were transferred to 96-well plates containing liquid media, bacterial cell culture was blotted onto nylon membranes, and DNA was denatured using an alkali solution and then hybridized with alkaline pho ...
... Briefly, bacterial cells containing recombinant DNA were plated on agar media, individual colonies were transferred to 96-well plates containing liquid media, bacterial cell culture was blotted onto nylon membranes, and DNA was denatured using an alkali solution and then hybridized with alkaline pho ...
Binding Protein HU has a Regulatory Role in the Acid Stress
... gel. When pH was risen to 7.0 or 8.0, protein affinity for DNA was progressively lowered, on the basis that a lower retardation of complexes in the agarose gel was observed. Migration distances of these complexes (expressed as percentage of retardation) at different pH conditions were statistically ...
... gel. When pH was risen to 7.0 or 8.0, protein affinity for DNA was progressively lowered, on the basis that a lower retardation of complexes in the agarose gel was observed. Migration distances of these complexes (expressed as percentage of retardation) at different pH conditions were statistically ...
Differential Gene Expression in the Gastrula of Xenopus Laevis
... Hybridization. Problem: 0.05% of 10000 mRNA too rare for detection ...
... Hybridization. Problem: 0.05% of 10000 mRNA too rare for detection ...
document
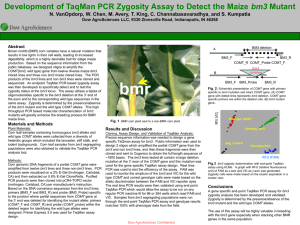
... allelic discrimination between the FAM and VIC reporter dyes. The real time PCR results were then validated using end-point TaqMan PCR which would allow the assay to be run on any regular PCR machine fit for 96 or 384 wells which read FAM and VIC. Samples from bm3 segregating populations were run th ...
... allelic discrimination between the FAM and VIC reporter dyes. The real time PCR results were then validated using end-point TaqMan PCR which would allow the assay to be run on any regular PCR machine fit for 96 or 384 wells which read FAM and VIC. Samples from bm3 segregating populations were run th ...
Chapter 13 Mutation, DNA Repair, and Recombination
... Mismatch Repair in E. coli Mismatching or mispairing of G and T (DNA polymerase/exonuclease proofreading activity) The A in GATC sequences is methylated subsequent to DNA replication. In newly replicated DNA, the parental strand is methylated, but the new strand is not. This difference allows ...
... Mismatch Repair in E. coli Mismatching or mispairing of G and T (DNA polymerase/exonuclease proofreading activity) The A in GATC sequences is methylated subsequent to DNA replication. In newly replicated DNA, the parental strand is methylated, but the new strand is not. This difference allows ...
DNA polymerase active site is highly mutable
... highly conserved region within DNA polymerases, motif A. Our random mutagenesis protocol allows creation of a large population of mutants in which each amino acid can be altered to potentially any of the other 19 (13, 14). When this protocol is coupled with a stringent selection scheme, we can deter ...
... highly conserved region within DNA polymerases, motif A. Our random mutagenesis protocol allows creation of a large population of mutants in which each amino acid can be altered to potentially any of the other 19 (13, 14). When this protocol is coupled with a stringent selection scheme, we can deter ...
RNA PCR Kit (AMV)
... change the annealing temperature (55 - 65℃) depending on the targets. It may be necessary to determine the optimal annealing temperature experimentally in the range of 45 - 65℃. ・Extension time The extension time depends on the target length. Usually, TaKaRa Ex Taq HS extends DNA at 1 kb per minute ...
... change the annealing temperature (55 - 65℃) depending on the targets. It may be necessary to determine the optimal annealing temperature experimentally in the range of 45 - 65℃. ・Extension time The extension time depends on the target length. Usually, TaKaRa Ex Taq HS extends DNA at 1 kb per minute ...
Book 12 Chapter 34 - From The Mountain Prophecies
... out of my body via an opening! Most often, it must work to create an opening, or an exitway for the waste; for these evil ones have put a maze of wires and cloth into my body in order to “seal” off and to shut up potential exitways! The locations of these exitways may vary from day to day; and once ...
... out of my body via an opening! Most often, it must work to create an opening, or an exitway for the waste; for these evil ones have put a maze of wires and cloth into my body in order to “seal” off and to shut up potential exitways! The locations of these exitways may vary from day to day; and once ...
The Relationship Between DNA Replication and the
... added early enough. When sporulation is induced by nutrient exhaustion, HPUra does indeed inhibit development if it is added within 2 h of the time at which growth ceases to be exponential (Leighton et al., 1975 ; Shibano et al., 1978). Unfortunately, in these experiments it is not possible to ascer ...
... added early enough. When sporulation is induced by nutrient exhaustion, HPUra does indeed inhibit development if it is added within 2 h of the time at which growth ceases to be exponential (Leighton et al., 1975 ; Shibano et al., 1978). Unfortunately, in these experiments it is not possible to ascer ...
Inheritance and monhybrid
... Why do members of the same family look similar? Humans, like all organisms, inherit characteristics from their parents. How are characteristics passed on? 3 of 8 ...
... Why do members of the same family look similar? Humans, like all organisms, inherit characteristics from their parents. How are characteristics passed on? 3 of 8 ...
Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium Vocabulary and Calculations Review
... A. How are traits passed down from parents to offspring? 1. Basic Genetics Information Given in Previous Notes: -“DNA (or deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule found in the cells of all living things. The code found in DNA determines the inherited traits found in an organism. An inherited trait is on ...
... A. How are traits passed down from parents to offspring? 1. Basic Genetics Information Given in Previous Notes: -“DNA (or deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule found in the cells of all living things. The code found in DNA determines the inherited traits found in an organism. An inherited trait is on ...
Lab 8: Population Genetics and Evolution
... 3. There is no mutation of alleles. 4. No differential migration occurs (no immigration or emigration). 5. All genotypes have an equal chance of surviving and reproducing, i.e., there is no selection. Basically, the Hardy-Weinberg equation describes the status quo. If the five conditions are met, th ...
... 3. There is no mutation of alleles. 4. No differential migration occurs (no immigration or emigration). 5. All genotypes have an equal chance of surviving and reproducing, i.e., there is no selection. Basically, the Hardy-Weinberg equation describes the status quo. If the five conditions are met, th ...
Embryo Genome Profiling by Single-Cell
... Traditionally, multiplex PCR has been used to detect the pathogenic variants of an embryo with short tandem repeat markers in close proximity to the causative gene as a diagnosis backup. With the introduction of whole-genome amplification (WGA) to amplify the biopsied embryonic single cell, the comp ...
... Traditionally, multiplex PCR has been used to detect the pathogenic variants of an embryo with short tandem repeat markers in close proximity to the causative gene as a diagnosis backup. With the introduction of whole-genome amplification (WGA) to amplify the biopsied embryonic single cell, the comp ...
msc_botnay_pre_pap1_bl2
... The histone proteins, which are integral parts of nucleosome undergo a variety of modifications to bring about decondensation of chromatin, to allow access of DNA replication or transcription machinery to naked DNA. These modifications include ubiquitination, acetylation, methylation and phosphoryl ...
... The histone proteins, which are integral parts of nucleosome undergo a variety of modifications to bring about decondensation of chromatin, to allow access of DNA replication or transcription machinery to naked DNA. These modifications include ubiquitination, acetylation, methylation and phosphoryl ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.