Chapter 21
... An insertion sequence is a transposon that codes for the enzyme(s) needed for transposition flanked by short inverted terminal repeats. The target site at which a transposon is inserted is duplicated during the insertion process to form two repeats in direct orientation at the ends of the transposon ...
... An insertion sequence is a transposon that codes for the enzyme(s) needed for transposition flanked by short inverted terminal repeats. The target site at which a transposon is inserted is duplicated during the insertion process to form two repeats in direct orientation at the ends of the transposon ...
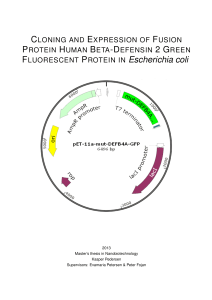
FLUORESCENT PROTEIN IN Escherichia coli
... paradigm to how infections were treated. Since then many other antiobiotics were developed, e.g. streptomycin against tuberculosis. This meant that the leading cause of death changed from being infections to being noninfectious diseases, i.e. cancer, stroke, etc. Meanwhile, extended use of antibioti ...
... paradigm to how infections were treated. Since then many other antiobiotics were developed, e.g. streptomycin against tuberculosis. This meant that the leading cause of death changed from being infections to being noninfectious diseases, i.e. cancer, stroke, etc. Meanwhile, extended use of antibioti ...
initial rates for many enzymatic reactions exhibit bell
... formation rather than the disappearance of S ii -many assay types impose some limitations on the assay conditions due to S instability under some conditions, which makes it difficult to estimate the rates of the E-catalyzed rxn accurately -in coupled assays one of the P is continuously removed and t ...
... formation rather than the disappearance of S ii -many assay types impose some limitations on the assay conditions due to S instability under some conditions, which makes it difficult to estimate the rates of the E-catalyzed rxn accurately -in coupled assays one of the P is continuously removed and t ...
Solving Heredity Problems Name______________________________ Class __________________ Date ______________
... the textbook before performing this investigation. Time required: 40 minutes ...
... the textbook before performing this investigation. Time required: 40 minutes ...
Population genetics and the modern synthesis of evolutionary theory
... in the same group, and little with outsiders − in reality, populations usually have fuzzy boundaries − individuals migrate into and out of groups − individuals mate with others from outside the group − but the breeding population concept is a useful first approximation − a population view of a speci ...
... in the same group, and little with outsiders − in reality, populations usually have fuzzy boundaries − individuals migrate into and out of groups − individuals mate with others from outside the group − but the breeding population concept is a useful first approximation − a population view of a speci ...
CB3 - Homework
... Use the pieces to construct a diagram to show what happens in meiosis. The organism you are modelling has three pairs of chromosomes in its body cells. You will need to draw circles around the chromosomes to show which cells they belong to, but you do not need to show the cell nuclei. ...
... Use the pieces to construct a diagram to show what happens in meiosis. The organism you are modelling has three pairs of chromosomes in its body cells. You will need to draw circles around the chromosomes to show which cells they belong to, but you do not need to show the cell nuclei. ...
Carcinoembryonic Antigens - The Journal of Cell Biology
... cated by the proposed domain structure illustrated in Fig. 3 and by the sequence relationships detailed in Table I. As is typical for other CEA isoantigens, the TM1-CEA polypeptide initiates with a M-amino acid leader sequence that ends at a short side-chain amino acid, alanine. The proposed NH2-ter ...
... cated by the proposed domain structure illustrated in Fig. 3 and by the sequence relationships detailed in Table I. As is typical for other CEA isoantigens, the TM1-CEA polypeptide initiates with a M-amino acid leader sequence that ends at a short side-chain amino acid, alanine. The proposed NH2-ter ...
File
... shape, pod color, flower position, and plant height. These traits are expressed as tall or short; round or wrinkled; there is no blending or intermediate trait. A ______________ is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. Hair color, skin color, height, and blood type wo ...
... shape, pod color, flower position, and plant height. These traits are expressed as tall or short; round or wrinkled; there is no blending or intermediate trait. A ______________ is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. Hair color, skin color, height, and blood type wo ...
Package `iECAT`
... a numeric vector of weights for the weighted kernels. It is w in the SKAT paper. So if you want to use the Madsen p and Browning (2009) weight, you should set each element of weights as 1/ p(1 − p), not 1/p(1 − p). When it is NULL, the beta weight with the “weights.beta” parameter is used. ...
... a numeric vector of weights for the weighted kernels. It is w in the SKAT paper. So if you want to use the Madsen p and Browning (2009) weight, you should set each element of weights as 1/ p(1 − p), not 1/p(1 − p). When it is NULL, the beta weight with the “weights.beta” parameter is used. ...
v2 PEBiosystems News 2 01/00
... ICAT is a trademark of the University of Washington, exclusively licensed to Applied Biosystems Group of Applera Corporation. Paracel is a registered trademark of Paracel Inc. The ABI PRISM 3100 and the 3100-Avant Genetic Analyzers include patented technology licensed from Hitachi, Ltd. as part of a ...
... ICAT is a trademark of the University of Washington, exclusively licensed to Applied Biosystems Group of Applera Corporation. Paracel is a registered trademark of Paracel Inc. The ABI PRISM 3100 and the 3100-Avant Genetic Analyzers include patented technology licensed from Hitachi, Ltd. as part of a ...
Population genetics and the modern synthesis of evolutionary theory
... − so the recessive trait is very rarely expressed, and natural selection cannot weed it out − rare dominant or codominant mutations − dominant or codominant mutations are expressed even when there is just the one mutated allele in the offspring − if it causes the individual to die or not reproduce, ...
... − so the recessive trait is very rarely expressed, and natural selection cannot weed it out − rare dominant or codominant mutations − dominant or codominant mutations are expressed even when there is just the one mutated allele in the offspring − if it causes the individual to die or not reproduce, ...
Mutational Analysis Defines the Roles of Conserved Amino Acid
... alanine resulted in decreased kcat ; indicating its role in catalysis, which might be mediated through the interaction with vicinal Y104. It is interesting though, that this mutation does not greatly affect the ErmC0 function in vivo, but this could be explained with different stability of mutant pr ...
... alanine resulted in decreased kcat ; indicating its role in catalysis, which might be mediated through the interaction with vicinal Y104. It is interesting though, that this mutation does not greatly affect the ErmC0 function in vivo, but this could be explained with different stability of mutant pr ...
Part I: Why Use Probes? - Centre for Intellectual Property Policy
... Distributive Justice Description Does a given patent regime provide a just allocation of goods, e.g., revenue, access to technology • Who benefits, by how much, and who bears the costs? • Are the competing interests appropriately resolved? ...
... Distributive Justice Description Does a given patent regime provide a just allocation of goods, e.g., revenue, access to technology • Who benefits, by how much, and who bears the costs? • Are the competing interests appropriately resolved? ...
Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of another variant of the
... Membranes were removed from the solution and placed in hybridization solution (6 X SSC/l:< SDS) together with the labelled oligonucleotide probe and incubated overnight at 42 "C. After hybridization, membranes were washed three times in 6 x SSCjl?; SDS for 10 min each wash and once for 5 min with 1 ...
... Membranes were removed from the solution and placed in hybridization solution (6 X SSC/l:< SDS) together with the labelled oligonucleotide probe and incubated overnight at 42 "C. After hybridization, membranes were washed three times in 6 x SSCjl?; SDS for 10 min each wash and once for 5 min with 1 ...
DO NOW - Kenwood Academy High School
... and expected results, but there could have been a difference. 2. Explain how a genetics counselor or a doctor could use these calculations of probability to counsel prospective parents. ...
... and expected results, but there could have been a difference. 2. Explain how a genetics counselor or a doctor could use these calculations of probability to counsel prospective parents. ...
Heredity
... Genes – sequence of triplets on DNA Humans have about – 23,000 genes Each chromosome contains many genes Like the chromosomes they are part of, genes occur in pairs of two. – Alleles - alternate forms of a gene ...
... Genes – sequence of triplets on DNA Humans have about – 23,000 genes Each chromosome contains many genes Like the chromosomes they are part of, genes occur in pairs of two. – Alleles - alternate forms of a gene ...
The use of glycogen and GlycoBlue reagent in Qubit DNA and RNA
... Glycogen (a branched-chain carbohydrate; Cat. No. 10814010) and Invitrogen™ GlycoBlue™ Coprecipitant (glycogen covalently linked to a blue dye; Cat. No. AM9515) are reagents commonly used to facilitate nucleic acid precipitation without adding extraneous nucleic acids to the sample. This study was c ...
... Glycogen (a branched-chain carbohydrate; Cat. No. 10814010) and Invitrogen™ GlycoBlue™ Coprecipitant (glycogen covalently linked to a blue dye; Cat. No. AM9515) are reagents commonly used to facilitate nucleic acid precipitation without adding extraneous nucleic acids to the sample. This study was c ...
The energetic basis of the DNA double helix: a
... and widely accepted, that the enthalpy of DNA duplex dissociation/association does not depend on temperature (10–13). On the other hand, the enthalpy of DNA dissociation at elevated temperatures, determined by DSC, was found to be in conflict with the enthalpy of association of the complementary str ...
... and widely accepted, that the enthalpy of DNA duplex dissociation/association does not depend on temperature (10–13). On the other hand, the enthalpy of DNA dissociation at elevated temperatures, determined by DSC, was found to be in conflict with the enthalpy of association of the complementary str ...
16S rRNA characterization of Bacillus strain and its
... (Watabe et al., 2004). For example, antractic coastal marine samples yielded novel Psychrobacter (Bozal et al., 2003), this would not have been known if not for the use of phylogeny and DNA-DNA hybridization. Novel eubacteria were isolated from spent mushroom compost (SMC). This study was important ...
... (Watabe et al., 2004). For example, antractic coastal marine samples yielded novel Psychrobacter (Bozal et al., 2003), this would not have been known if not for the use of phylogeny and DNA-DNA hybridization. Novel eubacteria were isolated from spent mushroom compost (SMC). This study was important ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.