Bereavement Synonyms Definition Introduction
... over time, normal functioning is restored while symptoms gradually decline. It is important to note that everybody grieves differently – for some it may be hardly noticeable, while others may react very strongly. And while some fundamental manifestations of grief appear to be universal across cultur ...
... over time, normal functioning is restored while symptoms gradually decline. It is important to note that everybody grieves differently – for some it may be hardly noticeable, while others may react very strongly. And while some fundamental manifestations of grief appear to be universal across cultur ...
Malingering - Rage University
... obtaining drugs. Under some circumstances, malingering may represent adaptive behavior for example, feigning illness while a captive of the enemy during wartime. ...
... obtaining drugs. Under some circumstances, malingering may represent adaptive behavior for example, feigning illness while a captive of the enemy during wartime. ...
Sleep apnoea, anxiety, depression and somatoform pain: a community-based high-risk sample
... (MDD or dysthymia). No participants reported psychosis, mania or hypomania. No relationship was observed between OSA and any DSM-IV psychiatric disorder (table 2). However, the odds ratio of participants with OSA having at least one psychiatric disorder was 0.54 (95% CI 0.33–0.88) compared with part ...
... (MDD or dysthymia). No participants reported psychosis, mania or hypomania. No relationship was observed between OSA and any DSM-IV psychiatric disorder (table 2). However, the odds ratio of participants with OSA having at least one psychiatric disorder was 0.54 (95% CI 0.33–0.88) compared with part ...
Hallucinations in children: Diagnostic and
... Clinical Point A diagnosis of psychotic disorder NOS should be avoided when hallucinations occur in nonpsychotic children ...
... Clinical Point A diagnosis of psychotic disorder NOS should be avoided when hallucinations occur in nonpsychotic children ...
Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents National Institute of Mental Health
... study participants made at least one serious suicide attempt.10 Some suicide attempts are carefully planned and others are not. Either way, it is important to understand that suicidal feelings and actions are symptoms of an illness that must be treated. For more information on suicide, see the NIMH ...
... study participants made at least one serious suicide attempt.10 Some suicide attempts are carefully planned and others are not. Either way, it is important to understand that suicidal feelings and actions are symptoms of an illness that must be treated. For more information on suicide, see the NIMH ...
What is Psychology?
... Learning, Culture, and Addiction • Addiction patterns vary according to cultural practices and the social environment. • Policies of total abstinence tend to increase addiction rates rather than reduce them. • Not all addicts have withdrawal symptoms when they stop taking a drug. • Addiction does n ...
... Learning, Culture, and Addiction • Addiction patterns vary according to cultural practices and the social environment. • Policies of total abstinence tend to increase addiction rates rather than reduce them. • Not all addicts have withdrawal symptoms when they stop taking a drug. • Addiction does n ...
Dissociative disorders
... Abnormal Behavior • The most commonly used criteria for distinguishing between normal and abnormal behaviors are statistical rarity, interference with normal functioning, personal distress, and deviance from social norms. • By the standard of statistical rarity, behavior is abnormal when it does no ...
... Abnormal Behavior • The most commonly used criteria for distinguishing between normal and abnormal behaviors are statistical rarity, interference with normal functioning, personal distress, and deviance from social norms. • By the standard of statistical rarity, behavior is abnormal when it does no ...
Personality Disorders
... A developmental disability involving short attention span, distractibility, and extreme difficulty in remaining inactive for any period of time.. ...
... A developmental disability involving short attention span, distractibility, and extreme difficulty in remaining inactive for any period of time.. ...
Birthplace
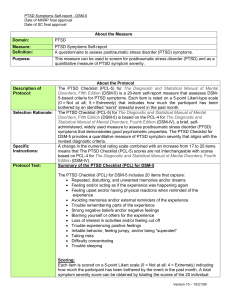
... Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) is a 20-item self-report measure that assesses DSM5-based criteria for PTSD symptoms. Each item is rated on a 5-point Likert-type scale (0 = Not at all; 5 = Extremely) that indicates how much the participant has been bothered by an identified “worst” stressful event ...
... Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) is a 20-item self-report measure that assesses DSM5-based criteria for PTSD symptoms. Each item is rated on a 5-point Likert-type scale (0 = Not at all; 5 = Extremely) that indicates how much the participant has been bothered by an identified “worst” stressful event ...
summary and conclusions - Sacramento
... more refined foods and less fruits and vegetables. The diet that is consumed today is very different from the one that was consumed a hundred years ago and our mental health interventions do not typically look at diet when assessing a client or when planning an intervention. The connection between f ...
... more refined foods and less fruits and vegetables. The diet that is consumed today is very different from the one that was consumed a hundred years ago and our mental health interventions do not typically look at diet when assessing a client or when planning an intervention. The connection between f ...
Chapter 12
... acquired through natural selection, to respond quickly and automatically to stimuli that posed a survival threat to our ancestors ...
... acquired through natural selection, to respond quickly and automatically to stimuli that posed a survival threat to our ancestors ...
Postpartum Depression Fall 2015
... Mean time for the onset of symptoms is 2 to 3 weeks and almost always within 8 weeks after birth ...
... Mean time for the onset of symptoms is 2 to 3 weeks and almost always within 8 weeks after birth ...
Deckblatt 242-11
... often have difficulty finding a job in which they can succeed (Harpin 2005). They also often have interpersonal difficulties with employers and colleagues in the workplace, and frequently experience problems related to lateness, absenteeism, work errors, and an inability to accomplish an expected wo ...
... often have difficulty finding a job in which they can succeed (Harpin 2005). They also often have interpersonal difficulties with employers and colleagues in the workplace, and frequently experience problems related to lateness, absenteeism, work errors, and an inability to accomplish an expected wo ...
Incidence of Eating Disorders
... and the first treatment intervention leads to the best outcome for recovery ...
... and the first treatment intervention leads to the best outcome for recovery ...
A BPD Brief - National Education Alliance for Borderline Personality
... societal and cultural factors which contribute to variations in its prevalence. A society which is fastpaced; highly mobile, and where family situations may be unstable due to divorce, economic factors or other pressures on the caregivers, may encourage development of this disorder. The Course of Bo ...
... societal and cultural factors which contribute to variations in its prevalence. A society which is fastpaced; highly mobile, and where family situations may be unstable due to divorce, economic factors or other pressures on the caregivers, may encourage development of this disorder. The Course of Bo ...
Westphal_AGRI_Conference_2010
... increased with SUD severity, but the pattern did not appear to be affected by MD co-occurrence. • Results suggest particular attention be given to SUD in treatment-seeking clients with co-occurring disorders. ...
... increased with SUD severity, but the pattern did not appear to be affected by MD co-occurrence. • Results suggest particular attention be given to SUD in treatment-seeking clients with co-occurring disorders. ...
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
... • Obsessions as defined by (1) and (2): 1. Recurrent and persistent thoughts, urges, or images that are experienced, at some time during the disturbance, as intrusive and unwanted and that in most individuals cause marked anxiety or distress 2. The person attempts to ignore or suppress such thoughts ...
... • Obsessions as defined by (1) and (2): 1. Recurrent and persistent thoughts, urges, or images that are experienced, at some time during the disturbance, as intrusive and unwanted and that in most individuals cause marked anxiety or distress 2. The person attempts to ignore or suppress such thoughts ...
FREE Sample Here
... 2. Abnormal psychology is a. the scientific study of troublesome feelings, thoughts, and behaviors associated with mental disorders. b. assertions about what might be abnormal emotional experience. c. a scientific study of how and why people become unique. d. the opposite of biological psychology. A ...
... 2. Abnormal psychology is a. the scientific study of troublesome feelings, thoughts, and behaviors associated with mental disorders. b. assertions about what might be abnormal emotional experience. c. a scientific study of how and why people become unique. d. the opposite of biological psychology. A ...
Anxiety and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in the Context
... to sustain for anxiety disorders. It is axiomatic that a mild degree of fear is often helpful, and that one can have “too much of a good thing.” Therefore, a prudent strategy in the research agenda for DSM-V may be to focus on evolutionary factors in the anxiety spectrum. A second prudent approach i ...
... to sustain for anxiety disorders. It is axiomatic that a mild degree of fear is often helpful, and that one can have “too much of a good thing.” Therefore, a prudent strategy in the research agenda for DSM-V may be to focus on evolutionary factors in the anxiety spectrum. A second prudent approach i ...
Running head: OPPOSITIONAL DEFIANT DISORDER AND
... typically observed in individuals of comparable age and developmental level. B. The disturbance in behavior causes clinically significant impairment in social, academic, or occupational functioning. C. The behaviors do not occur exclusively during the course of a Psychotic or Mood Disorder. D. Crite ...
... typically observed in individuals of comparable age and developmental level. B. The disturbance in behavior causes clinically significant impairment in social, academic, or occupational functioning. C. The behaviors do not occur exclusively during the course of a Psychotic or Mood Disorder. D. Crite ...
Cause - NAMI Iowa
... research regarding Neurological Brain Disorders, the status of major legislation at the federal level and in state and local governments, provocative editorials, book reviews, and more! NAMI IOWA’s newsletter, distributed three or four times a year, to keep you informed on mental health issues in Io ...
... research regarding Neurological Brain Disorders, the status of major legislation at the federal level and in state and local governments, provocative editorials, book reviews, and more! NAMI IOWA’s newsletter, distributed three or four times a year, to keep you informed on mental health issues in Io ...
CDI Issues Related to ICD-10-CM Mental and Behavioral Health
... 29. If a patient has alcoholic cirrhosis, and the patient has alcohol abuse, is it okay to code? As with all other diagnoses, the codes for substance use should only be assigned based on provider documentation and when they meet the definition of a reportable diagnosis. At this point in time, the c ...
... 29. If a patient has alcoholic cirrhosis, and the patient has alcohol abuse, is it okay to code? As with all other diagnoses, the codes for substance use should only be assigned based on provider documentation and when they meet the definition of a reportable diagnosis. At this point in time, the c ...
S3 Guidelines In Psychiatry And Psychtherapy
... http://www.dgppn.de/dgppn/struktur/referate/versorgung0/s3-leitliniepsychosoziale-therapien-bei-schweren-psychischen-erkrankungen.html). The target group of this guideline comprises people with severe mental illness (SMI). This group includes people with particular and mostly multi-professional care ...
... http://www.dgppn.de/dgppn/struktur/referate/versorgung0/s3-leitliniepsychosoziale-therapien-bei-schweren-psychischen-erkrankungen.html). The target group of this guideline comprises people with severe mental illness (SMI). This group includes people with particular and mostly multi-professional care ...
major mental disorders and behavior among american indians and
... Modem concepts of mental illness incorporate genetic, social, psychological, biochemical, cognitive, characterological, and functional neurophysiologic dimensions to understand the mechanisms of mental illness. In the majority American culture these dimensions of mental illness have been explored ov ...
... Modem concepts of mental illness incorporate genetic, social, psychological, biochemical, cognitive, characterological, and functional neurophysiologic dimensions to understand the mechanisms of mental illness. In the majority American culture these dimensions of mental illness have been explored ov ...
Mental disorder
A mental disorder, also called a mental illness, psychological disorder or psychiatric disorder, is mental or behavioral pattern that causes either suffering or a poor ability to function in ordinary life. Many disorders are described. Conditions that are excluded include social norms. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific disorder.The causes of mental disorders are often unclear. Theories may incorporate findings from a range of fields. Mental disorders are usually defined by a combination of how a person feels, acts, thinks or perceives. This may be associated with particular regions or functions of the brain, often in a social context. A mental disorder is one aspect of mental health. The scientific study of mental disorders is called psychopathology.Services are based in psychiatric hospitals or in the community, and assessments are carried out by psychiatrists, clinical psychologists and clinical social workers, using various methods but often relying on observation and questioning. Treatments are provided by various mental health professionals. Psychotherapy and psychiatric medication are two major treatment options. Other treatments include social interventions, peer support and self-help. In a minority of cases there might be involuntary detention or treatment. Prevention programs have been shown to reduce depression.Common mental disorders include depression, which affects about 400 million, dementia which affects about 35 million, and schizophrenia, which affects about 21 million people globally. Stigma and discrimination can add to the suffering and disability associated with mental disorders, leading to various social movements attempting to increase understanding and challenge social exclusion.