4.6_Weather
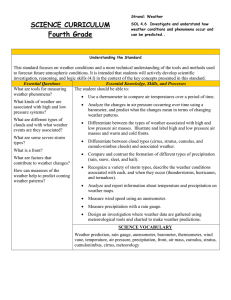
... Differentiate between the types of weather associated with high and clouds and with what weather low pressure air masses. Illustrate and label high and low pressure air events are they associated? masses and warm and cold fronts. What are some severe storm Differentiate between cloud types (cirr ...
... Differentiate between the types of weather associated with high and clouds and with what weather low pressure air masses. Illustrate and label high and low pressure air events are they associated? masses and warm and cold fronts. What are some severe storm Differentiate between cloud types (cirr ...
model output statistics and climate variability over
... Imoh B. Obioh Atmospheric Research and Information Analysis Laboratory (ARIAL) Centre for Energy Research and Development (CERD) Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria ...
... Imoh B. Obioh Atmospheric Research and Information Analysis Laboratory (ARIAL) Centre for Energy Research and Development (CERD) Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria ...
COURSE: Environmental and Atmospheric Physics CADEMIC YEAR
... The primary stock of knowledge provided by the course includes the fundamentals of environmental and atmospheric physics. More specifically, faced topics include: Atmospheric composition and its variability with height, thermal structure of the atmosphere, air pollution, dry and we ...
... The primary stock of knowledge provided by the course includes the fundamentals of environmental and atmospheric physics. More specifically, faced topics include: Atmospheric composition and its variability with height, thermal structure of the atmosphere, air pollution, dry and we ...
Meteorology - School in the Park
... processes of evaporation and condensation. As a basis for understanding this concept: b. Students know when liquid water evaporates, it turns into water vapor in the air and can reappear as a liquid when cooled or as a solid if cooled below the freezing point of water. c. Students know water vapor i ...
... processes of evaporation and condensation. As a basis for understanding this concept: b. Students know when liquid water evaporates, it turns into water vapor in the air and can reappear as a liquid when cooled or as a solid if cooled below the freezing point of water. c. Students know water vapor i ...
Physical Climatology
... cycle itself may also reciprocate and influence climate change. It is now recognized that climate change, or global warming, can directly effect precipitation, evapotranspiration, and soil moisture. It has been predicted, using various models all dependent on Global Circulation Models, that the hydr ...
... cycle itself may also reciprocate and influence climate change. It is now recognized that climate change, or global warming, can directly effect precipitation, evapotranspiration, and soil moisture. It has been predicted, using various models all dependent on Global Circulation Models, that the hydr ...
Atmospheric Sciences Undergraduate Program 2009
... This track is aimed at students with interests in chemistry and/or environmental engineering who would like to apply their knowledge of atmospheric sciences to environmental issues such as evolving atmospheric composition and air quality. ...
... This track is aimed at students with interests in chemistry and/or environmental engineering who would like to apply their knowledge of atmospheric sciences to environmental issues such as evolving atmospheric composition and air quality. ...
Three-Dimensional Structure of Atmospheric Fronts and
... 2) Tangential discontinuity – jump of temperature, density and tangential (to the discontinuity surface) velocity (wind) component. An atmospheric front – second kind discontinuity. Practical task: to construct (by using discrete grid) 3D surfaces of atmospheric fronts. Atmospheric fronts can be con ...
... 2) Tangential discontinuity – jump of temperature, density and tangential (to the discontinuity surface) velocity (wind) component. An atmospheric front – second kind discontinuity. Practical task: to construct (by using discrete grid) 3D surfaces of atmospheric fronts. Atmospheric fronts can be con ...
Meetings
... the Coupled General Circulation Model for the Earth Simulator (CFES) and the Multi-Scale Simulator for the Geoenvironment (MSSG) – all projects led by scientists at the Earth Simulator Center (ESC). In addition, University of Tokyo and JAMSTEC scientists have developed the Nonhydrostatic ICosahedral ...
... the Coupled General Circulation Model for the Earth Simulator (CFES) and the Multi-Scale Simulator for the Geoenvironment (MSSG) – all projects led by scientists at the Earth Simulator Center (ESC). In addition, University of Tokyo and JAMSTEC scientists have developed the Nonhydrostatic ICosahedral ...
Weather & Climate
... global warming continues, there will be an increased amount of clouds in our atmosphere, which may help or hurt. Forest Fires: Wildfires release carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. By trapping heat, carbon dioxide contributes to the planet’s warming. However, if a forest of simi ...
... global warming continues, there will be an increased amount of clouds in our atmosphere, which may help or hurt. Forest Fires: Wildfires release carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. By trapping heat, carbon dioxide contributes to the planet’s warming. However, if a forest of simi ...
misconceptions: barriers to improved climate literacy
... data on wind speed and direction indicate that a pronounced seasonal cycle exists and that the modal and mean patterns are quite similar. Development of models to assist in the explanation of atmospheric circulation began with Hadley’s (1735) single meridional cell based on his synthesis of surface- ...
... data on wind speed and direction indicate that a pronounced seasonal cycle exists and that the modal and mean patterns are quite similar. Development of models to assist in the explanation of atmospheric circulation began with Hadley’s (1735) single meridional cell based on his synthesis of surface- ...
Predicting Climate Change Impacts: Regional
... Professor Laprise is one of the many scientists who volunteer their time and expertise as Lead Authors on assessment reports produced by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The IPCC is the international body for assessing the science related to climate change. IPCC assessments prov ...
... Professor Laprise is one of the many scientists who volunteer their time and expertise as Lead Authors on assessment reports produced by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The IPCC is the international body for assessing the science related to climate change. IPCC assessments prov ...
No Slide Title
... producing the “first” fully coupled climate simulation using the T85 CAM atmospheric model with CCSM2.0 (all previous simulations have used T42), which will provide more regional climate change detail ...
... producing the “first” fully coupled climate simulation using the T85 CAM atmospheric model with CCSM2.0 (all previous simulations have used T42), which will provide more regional climate change detail ...
Atmospheric Sciences Undergraduate Program 2016
... ATM S 431 (3): Boundary-Layer Meteorology ATM S 441 (3): Atmospheric Motions I ...
... ATM S 431 (3): Boundary-Layer Meteorology ATM S 441 (3): Atmospheric Motions I ...
fluid dynamics - University of Guelph
... the global warming issue and was adopted by the IPCC and many governments as the poster graphic. The graphics’ prominence together with the fact that it is based on incorrect use of PCA puts Dr. Mann and his co-authors in a difficult facesaving position.” ...
... the global warming issue and was adopted by the IPCC and many governments as the poster graphic. The graphics’ prominence together with the fact that it is based on incorrect use of PCA puts Dr. Mann and his co-authors in a difficult facesaving position.” ...
In what layer of the atmosphere does weather
... temperature, humidity, precipitation, cloudiness, brightness, visibility, wind, and atmospheric pressure, as in high and low pressure, sunshine, rain, cloud cover, winds, hail, snow, sleet, freezing rain, flooding, blizzards, ice storms, thunderstorms, steady rains from a cold front or warm front, e ...
... temperature, humidity, precipitation, cloudiness, brightness, visibility, wind, and atmospheric pressure, as in high and low pressure, sunshine, rain, cloud cover, winds, hail, snow, sleet, freezing rain, flooding, blizzards, ice storms, thunderstorms, steady rains from a cold front or warm front, e ...
Climate Change: Science Issues
... will need to acknowledge that something is fundamentally wrong with our climate models…A 20-year pause in global warming does not occur in a single modeled scenario. But even today, we are finding it very difficult to reconcile actual ...
... will need to acknowledge that something is fundamentally wrong with our climate models…A 20-year pause in global warming does not occur in a single modeled scenario. But even today, we are finding it very difficult to reconcile actual ...
Meteorology - The Federation of Galaxy Explorers
... deal with fronts anyway? Well that is where the bad weather is. A cold front is associated with showers and thunder storms. Warm fronts usually bring steady rain. You can see that the clouds lie along the fronts on this weather map. Of course, the weather forecasters have a lot more information abo ...
... deal with fronts anyway? Well that is where the bad weather is. A cold front is associated with showers and thunder storms. Warm fronts usually bring steady rain. You can see that the clouds lie along the fronts on this weather map. Of course, the weather forecasters have a lot more information abo ...
Costs and Benefits of Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
... • Best studied sectors are market sectors— agriculture, forestry, energy, water, coastal infrastructure • Damages in developing countries—especially low latitude developing countries—are often a larger percent of GDP than in high income countries • To compare with global costs of mitigation, need to ...
... • Best studied sectors are market sectors— agriculture, forestry, energy, water, coastal infrastructure • Damages in developing countries—especially low latitude developing countries—are often a larger percent of GDP than in high income countries • To compare with global costs of mitigation, need to ...
toward a new generation of world climate research and
... example, the Met Office currently runs an operational limited-area model at 1.5 km, which is beginning to deliver substantial improvements in skill in forecasting extreme rainfall events, especially when the synoptic forcing is strong (Lean et al. 2008). Since a discrete model can reasonably resolve ...
... example, the Met Office currently runs an operational limited-area model at 1.5 km, which is beginning to deliver substantial improvements in skill in forecasting extreme rainfall events, especially when the synoptic forcing is strong (Lean et al. 2008). Since a discrete model can reasonably resolve ...
Atmospheric model
An atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, moist processes (clouds and precipitation), heat exchange, soil, vegetation, surface water, the kinematic effects of terrain, and convection. Most atmospheric models are numerical, i.e. they discretize equations of motion. They can predict microscale phenomena such as tornadoes and boundary layer eddies, sub-microscale turbulent flow over buildings, as well as synoptic and global flows. The horizontal domain of a model is either global, covering the entire Earth, or regional (limited-area), covering only part of the Earth. The different types of models run are thermotropic, barotropic, hydrostatic, and nonhydrostatic. Some of the model types make assumptions about the atmosphere which lengthens the time steps used and increases computational speed.Forecasts are computed using mathematical equations for the physics and dynamics of the atmosphere. These equations are nonlinear and are impossible to solve exactly. Therefore, numerical methods obtain approximate solutions. Different models use different solution methods. Global models often use spectral methods for the horizontal dimensions and finite-difference methods for the vertical dimension, while regional models usually use finite-difference methods in all three dimensions. For specific locations, model output statistics use climate information, output from numerical weather prediction, and current surface weather observations to develop statistical relationships which account for model bias and resolution issues.























