Macroeconomics
... • As output falls, unemployment rises. – Changes in real GDP are inversely related to changes in the unemployment rate. – During times of recession, unemployment rises substantially. ...
... • As output falls, unemployment rises. – Changes in real GDP are inversely related to changes in the unemployment rate. – During times of recession, unemployment rises substantially. ...
1 .A production possibilities frontier can shift outward if a
... a). the price floor is higher than the equilibrium price of the good. b). the quantity of the good demanded with the price floor is less than the quantity demanded of the good without the price floor. c). the quantity of the good supplied with the price floor is less than the quantity supplied of th ...
... a). the price floor is higher than the equilibrium price of the good. b). the quantity of the good demanded with the price floor is less than the quantity demanded of the good without the price floor. c). the quantity of the good supplied with the price floor is less than the quantity supplied of th ...
Marxian Political Economy: Legacy and Renewal
... of the active capitalists to salaried personnel was the object of a strong “polarization” between upper and lower segments. The division of tasks did not follow dividing lines reflecting various fields such as technical processes, commercial tasks, accounting, or finance. In each field, hierarchies ...
... of the active capitalists to salaried personnel was the object of a strong “polarization” between upper and lower segments. The division of tasks did not follow dividing lines reflecting various fields such as technical processes, commercial tasks, accounting, or finance. In each field, hierarchies ...
Productivity - Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
... Critics of Young’s work that because of data mismeasurement, they assumed that East Asian production functions were different (greater capital intensity) than developed economies. Even using same production functions, most East Asian growth differentials are due to factor ...
... Critics of Young’s work that because of data mismeasurement, they assumed that East Asian production functions were different (greater capital intensity) than developed economies. Even using same production functions, most East Asian growth differentials are due to factor ...
Intermediate Macroeconomics, Sciences Po, 2014 Zsófia Bárány
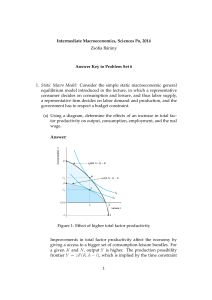
... Figure 2: Effect of higher total factor productivity when T = G/z When T = G/z, the consumption possibilities frontier is given by C = Y − T = zF (K, h − l) − G/z. Note: for z = 1 the frontier is the same as in the previous part of the problem set. When z increases, the private sector is more produ ...
... Figure 2: Effect of higher total factor productivity when T = G/z When T = G/z, the consumption possibilities frontier is given by C = Y − T = zF (K, h − l) − G/z. Note: for z = 1 the frontier is the same as in the previous part of the problem set. When z increases, the private sector is more produ ...
answers
... 6. In the IS-LM model (a model of the short run), equilibrium output is determined by the demand side of the economy (how much households, businesses and governments want to buy). It is assumed that …rms do whatever it takes to produce the output that demand requires. Now suppose that a positive tec ...
... 6. In the IS-LM model (a model of the short run), equilibrium output is determined by the demand side of the economy (how much households, businesses and governments want to buy). It is assumed that …rms do whatever it takes to produce the output that demand requires. Now suppose that a positive tec ...
ecomacro2005_avec_co..
... the government spend to reach this objective ? (without collecting taxes) 3/ If we now consider that government spending should be funded by tax receipts, what should be the tax rate (t) to attain the level of output compatible with full employment ? 4/ Keeping the objective of full employment, with ...
... the government spend to reach this objective ? (without collecting taxes) 3/ If we now consider that government spending should be funded by tax receipts, what should be the tax rate (t) to attain the level of output compatible with full employment ? 4/ Keeping the objective of full employment, with ...
3. National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes
... 2. Competitive firms hire each factor until its marginal product equals its price. 3. If the production function has constant returns to scale, then labor income plus capital income equals total income (output). ...
... 2. Competitive firms hire each factor until its marginal product equals its price. 3. If the production function has constant returns to scale, then labor income plus capital income equals total income (output). ...
Study Questions. More sample multiple choice
... 5) e. natural resources (land), tools (or capital) and labor are all factors of the production of national income. The inflation rate is not a theorized factor of production. Inflation is not a resource used to make things (did Tom Hanks need inflation to make stuff on his island?). 6) b. The produc ...
... 5) e. natural resources (land), tools (or capital) and labor are all factors of the production of national income. The inflation rate is not a theorized factor of production. Inflation is not a resource used to make things (did Tom Hanks need inflation to make stuff on his island?). 6) b. The produc ...
Theory of measurement for site-specific evolutionary rates in
... captures exchangeabilities between all pairs of amino acids. The substitution matrices are made by analyzing large protein data sets and even protein sequences specific to an organism or an organelle. However, it remains an open question which substitution matrix is the most suitable for site-wise r ...
... captures exchangeabilities between all pairs of amino acids. The substitution matrices are made by analyzing large protein data sets and even protein sequences specific to an organism or an organelle. However, it remains an open question which substitution matrix is the most suitable for site-wise r ...
Reasons of Inflation
... current money purchasing power decreases price falls 1.2 expenses when borrowing money will increase purchasing power decreases price falls ...
... current money purchasing power decreases price falls 1.2 expenses when borrowing money will increase purchasing power decreases price falls ...
doc
... 7) Consider an economy in which the labor force grows by 2.7 percent per annum, while the capital stock grows by 4 percent per annum. Suppose 55 percent of national income goes to labor and 45 percent to capital. a. If the residual were a = 0, what rate of growth would the economy achieve? b. The co ...
... 7) Consider an economy in which the labor force grows by 2.7 percent per annum, while the capital stock grows by 4 percent per annum. Suppose 55 percent of national income goes to labor and 45 percent to capital. a. If the residual were a = 0, what rate of growth would the economy achieve? b. The co ...
The Harrod-Domar model:
... 7) Consider an economy in which the labor force grows by 2.7 percent per annum, while the capital stock grows by 4 percent per annum. Suppose 55 percent of national income goes to labor and 45 percent to capital. a. If the residual were a = 0, what rate of growth would the economy achieve? b. The co ...
... 7) Consider an economy in which the labor force grows by 2.7 percent per annum, while the capital stock grows by 4 percent per annum. Suppose 55 percent of national income goes to labor and 45 percent to capital. a. If the residual were a = 0, what rate of growth would the economy achieve? b. The co ...
2 National Income Accounting
... an endogenous variable. A change in an endogenous variable is always the result of some more fundamental change in one or more exogenous variables. You should have at least as many equations as endogenous variables in your model. If you have more, some of your equations must be combinations of the o ...
... an endogenous variable. A change in an endogenous variable is always the result of some more fundamental change in one or more exogenous variables. You should have at least as many equations as endogenous variables in your model. If you have more, some of your equations must be combinations of the o ...
Singapore
... 1.02 Impact of rules on FDI†......................................... 6.3...............2 1.03 Efficiency of legal framework settling disputes†..... 6.2...............1 1.04 Efficiency of legal framework challenging regs.†.... 4.4.............21 1.05 No. of days to deal with construction ...
... 1.02 Impact of rules on FDI†......................................... 6.3...............2 1.03 Efficiency of legal framework settling disputes†..... 6.2...............1 1.04 Efficiency of legal framework challenging regs.†.... 4.4.............21 1.05 No. of days to deal with construction ...
Sweden
... 1.02 Impact of rules on FDI†......................................... 5.0.............25 1.03 Efficiency of legal framework settling disputes†..... 5.4.............13 1.04 Efficiency of legal framework challenging regs.†.... 4.7.............14 1.05 No. of days to deal with construction p ...
... 1.02 Impact of rules on FDI†......................................... 5.0.............25 1.03 Efficiency of legal framework settling disputes†..... 5.4.............13 1.04 Efficiency of legal framework challenging regs.†.... 4.7.............14 1.05 No. of days to deal with construction p ...
France
... 1.02 Impact of rules on FDI†......................................... 4.5.............66 1.03 Efficiency of legal framework settling disputes†..... 4.2.............41 1.04 Efficiency of legal framework challenging regs.†.... 4.2.............25 1.05 No. of days to deal with construction p ...
... 1.02 Impact of rules on FDI†......................................... 4.5.............66 1.03 Efficiency of legal framework settling disputes†..... 4.2.............41 1.04 Efficiency of legal framework challenging regs.†.... 4.2.............25 1.05 No. of days to deal with construction p ...
Course Outline 7.
... But then the sequence of short run adjustments under a) – d), above, will occur, which leaves the final short run equilib. the same as described in e), above (Study sequence diagram on p. 360) The difference between the two e.g.s is that an incr. in G will definitely ____________ the i rate, but an ...
... But then the sequence of short run adjustments under a) – d), above, will occur, which leaves the final short run equilib. the same as described in e), above (Study sequence diagram on p. 360) The difference between the two e.g.s is that an incr. in G will definitely ____________ the i rate, but an ...
Chapter 27
... 10. Suppose the government shown in Exhibit 10 uses contractionary monetary policy to reduce inflation from 9 to 6 percent. If people have rational expectations, then a. the economy will remain stuck at point E1. b. the natural rate will permanently increase to 8 percent. c. unemployment will rise t ...
... 10. Suppose the government shown in Exhibit 10 uses contractionary monetary policy to reduce inflation from 9 to 6 percent. If people have rational expectations, then a. the economy will remain stuck at point E1. b. the natural rate will permanently increase to 8 percent. c. unemployment will rise t ...
INTERNATIONAL FINANCE
... C. national income declines D. unemployment rate rises 14. Country B does not put any restrictions on capital account transactions. What is NOT true ...
... C. national income declines D. unemployment rate rises 14. Country B does not put any restrictions on capital account transactions. What is NOT true ...
Project Syndicate, September 2012. Since the integration of
... households are able to borrow. The astute observer may argue that ‘thrifty’ Asians and the ‘profligate’ Americans reflect not so much large differences in the supply of credit from financial markets as asymmetric demands for credit--- the Asians being intrinsically more reluctant to borrow. Yet argu ...
... households are able to borrow. The astute observer may argue that ‘thrifty’ Asians and the ‘profligate’ Americans reflect not so much large differences in the supply of credit from financial markets as asymmetric demands for credit--- the Asians being intrinsically more reluctant to borrow. Yet argu ...