Week 2 guide
... lower amount, prices would lower until they met demand, at the original $600/60,000 equilibrium point. Hence at $700, there would be no shortage. iv. ...
... lower amount, prices would lower until they met demand, at the original $600/60,000 equilibrium point. Hence at $700, there would be no shortage. iv. ...
Chapter 1
... Pricing without market power such as in perfect competition is determined by market supply and demand. Pricing with market power (imperfect competition) requires the individual producer to know much more about the characteristics of demand as well as manage production. The main objective of al ...
... Pricing without market power such as in perfect competition is determined by market supply and demand. Pricing with market power (imperfect competition) requires the individual producer to know much more about the characteristics of demand as well as manage production. The main objective of al ...
Negative Externalities
... Demand curve for firms in the market shifts downward to represent the net price of each unit sold. The net price, or Net Marginal Benefit (NMB), is the Marginal Benefit of consumers less the level of the sales tax (NMB = D - t*). Q*=Social Optimum output Pc*=Optimal Consumer price Ps*=Pc*-t=net prod ...
... Demand curve for firms in the market shifts downward to represent the net price of each unit sold. The net price, or Net Marginal Benefit (NMB), is the Marginal Benefit of consumers less the level of the sales tax (NMB = D - t*). Q*=Social Optimum output Pc*=Optimal Consumer price Ps*=Pc*-t=net prod ...
Class 4 PPT
... A country is isolated from rest of the world and produces steel. The market for steel consists of the buyers and sellers in the country. No one in the country is allowed to import or ...
... A country is isolated from rest of the world and produces steel. The market for steel consists of the buyers and sellers in the country. No one in the country is allowed to import or ...
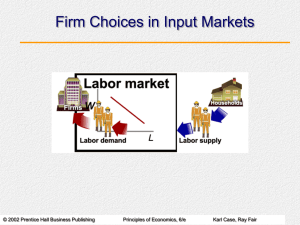
Economics 301 – Revision Checklist Marginal Analysis I can
... Identify the profit maximising position for a perfect competitor Illustrate clearly using the MR, AR, AC and MC curves the profit max position on a graph for a perfect competitor Identify the profit max price and quantity for a perfect competitor on a graph Explain the difference between normal, su ...
... Identify the profit maximising position for a perfect competitor Illustrate clearly using the MR, AR, AC and MC curves the profit max position on a graph for a perfect competitor Identify the profit max price and quantity for a perfect competitor on a graph Explain the difference between normal, su ...
aggregate demand, aggregate supply, and modern macroeconomics
... The slope of the indifference curve is the marginal rate of substitution – the rate at which one good must be added when the other is taken away in order to keep the individual indifferent between the two combinations. Indifference curves are downward sloping and bowed inward. ...
... The slope of the indifference curve is the marginal rate of substitution – the rate at which one good must be added when the other is taken away in order to keep the individual indifferent between the two combinations. Indifference curves are downward sloping and bowed inward. ...
Sample
... 23) During the winter of 1997-1998, the northeastern United States experienced warmer than usual conditions. The price of home heating oil was less than it was during the previous winter, but people bought less home heating oil. This contradicts the Law of Demand. Answer: False. The statement claim ...
... 23) During the winter of 1997-1998, the northeastern United States experienced warmer than usual conditions. The price of home heating oil was less than it was during the previous winter, but people bought less home heating oil. This contradicts the Law of Demand. Answer: False. The statement claim ...
Economics Principles and Applications
... to keep out potential competitors – Maintain excess production capacity as a signal to a potential entrant that they could easily saturate market and leave new entrant with little or no revenue – Make special deals with distributors to receive best shelf space in retail stores – Make long-term arran ...
... to keep out potential competitors – Maintain excess production capacity as a signal to a potential entrant that they could easily saturate market and leave new entrant with little or no revenue – Make special deals with distributors to receive best shelf space in retail stores – Make long-term arran ...
Chapter 4 - Faculty Personal Web Page
... Consumer surplus measures the net benefit to consumers from participating in a market, rather than the total benefit. Consumer surplus in a market is equal to the total benefit received by consumers minus the total amount they must pay to buy the good or service. Similarly, producer surplus measu ...
... Consumer surplus measures the net benefit to consumers from participating in a market, rather than the total benefit. Consumer surplus in a market is equal to the total benefit received by consumers minus the total amount they must pay to buy the good or service. Similarly, producer surplus measu ...
Monopoly
... Pure monopoly is rare. However, a market with several firms, each facing a downward sloping demand curve will produce so that price exceeds marginal cost. Firms often product similar goods that have some differences thereby differentiating themselves from other firms ...
... Pure monopoly is rare. However, a market with several firms, each facing a downward sloping demand curve will produce so that price exceeds marginal cost. Firms often product similar goods that have some differences thereby differentiating themselves from other firms ...
Expenditure minimization
... the same indifference curve to a point which is tangent to the new price vector; the wealth effect shifts consumption out from this point to return wealth to its original value. Note that the “rotation” of the budget frontier through x0 is a consequence of the particular wealth and prices used in th ...
... the same indifference curve to a point which is tangent to the new price vector; the wealth effect shifts consumption out from this point to return wealth to its original value. Note that the “rotation” of the budget frontier through x0 is a consequence of the particular wealth and prices used in th ...
Marketing - cungeheier
... type of inefficiency as monopoly. – Because oligopoly is inefficient, antitrust laws and regulations are used to try to reduce market power and move the outcome closer to that of competition and efficiency. (Bade 416) ...
... type of inefficiency as monopoly. – Because oligopoly is inefficient, antitrust laws and regulations are used to try to reduce market power and move the outcome closer to that of competition and efficiency. (Bade 416) ...
Chapter 4 - Faculty Personal Web Page
... Consumer surplus measures the net benefit to consumers from participating in a market, rather than the total benefit. Consumer surplus in a market is equal to the total benefit received by consumers minus the total amount they must pay to buy the good or service. Similarly, producer surplus measu ...
... Consumer surplus measures the net benefit to consumers from participating in a market, rather than the total benefit. Consumer surplus in a market is equal to the total benefit received by consumers minus the total amount they must pay to buy the good or service. Similarly, producer surplus measu ...
Chapter 14
... Firms in a monopolistically competitive industry are small relative to the total market. New firms can enter the industry in pursuit of profit, and relatively good substitutes for the firms’ products are available. Firms in monopolistically competitive industries try to achieve a degree of market po ...
... Firms in a monopolistically competitive industry are small relative to the total market. New firms can enter the industry in pursuit of profit, and relatively good substitutes for the firms’ products are available. Firms in monopolistically competitive industries try to achieve a degree of market po ...
monopolistic competition
... Firms in a monopolistically competitive industry are small relative to the total market. New firms can enter the industry in pursuit of profit, and relatively good substitutes for the firms’ products are available. Firms in monopolistically competitive industries try to achieve a degree of market po ...
... Firms in a monopolistically competitive industry are small relative to the total market. New firms can enter the industry in pursuit of profit, and relatively good substitutes for the firms’ products are available. Firms in monopolistically competitive industries try to achieve a degree of market po ...
Practice Problem Answers
... differs from a controlled experiment primarily because they occur naturally without design but they produce similar effects. Natural experiments create a situation where by chance two otherwise identical groups may differ, creating the same effect as separating subjects into controlled and treatment ...
... differs from a controlled experiment primarily because they occur naturally without design but they produce similar effects. Natural experiments create a situation where by chance two otherwise identical groups may differ, creating the same effect as separating subjects into controlled and treatment ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑