Review Sheet #1
... the price of the other good rises. - Supply versus quantity supplied - Shifts of the supply curve versus movements along the supply curve -Determinants of supply (input prices, technology, number of sellers, expectations) (Note). Do not confuse determinants of supply with determinant of demand. You ...
... the price of the other good rises. - Supply versus quantity supplied - Shifts of the supply curve versus movements along the supply curve -Determinants of supply (input prices, technology, number of sellers, expectations) (Note). Do not confuse determinants of supply with determinant of demand. You ...
Lecture 5 The Market Equilibrium
... ►Their efforts tend to push price up, enriching suppliers ■ Suppliers compete with each other ► Their efforts tend to push price down, enriching demanders ■ Demanders do NOT compete with suppliers, even thought it sometimes seems that way! ► What about bargaining? Each party tries to convince the ot ...
... ►Their efforts tend to push price up, enriching suppliers ■ Suppliers compete with each other ► Their efforts tend to push price down, enriching demanders ■ Demanders do NOT compete with suppliers, even thought it sometimes seems that way! ► What about bargaining? Each party tries to convince the ot ...
EC 203
... up with coconuts, decides to sell the coconuts that he collects in the local market at the going selling price, ps. In equilibrium, the number of coconuts that will now be produced is a. ...
... up with coconuts, decides to sell the coconuts that he collects in the local market at the going selling price, ps. In equilibrium, the number of coconuts that will now be produced is a. ...
Power Point Notes on Supply Demand Concepts
... usually means more goods/services are purchased, however it could mean less) Change in consumers’ tastes (why don’t people buy neon pink headbands anymore?) Changes in what we expect in the future (e.g. if we think the price will decrease, we’ll wait to buy) Change in population (why was this school ...
... usually means more goods/services are purchased, however it could mean less) Change in consumers’ tastes (why don’t people buy neon pink headbands anymore?) Changes in what we expect in the future (e.g. if we think the price will decrease, we’ll wait to buy) Change in population (why was this school ...
ECO 1101 Test 1 Spring 2004 Dr. Olsh Name_________________
... c. the price of gasoline rises. d. the weather is so pleasant everyone prefers to walk. e. there are lots of other cabs out on the streets. 9. The rules of the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) that limit the amount of money colleges can offer to athletes a. assure balanced competition ...
... c. the price of gasoline rises. d. the weather is so pleasant everyone prefers to walk. e. there are lots of other cabs out on the streets. 9. The rules of the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) that limit the amount of money colleges can offer to athletes a. assure balanced competition ...
U-2 answers
... At equilibrium, buyers do not confront shortages and sellers find enough buyers: both benefit. TOP: Free Market Economy | Choice and Efficiency 5. ANS: D A shift of the demand curve is caused by something other than price changes. A shift to the right is caused by an increase in demand, and colder w ...
... At equilibrium, buyers do not confront shortages and sellers find enough buyers: both benefit. TOP: Free Market Economy | Choice and Efficiency 5. ANS: D A shift of the demand curve is caused by something other than price changes. A shift to the right is caused by an increase in demand, and colder w ...
Group Assignment 4 Due: Monday December 6th before class. 1
... b. Draw the supply and demand for smoking. Illustrate how equilibrium quantity of cigarettes smoked will differ from the socially optimal level. Will it be higher or lower? Be sure to show and label the marginal social and private costs and benefits. Label the socially optimal price and quantity as ...
... b. Draw the supply and demand for smoking. Illustrate how equilibrium quantity of cigarettes smoked will differ from the socially optimal level. Will it be higher or lower? Be sure to show and label the marginal social and private costs and benefits. Label the socially optimal price and quantity as ...
What are Wants and Needs?
... 1. What will be produced? 2. How will it be produced? 3. For whom will it be produced? ...
... 1. What will be produced? 2. How will it be produced? 3. For whom will it be produced? ...
price determination
... “The amount of good or service producers are willing and able to produce at different prices” ...
... “The amount of good or service producers are willing and able to produce at different prices” ...
2.02-Supply-and
... producer is willing and able to produce at different prices. Supply is produced by the businesses in hopes of making money. ...
... producer is willing and able to produce at different prices. Supply is produced by the businesses in hopes of making money. ...
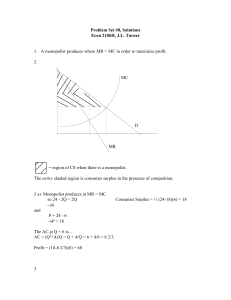
Problem Set #8, Solutions Econ 2106H, J.L. Turner 1. A monopolist
... AC = C/Q = (2+2Q2)/Q = 2Q + 2/Q b-d) The long run equilibrium quantity will be set where MC = AC. 4Q = 2/Q + 2Q 2Q = 2/Q Q2 = 1 Q=1 ( Q= -1 is ruled out on economic grounds...it doesn’t make sense) so each firm will produce one unit. In equilibrium (long run), profits are zero. By definition, the eq ...
... AC = C/Q = (2+2Q2)/Q = 2Q + 2/Q b-d) The long run equilibrium quantity will be set where MC = AC. 4Q = 2/Q + 2Q 2Q = 2/Q Q2 = 1 Q=1 ( Q= -1 is ruled out on economic grounds...it doesn’t make sense) so each firm will produce one unit. In equilibrium (long run), profits are zero. By definition, the eq ...
Supply and Demand
... Some of the more important factors affecting supply are the good's own price, the prices of related goods, production costs, technology and expectations of sellers. Innumerable factors and circumstances could affect a seller's willingness or ability to produce and sell a good. Some of the more commo ...
... Some of the more important factors affecting supply are the good's own price, the prices of related goods, production costs, technology and expectations of sellers. Innumerable factors and circumstances could affect a seller's willingness or ability to produce and sell a good. Some of the more commo ...
Civics Core 100, Goal 8
... service that producers are willing to sell at all possible market prices Opposite of demand The higher the price, the more producers will be willing to make. The lower the price, the fewer items they want to make ...
... service that producers are willing to sell at all possible market prices Opposite of demand The higher the price, the more producers will be willing to make. The lower the price, the fewer items they want to make ...
Supply and demand
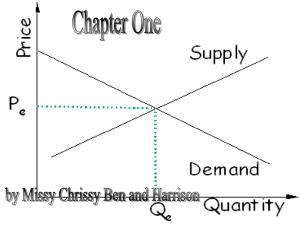
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑