supply - OCPS TeacherPress
... a change in price causes little change in the quantity supplied Supply in the short-term will be inelastic – why? UNITARY ELASTIC % Price Changes = % change in quantity supplied e.g., doubling in price = doubling in quantity supplied ...
... a change in price causes little change in the quantity supplied Supply in the short-term will be inelastic – why? UNITARY ELASTIC % Price Changes = % change in quantity supplied e.g., doubling in price = doubling in quantity supplied ...
1013 P3 Quiz 1
... A) an increase in the supply of pizza B) a rise in the price of hamburgers, a substitute for pizza C) a rise in the price of pizza D) a fall in the price of pizza E) a rise in the price of Coke, a complement of pizza 16) If Hamburger Helper is an inferior good, then, a decrease in income will lead t ...
... A) an increase in the supply of pizza B) a rise in the price of hamburgers, a substitute for pizza C) a rise in the price of pizza D) a fall in the price of pizza E) a rise in the price of Coke, a complement of pizza 16) If Hamburger Helper is an inferior good, then, a decrease in income will lead t ...
EFL Lesson 4
... An increase in the price of a good or service enables producers to cover higher perunit costs and earn profits, causing the quantity supplied to increase, and vice versa. This relationship between price and quantity supplied is normally true as long as other factors influencing costs of production ...
... An increase in the price of a good or service enables producers to cover higher perunit costs and earn profits, causing the quantity supplied to increase, and vice versa. This relationship between price and quantity supplied is normally true as long as other factors influencing costs of production ...
Enlightenment Thinking on Economic Theory Adam Smith
... laissez-faire economics • Believed in a free-market economy, supply and demand would determine prices and other economic decisions. • He also believed that while governments should not interfere in economics, they did have a duty to protect citizens and provide public works for the betterment of soc ...
... laissez-faire economics • Believed in a free-market economy, supply and demand would determine prices and other economic decisions. • He also believed that while governments should not interfere in economics, they did have a duty to protect citizens and provide public works for the betterment of soc ...
1 st runner up
... To Hong Kong, the shirts are treated as imports. It is mentioned that the demand for the sports shirts (no.23) increased rapidly, in another words, producers need to pay more (in terms of foreign currencies) for the imports in order to meet the increasing demand. Hence, the demand for foreign curren ...
... To Hong Kong, the shirts are treated as imports. It is mentioned that the demand for the sports shirts (no.23) increased rapidly, in another words, producers need to pay more (in terms of foreign currencies) for the imports in order to meet the increasing demand. Hence, the demand for foreign curren ...
mock midterm WITH ANSWERS
... 1. b) the increase in the price of fish will shift part of the demand for fish to the chicken market; answer a) is wrong because it presents a change in quantity demanded, not in demand; answer c) relates to supply of chicken, not demand. 2. c) the fall in the price of tomatoes will increase the su ...
... 1. b) the increase in the price of fish will shift part of the demand for fish to the chicken market; answer a) is wrong because it presents a change in quantity demanded, not in demand; answer c) relates to supply of chicken, not demand. 2. c) the fall in the price of tomatoes will increase the su ...
File
... • To limit their costs, Central planners restrict production to a few varieties of each product. • As a result, consumers in the former Communist states of Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union had fewer choices of goods than the consumers in Western Europe and the U.S. • Black Market: a market in wh ...
... • To limit their costs, Central planners restrict production to a few varieties of each product. • As a result, consumers in the former Communist states of Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union had fewer choices of goods than the consumers in Western Europe and the U.S. • Black Market: a market in wh ...
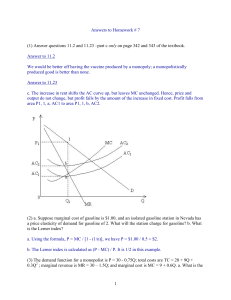
1 Answers to Homework # 7 (1) Answer questions 11.2 and 11.23
... profit-maximizing rate of output? b. What are the profits? c. What would be the price and output under perfect competition if the monopolist's marginal cost curve is the competitive industry's supply curve? d. Calculate the amount of the deadweight loss associated with the monopoly outcome. a. The ...
... profit-maximizing rate of output? b. What are the profits? c. What would be the price and output under perfect competition if the monopolist's marginal cost curve is the competitive industry's supply curve? d. Calculate the amount of the deadweight loss associated with the monopoly outcome. a. The ...
Introduction to Economics – 4 weeks (Chapters 1,2,3
... Quantity demanded is a specific amount an individual is willing and able to buy at a given price. A demand schedule is a table that shows the quantity demanded at each price. When the data are graphed, the result is a demand curve. The law of demand states that as price increases, the quantity d ...
... Quantity demanded is a specific amount an individual is willing and able to buy at a given price. A demand schedule is a table that shows the quantity demanded at each price. When the data are graphed, the result is a demand curve. The law of demand states that as price increases, the quantity d ...
Quantity Demanded
... schedule on to the demand graph. Each plotted point on the graph represents a specific combination of price and quantity demanded. The demand curve slopes downward, right. ...
... schedule on to the demand graph. Each plotted point on the graph represents a specific combination of price and quantity demanded. The demand curve slopes downward, right. ...
File
... Changes in price expectations: • of the future price of a product • difficult to generalize Changes in number of sellers: • as the number of sellers increases, so does supply ...
... Changes in price expectations: • of the future price of a product • difficult to generalize Changes in number of sellers: • as the number of sellers increases, so does supply ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑