Exam 1 Spring 2004
... producers a subsidy of $9 per unit. What price will consumer’s pay and how many hog hats will they buy? (2 points each) How much will the UA spend on the subsidy? (3 points) What will be the change in producer surplus? (5 points.) With the subsidy, the sellers can accept 9 less than on the price so ...
... producers a subsidy of $9 per unit. What price will consumer’s pay and how many hog hats will they buy? (2 points each) How much will the UA spend on the subsidy? (3 points) What will be the change in producer surplus? (5 points.) With the subsidy, the sellers can accept 9 less than on the price so ...
CHAPTER 3 – Demand and Supply
... This chapter introduces one of the major analytical areas of economics, demand and supply, that form the basis for much of theoretical analysis used throughout the text. The concepts of the difference between money price and relative price, the law of demand, income and substitution effects, the dis ...
... This chapter introduces one of the major analytical areas of economics, demand and supply, that form the basis for much of theoretical analysis used throughout the text. The concepts of the difference between money price and relative price, the law of demand, income and substitution effects, the dis ...
Chapter 3 - Jacob Schulman
... money income, enabling the buyer to purchase more of the product than before E. Substitution Effect: suggests that at a lower price buyers have the incentive to substitute what is now a less expensive product for similar ones that are more expensive (it’s a better deal) The Demand Curve: A. Demand C ...
... money income, enabling the buyer to purchase more of the product than before E. Substitution Effect: suggests that at a lower price buyers have the incentive to substitute what is now a less expensive product for similar ones that are more expensive (it’s a better deal) The Demand Curve: A. Demand C ...
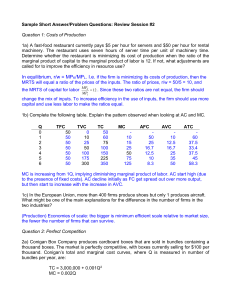
Review Session #2
... 4c) Define a natural monopoly, explaining what the size of the market has to do with whether an industry is a natural monopoly. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge its average cost. Draw a diagram, label the price charged, and the deadweight loss to society relative to m ...
... 4c) Define a natural monopoly, explaining what the size of the market has to do with whether an industry is a natural monopoly. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge its average cost. Draw a diagram, label the price charged, and the deadweight loss to society relative to m ...
File - Mr. P. Ronan
... markets and community welfare 1: Suppose we are given the following demand and supply functions: Qd = 60 – 2P Qs = -20+ 2P (a) Solve for the equilibrium price and quantity. (b) Plot the two curves on a coordinate map. Suppose the government grants a subsidy of $4 per unit. This means that the supply ...
... markets and community welfare 1: Suppose we are given the following demand and supply functions: Qd = 60 – 2P Qs = -20+ 2P (a) Solve for the equilibrium price and quantity. (b) Plot the two curves on a coordinate map. Suppose the government grants a subsidy of $4 per unit. This means that the supply ...
Net Surplus
... Therefore, economists tend to focus on evaluating how much efficiency might we have to give up to get more equality and/or achieve other social goals (This leads to Taxation) ...
... Therefore, economists tend to focus on evaluating how much efficiency might we have to give up to get more equality and/or achieve other social goals (This leads to Taxation) ...
Supply and Demand II
... • Why does stuff cost what it costs? • TR=P*Q • If purchases increase enough (elastic) after a price drop then it’s all Good. • If the price drops by 10% but the demand increases by more than 10% the supplier wins. • Demand is inelastic if there is a price drop but the demand does not increase enoug ...
... • Why does stuff cost what it costs? • TR=P*Q • If purchases increase enough (elastic) after a price drop then it’s all Good. • If the price drops by 10% but the demand increases by more than 10% the supplier wins. • Demand is inelastic if there is a price drop but the demand does not increase enoug ...
Micro quiz 2 - Learn Group
... A) a newly discovered increase in the nutritional value of oranges B) an increase in income for all orange consumers C) an increase in the price of bananas, a substitute in consumption for oranges D) disastrous weather that destroys about half of this yearʹs orange crop 18) Which of the following is ...
... A) a newly discovered increase in the nutritional value of oranges B) an increase in income for all orange consumers C) an increase in the price of bananas, a substitute in consumption for oranges D) disastrous weather that destroys about half of this yearʹs orange crop 18) Which of the following is ...
Equilibrium
... So why are prices so important? • Prices are vital in a free market economy. • They help move land, labor and capital into the hands of producers and finished goods into the hands of buyers. • Price is a language both consumers and producers can use to determine value. ...
... So why are prices so important? • Prices are vital in a free market economy. • They help move land, labor and capital into the hands of producers and finished goods into the hands of buyers. • Price is a language both consumers and producers can use to determine value. ...
Homework 1
... 3. The cross price elasticity of oil with respect to Sport Utility Vehicles is -.1. The governments of the world agree to a tax on SUV’s which raise the price of SUV’s world-wide by 10%. Calculate the size of the shift in the demand curve for oil that results. The short-term price elasticity of dem ...
... 3. The cross price elasticity of oil with respect to Sport Utility Vehicles is -.1. The governments of the world agree to a tax on SUV’s which raise the price of SUV’s world-wide by 10%. Calculate the size of the shift in the demand curve for oil that results. The short-term price elasticity of dem ...
Preview Sample 1
... The transition of China’s economy from centralized planning to a market-oriented economy provides an outstanding backdrop against which the efficiency of the market economy can be compared to that of a command economy. While this analysis is of necessity limited, students should come away with a cle ...
... The transition of China’s economy from centralized planning to a market-oriented economy provides an outstanding backdrop against which the efficiency of the market economy can be compared to that of a command economy. While this analysis is of necessity limited, students should come away with a cle ...
SEM_I-301
... Government tries to reduce the differences between the rich and poor. Based on the welfare of people. Examples: ___________________ ...
... Government tries to reduce the differences between the rich and poor. Based on the welfare of people. Examples: ___________________ ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑