Welfare Economics and the Gains from Trade
... – The value of an object is determined by the amount of labor needed to produce it – Determine value not by cost of inputs but by consumer willingness to pay for good ...
... – The value of an object is determined by the amount of labor needed to produce it – Determine value not by cost of inputs but by consumer willingness to pay for good ...
Setting Prices
... Demand is the amount consumers are willing to buy at all prices. Consumers control the demand-side of our economy. Must have want, willingness, & resources! The Law of Demand says as prices increase, the quantity demanded decreases. This principle is illustrated by an auction. The price increases un ...
... Demand is the amount consumers are willing to buy at all prices. Consumers control the demand-side of our economy. Must have want, willingness, & resources! The Law of Demand says as prices increase, the quantity demanded decreases. This principle is illustrated by an auction. The price increases un ...
Principles of Microeconomics Test 1 Dr. Hossain Note: This is short
... Example: Government should pass pay roll tax to stimulate the economy and reduce unemployment rate. b. What is the difference between change in demand and change in quantity demanded? Explain using appropriately labeled graphs. Change in demand is increase or decrease in demand usually expressed as ...
... Example: Government should pass pay roll tax to stimulate the economy and reduce unemployment rate. b. What is the difference between change in demand and change in quantity demanded? Explain using appropriately labeled graphs. Change in demand is increase or decrease in demand usually expressed as ...
ECON 2010-100 Principles of Microeconomics
... Course description: Microeconomics is about what goods get produced and sold at what prices. The individual must decide what goods to buy, how much to save and how hard to work. The firm must decide how much to produce and with what technology. The course explores how "the magic of the market" coord ...
... Course description: Microeconomics is about what goods get produced and sold at what prices. The individual must decide what goods to buy, how much to save and how hard to work. The firm must decide how much to produce and with what technology. The course explores how "the magic of the market" coord ...
Chapter 14
... Buyers and sellers have absolutely no effect on price Three characteristics: Absence of transaction costs Product homogeneity: products are identical in the eyes of their purchasers Presence of a large number of sellers, each accounts for a small fraction of market supply ...
... Buyers and sellers have absolutely no effect on price Three characteristics: Absence of transaction costs Product homogeneity: products are identical in the eyes of their purchasers Presence of a large number of sellers, each accounts for a small fraction of market supply ...
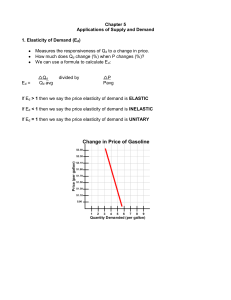
Elasticity of Demand (Ed)
... easier to increase the production of CD’s compared to that of automobiles. 6. Government Intervention in The Markets For the most part, the governments of modern industrialized countries allow markets to operate relatively freely. There are times, however, when the government feels it is necessary t ...
... easier to increase the production of CD’s compared to that of automobiles. 6. Government Intervention in The Markets For the most part, the governments of modern industrialized countries allow markets to operate relatively freely. There are times, however, when the government feels it is necessary t ...
Section 4-1: System of linear equations in two variables Solving a
... d. Graph the two equations in the same coordinate system and identify the equilibrium point, supply curve, and ...
... d. Graph the two equations in the same coordinate system and identify the equilibrium point, supply curve, and ...
Profit Maximization and the Decision to Supply
... the equilibrium price and quantity and the price that buyers will pay and sellers receive • As with producer surplus, sellers are price takers and the price they receive is their MR. The marginal revenue and the price remain the same no matter how much output is sold. ...
... the equilibrium price and quantity and the price that buyers will pay and sellers receive • As with producer surplus, sellers are price takers and the price they receive is their MR. The marginal revenue and the price remain the same no matter how much output is sold. ...
Microeconomics II Due: June 14, 2013 (16:00) HOMEWORK Mr
... a. What is the total cost of the fertilizer needed to produce 100 cabbages? b. What is the total cost of the amount of fertilizer needed to produce y cabbages? c. If the only way that Mr. McGregor can vary his output is by varying the amount of fertilizer applied to his cabbage patch, write an expre ...
... a. What is the total cost of the fertilizer needed to produce 100 cabbages? b. What is the total cost of the amount of fertilizer needed to produce y cabbages? c. If the only way that Mr. McGregor can vary his output is by varying the amount of fertilizer applied to his cabbage patch, write an expre ...
Inelastic Supply
... Make a mental note to connect the words quantity and price. A change in price creates a change in the quantity supplied. This is movement along the supply curve, it is a positive slope curve and reflects a direct relationship. When the price goes up the quantity supplied goes up as well. A change in ...
... Make a mental note to connect the words quantity and price. A change in price creates a change in the quantity supplied. This is movement along the supply curve, it is a positive slope curve and reflects a direct relationship. When the price goes up the quantity supplied goes up as well. A change in ...
P 1
... Prices quite flexible in unfettered markets can be less flexible in other market scenarios. May ...
... Prices quite flexible in unfettered markets can be less flexible in other market scenarios. May ...
3.02 Supply and Demand
... A. Explain supply and demand. 1. Supply: The amount of goods producers are willing and able to produce and sell at a given price during a certain period of time. Producers prefer to supply when the price is high; this is known as a sellers’ market. For example, when a popular music artist releases a ...
... A. Explain supply and demand. 1. Supply: The amount of goods producers are willing and able to produce and sell at a given price during a certain period of time. Producers prefer to supply when the price is high; this is known as a sellers’ market. For example, when a popular music artist releases a ...
Price of related goods
... economy is utilizing all of its resources efficiently, and getting the most output for the least input. Allocative efficiency is a type of efficiency in which the economy/producers produce only that type of good which are more desirable in society. The point of allocative efficiency is where price ...
... economy is utilizing all of its resources efficiently, and getting the most output for the least input. Allocative efficiency is a type of efficiency in which the economy/producers produce only that type of good which are more desirable in society. The point of allocative efficiency is where price ...
Price - Grosse Pointe Public School System
... Whether a person considers a good Demand sometimes becomes more elastic over time because people to be a necessity or a luxury has a can eventually find substitutes. great impact on the good’s elasticity of demand for that person. ...
... Whether a person considers a good Demand sometimes becomes more elastic over time because people to be a necessity or a luxury has a can eventually find substitutes. great impact on the good’s elasticity of demand for that person. ...
1 Problem Set 1 Answer Key 1) a) False. Even if a PPF was linear
... rather about increasing opportunity costs; which is because producing more and more of one particular good would require giving up on more and more of the other good. For instance, in an economy that produces tanks and butter only, as the economy specializes more in the production of tanks, it would ...
... rather about increasing opportunity costs; which is because producing more and more of one particular good would require giving up on more and more of the other good. For instance, in an economy that produces tanks and butter only, as the economy specializes more in the production of tanks, it would ...
Economics: Chapter 4.1: Nature of Supply
... Supply is the amount of goods that producers are willing to offer at various prices during given time period. Quantity supplied is the same except at a particular price. Law of Supply Price is key factor. Law of supply states, “producers supply more product when prices are high and less when its low ...
... Supply is the amount of goods that producers are willing to offer at various prices during given time period. Quantity supplied is the same except at a particular price. Law of Supply Price is key factor. Law of supply states, “producers supply more product when prices are high and less when its low ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑