Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones
... demand to analyze competitive markets. • In a competitive market, there are many buyers and sellers, each of whom has little or no influence on the market price. ...
... demand to analyze competitive markets. • In a competitive market, there are many buyers and sellers, each of whom has little or no influence on the market price. ...
document
... price of another related product, other factors remaining constant. If the two products are good substitutes, the value of cross elasticity will be positive. If the two products are good complementary, the value of cross elasticity will be negative. ...
... price of another related product, other factors remaining constant. If the two products are good substitutes, the value of cross elasticity will be positive. If the two products are good complementary, the value of cross elasticity will be negative. ...
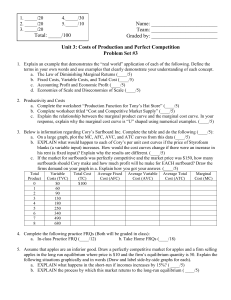
AP Micro Problem Set 3 Production Costs and Perfect Competition
... c. Explain the relationship between the marginal product curve and the marginal cost curve. In your response, explain why the marginal cost curve is “U” shaped using numerical examples. (____/5) 3. Below is information regarding Cory’s Surfboard Inc. Complete the table and do the following (____/5): ...
... c. Explain the relationship between the marginal product curve and the marginal cost curve. In your response, explain why the marginal cost curve is “U” shaped using numerical examples. (____/5) 3. Below is information regarding Cory’s Surfboard Inc. Complete the table and do the following (____/5): ...
1 - Kuwait University - College of Business Administration
... c. Individual buyers in a competitive market have the power to influence price, and thus can impose prices and other conditions on powerless sellers. d. There are many small sellers, and so the market process generates an equilibrium price that cannot be influenced by any one seller. Thus they have ...
... c. Individual buyers in a competitive market have the power to influence price, and thus can impose prices and other conditions on powerless sellers. d. There are many small sellers, and so the market process generates an equilibrium price that cannot be influenced by any one seller. Thus they have ...
Chapter 14 - Firms in competitive markets
... – Quantity – increases • Because there are more firms in the market ...
... – Quantity – increases • Because there are more firms in the market ...
Chapter 4 - The market forces of supply and demand
... • Prices of related goods – Substitutes - two goods • An increase in the price of one • Leads to an increase in the demand for the other ...
... • Prices of related goods – Substitutes - two goods • An increase in the price of one • Leads to an increase in the demand for the other ...
lecture six - Webster in china
... Number of firms is small Products are same or different High barriers to entry Interdependence of firms example: ...
... Number of firms is small Products are same or different High barriers to entry Interdependence of firms example: ...
Elastic
... Income increases 20%, and quantity decreases 15% then the good is a… INFERIOR GOOD • If coefficient is positive (shows direct relationship) then the good is normal • If coefficient is negative (shows inverse relationship) then the good is inferior Ex: If income falls 10% and quantity falls 20%… Copy ...
... Income increases 20%, and quantity decreases 15% then the good is a… INFERIOR GOOD • If coefficient is positive (shows direct relationship) then the good is normal • If coefficient is negative (shows inverse relationship) then the good is inferior Ex: If income falls 10% and quantity falls 20%… Copy ...
Chapter 17
... regulate them to deal with the negative consequences May create a monopoly to ensure that goods are produced at least cost A market is a natural monopoly when a good is produced most economically through a single firm Average cost falls as quantity increases Second firm may enter but this wo ...
... regulate them to deal with the negative consequences May create a monopoly to ensure that goods are produced at least cost A market is a natural monopoly when a good is produced most economically through a single firm Average cost falls as quantity increases Second firm may enter but this wo ...
Econ 310 Practice Questions
... D) Unable to determine without knowing input costs. 2. In the production possibilities frontier in Figure 1-1, the opportunity cost of producing 10 more computers and moving from point B to point A is A) 15 apples. B) 10 apples. C) 5 apples. D) The economy cannot move to point A. 3. "If, at the init ...
... D) Unable to determine without knowing input costs. 2. In the production possibilities frontier in Figure 1-1, the opportunity cost of producing 10 more computers and moving from point B to point A is A) 15 apples. B) 10 apples. C) 5 apples. D) The economy cannot move to point A. 3. "If, at the init ...
CH7 Consumer Choice The Marginal Principle and Individual
... Marginal utility: change in utility resulting from buying one additional unit Law of diminishing marginal utility: as consumption increases, utility decreases, even negatively if too far The Marginal Benefit Curve Decreases with each increase in unit, negatively sloped The Marginal Cost Curve ...
... Marginal utility: change in utility resulting from buying one additional unit Law of diminishing marginal utility: as consumption increases, utility decreases, even negatively if too far The Marginal Benefit Curve Decreases with each increase in unit, negatively sloped The Marginal Cost Curve ...
Chapter 6 Prices_Brown
... equals Demand1 with a market price of $18 and output of Q1. • The bad weather arrives: the supply of wine falls, decreasing the supply from supply1 to supply2. What happens to the equilibrium price and output level? • At $18 a bottle the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. There is upwa ...
... equals Demand1 with a market price of $18 and output of Q1. • The bad weather arrives: the supply of wine falls, decreasing the supply from supply1 to supply2. What happens to the equilibrium price and output level? • At $18 a bottle the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. There is upwa ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑