Homework 2
... 1. N bidders have IID private valuations vi ∼ F for the right to harvest a forest. In stage 1 this right is sold via an English auction. After the auction, in stage 2, there is then a resale market. M different bidders with IID private valuations ui (with the same distribution as vi ) are interested ...
... 1. N bidders have IID private valuations vi ∼ F for the right to harvest a forest. In stage 1 this right is sold via an English auction. After the auction, in stage 2, there is then a resale market. M different bidders with IID private valuations ui (with the same distribution as vi ) are interested ...
ECO 232 Microeconomics
... Economics is defined as the study of: how society manages its scarce resources. What you give up to obtain an item is called your: opportunity cost. The amount of goods and services produced from each hour of a worker’s time is called: productivity. Chapter 2 In economics, capital refers to: buildin ...
... Economics is defined as the study of: how society manages its scarce resources. What you give up to obtain an item is called your: opportunity cost. The amount of goods and services produced from each hour of a worker’s time is called: productivity. Chapter 2 In economics, capital refers to: buildin ...
1 - Сумський державний університет
... income increases from $3,000 to $4,000. Show what happens if both wine and cheese are normal goods. Now show what happens if cheese belongs to inferior goods. 6. The price of cheese rises from $6 to $10 for a pound, while the price of wine remains $3 for a glass. Show what happens to consumption of ...
... income increases from $3,000 to $4,000. Show what happens if both wine and cheese are normal goods. Now show what happens if cheese belongs to inferior goods. 6. The price of cheese rises from $6 to $10 for a pound, while the price of wine remains $3 for a glass. Show what happens to consumption of ...
Economics “Ask the Instructor” Clip 59 Transcript
... In the case of demand-pull inflation, the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right. This could be triggered by a number of events, including a drop in the international value of the dollar, an increase in government spending, a tax cut, or an increase in consumer or business optimism that leads to ...
... In the case of demand-pull inflation, the aggregate demand curve shifts to the right. This could be triggered by a number of events, including a drop in the international value of the dollar, an increase in government spending, a tax cut, or an increase in consumer or business optimism that leads to ...
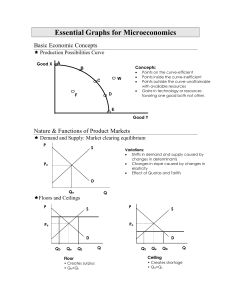
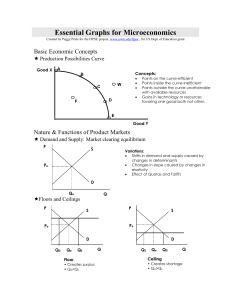
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rate. Theory: It will be profitable for a firm to hire additional units of a resource up to the point at which that resource’s MRP is equal to its MRC. Essential G ...
... MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rate. Theory: It will be profitable for a firm to hire additional units of a resource up to the point at which that resource’s MRP is equal to its MRC. Essential G ...
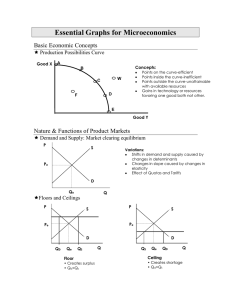
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics - pm
... MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rate. Theory: It will be profitable for a firm to hire additional units of a resource up to the point at which that resource’s MRP is equal to its MRC. Essential G ...
... MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rate. Theory: It will be profitable for a firm to hire additional units of a resource up to the point at which that resource’s MRP is equal to its MRC. Essential G ...
Price
... increasing-cost industry in the long run Long run: the production period during which all resources required to make a product can be varied, and business may either enter or leave the industry Constant-cost industry: an industry that is not a major user of any single resource Increasing-cost ...
... increasing-cost industry in the long run Long run: the production period during which all resources required to make a product can be varied, and business may either enter or leave the industry Constant-cost industry: an industry that is not a major user of any single resource Increasing-cost ...
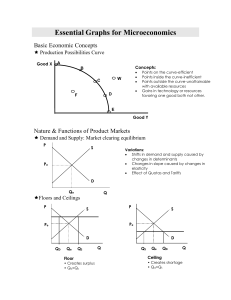
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rate. Theory: It will be profitable for a firm to hire additional units of a resource up to the point at which that resource’s MRP is equal to its MRC. Essential G ...
... MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employment of each additional unit of a resource; so for labor, the MRC is the wage rate. Theory: It will be profitable for a firm to hire additional units of a resource up to the point at which that resource’s MRP is equal to its MRC. Essential G ...
Augusta State University | Hull College of Business | Spring 2011
... 12) Consider the market for peanut butter. If there is a decrease in the price of deli turkey slices (a substitute in consumption for peanut butter) along with a decrease in the price of peanut brittle (a substitute in production for peanut butter), the A) equilibrium quantity of peanut definitely ...
... 12) Consider the market for peanut butter. If there is a decrease in the price of deli turkey slices (a substitute in consumption for peanut butter) along with a decrease in the price of peanut brittle (a substitute in production for peanut butter), the A) equilibrium quantity of peanut definitely ...
evansberman_chapter_20
... The Role of Price in Balancing Supply and Demand (2) • At equilibrium (PE QE), the quantity demanded equals the supply. • At price P1, consumers demand Q1 of an item. However, at this prices, suppliers will make available only Q2. There is a shortage of supply of Q1—Q2. The price is bid up as consu ...
... The Role of Price in Balancing Supply and Demand (2) • At equilibrium (PE QE), the quantity demanded equals the supply. • At price P1, consumers demand Q1 of an item. However, at this prices, suppliers will make available only Q2. There is a shortage of supply of Q1—Q2. The price is bid up as consu ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑