Econ160SQ2(Elasticity, PPF, Comparative Advantage)
... 3. Set up the problem as follows: e = (Q/Q1) / (P/P1) = (200,000/ 1,000,000)/(P/P1)=1 = (0.20)/(P/P1) = 1. This tells us that (P/P1 ) must be equal to 0.20 also. That is, the price must be increased by 20%. Since the original price of cigarettes was $4, the new price would have to be $4.80. (No ...
... 3. Set up the problem as follows: e = (Q/Q1) / (P/P1) = (200,000/ 1,000,000)/(P/P1)=1 = (0.20)/(P/P1) = 1. This tells us that (P/P1 ) must be equal to 0.20 also. That is, the price must be increased by 20%. Since the original price of cigarettes was $4, the new price would have to be $4.80. (No ...
demand in product/output markets
... It is reasonable to expect quantity demanded to fall when price rises, ceteris paribus, and to expect quantity demanded to rise when price falls, ceteris paribus. Demand curves have a negative slope. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair ...
... It is reasonable to expect quantity demanded to fall when price rises, ceteris paribus, and to expect quantity demanded to rise when price falls, ceteris paribus. Demand curves have a negative slope. © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing Principles of Economics 8e by Case and Fair ...
Supply and Demand
... Demand is the amount of a product that people are willing and able to purchase at each possible price during a given period of time. ...
... Demand is the amount of a product that people are willing and able to purchase at each possible price during a given period of time. ...
p($) - City University of Hong Kong
... equilibrium. a. Hi-Tech Printing Company employs an extra-ordinary manager that sharply reduces the cost of administrative costs (i.e. fixed cost in the short run). What happens to Hi-Tech’s profits and the price of books in short run? Will it attract new firms to enter the market in long run? b. Su ...
... equilibrium. a. Hi-Tech Printing Company employs an extra-ordinary manager that sharply reduces the cost of administrative costs (i.e. fixed cost in the short run). What happens to Hi-Tech’s profits and the price of books in short run? Will it attract new firms to enter the market in long run? b. Su ...
(JW)edited - UK Master Papers
... purchasing and supply, 2014). Additionally, technology has an effect on the pricing, especially when the costs are low and the production is high. In the current century, technological advancement is embraced in all sectors so that the marginal costs of production are reduced. Consequently, the valu ...
... purchasing and supply, 2014). Additionally, technology has an effect on the pricing, especially when the costs are low and the production is high. In the current century, technological advancement is embraced in all sectors so that the marginal costs of production are reduced. Consequently, the valu ...
MEASURING PRODUCTION AND INCOME, Chapter 2
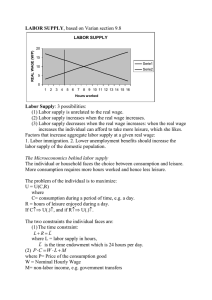
... Labor Supply: 3 possibilities: (1) Labor supply is unrelated to the real wage. (2) Labor supply increases when the real wage increases. (3) Labor supply decreases when the real wage increases: when the real wage increases the individual can afford to take more leisure, which she likes. Factors that ...
... Labor Supply: 3 possibilities: (1) Labor supply is unrelated to the real wage. (2) Labor supply increases when the real wage increases. (3) Labor supply decreases when the real wage increases: when the real wage increases the individual can afford to take more leisure, which she likes. Factors that ...
Tax Incidence
... We call 50 + 50 ∗ 0.08 = 54 as the market price. This is different from what we see in the market. In stores, they only mark the price as ”what they receive”, but when you actually purchase the good, you are paying the marked price plus the tax. In our example, consumers are paying 54, while produce ...
... We call 50 + 50 ∗ 0.08 = 54 as the market price. This is different from what we see in the market. In stores, they only mark the price as ”what they receive”, but when you actually purchase the good, you are paying the marked price plus the tax. In our example, consumers are paying 54, while produce ...
Revenue management - owen.vanderbilt.edu
... Capacity constraints on merging lots attenuate price effects by more than constraints on nonmerging lots amplify them ...
... Capacity constraints on merging lots attenuate price effects by more than constraints on nonmerging lots amplify them ...
Chapter 3 Market Demand, Supply, and Elasticity
... B) The Supply Curve, illustrated above, shows the quantities of a good supplied at different prices. The positive slope of the supply curve indicates that higher prices result in an increase in the quantity supplied. C) Along a particular supply curve all factors that affect the supply, other than t ...
... B) The Supply Curve, illustrated above, shows the quantities of a good supplied at different prices. The positive slope of the supply curve indicates that higher prices result in an increase in the quantity supplied. C) Along a particular supply curve all factors that affect the supply, other than t ...
Ch#
... Goods that are produced as alternatives to each other The effect on quantity demanded caused by people switching to or from a product as its price changes The various quantities of a good or service that sellers are willing and able to offer for sale (place on the market) at various prices during a ...
... Goods that are produced as alternatives to each other The effect on quantity demanded caused by people switching to or from a product as its price changes The various quantities of a good or service that sellers are willing and able to offer for sale (place on the market) at various prices during a ...
Market Price Under Perfect Competition
... Costas Megalodrachmas is the owner of the monopoly operation. In a recent statement he said; “people in the Midwest are very price-conscious and our managers there know what to charge”. A. Are the demand curves in the two regions mentioned the same? If so why, If not how do they differ? B. CM also s ...
... Costas Megalodrachmas is the owner of the monopoly operation. In a recent statement he said; “people in the Midwest are very price-conscious and our managers there know what to charge”. A. Are the demand curves in the two regions mentioned the same? If so why, If not how do they differ? B. CM also s ...
Midterm Two from the Morning Lecture
... 13) If the total cost curve is upward sloping over some range of output with an increasing slope, then this fact must reflect: a. Decreasing average variable cost b. Increasing fixed costs. c. Increasing variable costs. d. both (a) and (b). e. both (b) and (c). ...
... 13) If the total cost curve is upward sloping over some range of output with an increasing slope, then this fact must reflect: a. Decreasing average variable cost b. Increasing fixed costs. c. Increasing variable costs. d. both (a) and (b). e. both (b) and (c). ...
Homework 2
... 1. N bidders have IID private valuations vi ∼ F for the right to harvest a forest. In stage 1 this right is sold via an English auction. After the auction, in stage 2, there is then a resale market. M different bidders with IID private valuations ui (with the same distribution as vi ) are interested ...
... 1. N bidders have IID private valuations vi ∼ F for the right to harvest a forest. In stage 1 this right is sold via an English auction. After the auction, in stage 2, there is then a resale market. M different bidders with IID private valuations ui (with the same distribution as vi ) are interested ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑