DRAFT REPORT OF - Department of Consumer Affairs
... agencies (PSUs/Cooperatives) at subsidized rates by State Governments, at the rate of Rs 10 per kg, since 2008-09. Currently, this scheme is being implemented under which five designated agencies (viz., MMTC Ltd., STC Ltd., PEC Ltd., NAFED and NCCF), import pulses and supply to the States/UTs for di ...
... agencies (PSUs/Cooperatives) at subsidized rates by State Governments, at the rate of Rs 10 per kg, since 2008-09. Currently, this scheme is being implemented under which five designated agencies (viz., MMTC Ltd., STC Ltd., PEC Ltd., NAFED and NCCF), import pulses and supply to the States/UTs for di ...
File
... Long-Run Equilibrium in a Perfectly Competitive Market Long-run competitive equilibrium The situation in which the entry and exit of firms has resulted in the typical firm ...
... Long-Run Equilibrium in a Perfectly Competitive Market Long-run competitive equilibrium The situation in which the entry and exit of firms has resulted in the typical firm ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,9e
... © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall ...
... © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall ...
Chapter 25 - The Citadel
... • Definition of a Monopolist • Barriers to Entry • The Demand Curve a Monopolist Faces • Elasticity and Monopoly • Cost and Monopoly Profit Maximization ...
... • Definition of a Monopolist • Barriers to Entry • The Demand Curve a Monopolist Faces • Elasticity and Monopoly • Cost and Monopoly Profit Maximization ...
Review for lecture midterm 2.ef
... a) a falling interest rate that can be expected as one's investment in a single asset increases. b) a reduction in profits caused by increasing output beyond the optimal point. c) a decrease in total output due to overcrowding, when too much labor is used with too little land or capital. d) a decrea ...
... a) a falling interest rate that can be expected as one's investment in a single asset increases. b) a reduction in profits caused by increasing output beyond the optimal point. c) a decrease in total output due to overcrowding, when too much labor is used with too little land or capital. d) a decrea ...
ExamView - CH 11 short answer study questions.tst
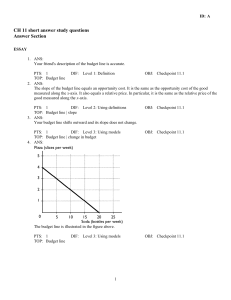
... a. The budget line is in the figure above and is the budget line labeled BL1. b. The slope of the budget line is 20 key chains divided by 5 T-shirts, which equals 4 key chains per T-shirt. 4 key chains per T-shirt is an opportunity cost because it represents the quantity of key chains that must be g ...
... a. The budget line is in the figure above and is the budget line labeled BL1. b. The slope of the budget line is 20 key chains divided by 5 T-shirts, which equals 4 key chains per T-shirt. 4 key chains per T-shirt is an opportunity cost because it represents the quantity of key chains that must be g ...
MARKET EQUILIBRIUM UNDER THE CIRCUMSTANCES OF
... We shall extend an analysis of the typical market model to show the existence of market equilibrium of an extended model in which the choice of location means the choice of the prices of goods dependent on locations. There has been made a lot of works on the general equilibrium model so far. Among t ...
... We shall extend an analysis of the typical market model to show the existence of market equilibrium of an extended model in which the choice of location means the choice of the prices of goods dependent on locations. There has been made a lot of works on the general equilibrium model so far. Among t ...
CHAPTER 14|Monopoly and Antitrust Policy
... A monopoly requires that barriers to entry into the market must be so high that no other firms can enter. There are four reasons entry barriers may be high enough to keep out competing firms: 1. Government can block the entry of more than one firm into a market by granting a patent or copyright or b ...
... A monopoly requires that barriers to entry into the market must be so high that no other firms can enter. There are four reasons entry barriers may be high enough to keep out competing firms: 1. Government can block the entry of more than one firm into a market by granting a patent or copyright or b ...
Public Goods, Regulation, and Public Information
... offer consumers an efficient variety of goods and services, which are produced at least cost, and in efficient quantities. o Efficiency is the market’s great success, and is the reason market economies have been able to improve living standards over time. o However, there are also instances of marke ...
... offer consumers an efficient variety of goods and services, which are produced at least cost, and in efficient quantities. o Efficiency is the market’s great success, and is the reason market economies have been able to improve living standards over time. o However, there are also instances of marke ...
Recovering Markups from Production Data
... production data by not having to assume any particular form of consumer demand and any specific model of price setting, while directly addressing the econometric concerns of identifying production function coefficients. The approach relies on cost minimization and there being (at least) one variable i ...
... production data by not having to assume any particular form of consumer demand and any specific model of price setting, while directly addressing the econometric concerns of identifying production function coefficients. The approach relies on cost minimization and there being (at least) one variable i ...
Name Block ______ Date ______ Utility and consumer decision
... 3. Read Krugman Ch 10. 269-277, 279-285 Work problems 1, 2, 5, 6, 12, 14. Check solutions online. What meaning / relevance do the following terms have for examining consumer behavior? (I will check these, but use this as a guide to think through the chapter.) Consumption bundle Marginal utility per ...
... 3. Read Krugman Ch 10. 269-277, 279-285 Work problems 1, 2, 5, 6, 12, 14. Check solutions online. What meaning / relevance do the following terms have for examining consumer behavior? (I will check these, but use this as a guide to think through the chapter.) Consumption bundle Marginal utility per ...
General Equilibrium and the Efficiency of Perfect Competition
... • Partial equilibrium analysis is the process of examining the equilibrium conditions in individual markets and for households and firms separately. • General equilibrium is the condition that exists when all markets in an economy are in simultaneous equilibrium. ...
... • Partial equilibrium analysis is the process of examining the equilibrium conditions in individual markets and for households and firms separately. • General equilibrium is the condition that exists when all markets in an economy are in simultaneous equilibrium. ...
PDF
... hence, market power at both levels, by introducing “conduct parameters” into the retail and supplier models (Draganska and Klapper, 2007; Richards, Hamilton and Patterson, 2009; Richards and Hamilton, 2006). Unlike models of conjectural variations, the conduct parameters in this model are atheoretic ...
... hence, market power at both levels, by introducing “conduct parameters” into the retail and supplier models (Draganska and Klapper, 2007; Richards, Hamilton and Patterson, 2009; Richards and Hamilton, 2006). Unlike models of conjectural variations, the conduct parameters in this model are atheoretic ...
Prices - Joshua Goldstein
... period from 1531 and 1658, respectively, through the end of preindustrial time s (1785, 1769) . Neither series fits the long wave datings very well, although both series weakly correlate with the long wave . 8 Prices for Prussian rye on the Amster dam produce exchange cover roughly the same period . ...
... period from 1531 and 1658, respectively, through the end of preindustrial time s (1785, 1769) . Neither series fits the long wave datings very well, although both series weakly correlate with the long wave . 8 Prices for Prussian rye on the Amster dam produce exchange cover roughly the same period . ...
PDF
... Granger Causal relationship between weekly grid premiums and discounts (Pi) and proportional slaughter volume reflecting those carcass attributes (Qi). We propose the following interpretation for the possible Granger Causality outcomes between Pi and Qi within a time series context for scenarios a t ...
... Granger Causal relationship between weekly grid premiums and discounts (Pi) and proportional slaughter volume reflecting those carcass attributes (Qi). We propose the following interpretation for the possible Granger Causality outcomes between Pi and Qi within a time series context for scenarios a t ...
11PERFECT COMPETITION
... 56) For a firm in perfect competition, a diagram shows quantity on the horizontal axis and both the firm’s marginal cost (MC) and its marginal revenue (MR) on the vertical axis. The firm’s profit-maximizing quantity occurs at the point where the A) slope of the MC curve is zero. B) MC and MR curves ...
... 56) For a firm in perfect competition, a diagram shows quantity on the horizontal axis and both the firm’s marginal cost (MC) and its marginal revenue (MR) on the vertical axis. The firm’s profit-maximizing quantity occurs at the point where the A) slope of the MC curve is zero. B) MC and MR curves ...
An Example
... demand for alcohol tends to be rather price inelastic. Elasticity of demand measures the degree of responsiveness of the quantity demanded when there is a change in price. If the proportionate change in quantity demanded is less than the change in price of a good it is said to have inelastic demand. ...
... demand for alcohol tends to be rather price inelastic. Elasticity of demand measures the degree of responsiveness of the quantity demanded when there is a change in price. If the proportionate change in quantity demanded is less than the change in price of a good it is said to have inelastic demand. ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑