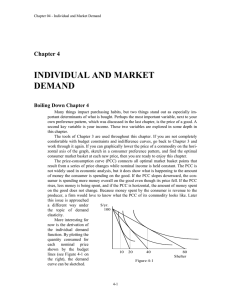
Chapter 4
... fraction of the cost of providing the services. If a nation were to cut its subsidies and thus increase the price of medical care for consumers, how would the higher price affect its poor and wealthy households? • In Côte d’Ivoire in Africa, the price elasticity of demand for hospital services is 0. ...
... fraction of the cost of providing the services. If a nation were to cut its subsidies and thus increase the price of medical care for consumers, how would the higher price affect its poor and wealthy households? • In Côte d’Ivoire in Africa, the price elasticity of demand for hospital services is 0. ...
06.Elasticity of demand – price, income and cross elasticities
... is inelastic or less elastic than that for comforts and luxuries. The reason is simple. The necessities must be bought whatever be the price because no one can live without them. The demand for a necessity without a substitute is less elastic than the demand for a necessity with a substitute. For ex ...
... is inelastic or less elastic than that for comforts and luxuries. The reason is simple. The necessities must be bought whatever be the price because no one can live without them. The demand for a necessity without a substitute is less elastic than the demand for a necessity with a substitute. For ex ...
producer surplus
... A situation in which people do the best they can, given their limited resources. ...
... A situation in which people do the best they can, given their limited resources. ...
Unit 4 – The Price System - Virginia Council on Economic Education
... of prices for some desirable item with some prices higher and some prices lower than the usual market price for the item. (e.g. possible prices for a candy bar: $1.75, $1.50, $1.25, 1.00, .75, .50, .25). The handout will say “For each price, how many candy bars will you buy today (cash only) if this ...
... of prices for some desirable item with some prices higher and some prices lower than the usual market price for the item. (e.g. possible prices for a candy bar: $1.75, $1.50, $1.25, 1.00, .75, .50, .25). The handout will say “For each price, how many candy bars will you buy today (cash only) if this ...
(a) Firm
... exit, firms that remain must be making zero economic profit. The process of entry & exit ends only when price and average total cost are driven to equality. Long-run equilibrium must have firms operating at their efficient scale. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcour ...
... exit, firms that remain must be making zero economic profit. The process of entry & exit ends only when price and average total cost are driven to equality. Long-run equilibrium must have firms operating at their efficient scale. Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright © 2001 by Harcour ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,9e
... Demand in Product/Output Markets Changes in Quantity Demanded versus Changes in Demand Price and Quantity Demanded: The Law of Demand Other Determinants of Household Demand Shift of Demand versus Movement Along the Demand Curve From Household Demand to Market Demand Supply in Product/Output Markets ...
... Demand in Product/Output Markets Changes in Quantity Demanded versus Changes in Demand Price and Quantity Demanded: The Law of Demand Other Determinants of Household Demand Shift of Demand versus Movement Along the Demand Curve From Household Demand to Market Demand Supply in Product/Output Markets ...
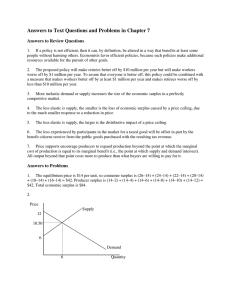
Answers to Text Questions and Problems in
... pays $45 in compensation payments to the three volunteers, which causes him a loss in economic surplus of $45 that is exactly offset by the gain in economic surplus to the three volunteers. Total economic surplus from the tour operation is now $107—$28 higher than before. c. The compensation policy ...
... pays $45 in compensation payments to the three volunteers, which causes him a loss in economic surplus of $45 that is exactly offset by the gain in economic surplus to the three volunteers. Total economic surplus from the tour operation is now $107—$28 higher than before. c. The compensation policy ...
Solution sketches, Test 1
... If the correct answer does not match with one of the five answers on a multiple-choice question, pick the answer closest to the correct answer. Unless otherwise specified, you can assume the following: Supply curves have positive slope and demand curves have negative slope. Negative quantities c ...
... If the correct answer does not match with one of the five answers on a multiple-choice question, pick the answer closest to the correct answer. Unless otherwise specified, you can assume the following: Supply curves have positive slope and demand curves have negative slope. Negative quantities c ...
25 Monopolistic Competition
... into account the reactions of rivals, and each firm has (a little, much, no) control over its selling price. 3. The demand curve for the monopolistic competitor is _________________ sloped. Consequently, the monopolistic competitor’s marginal revenue curve is (below, above) its demand, or AR curve. ...
... into account the reactions of rivals, and each firm has (a little, much, no) control over its selling price. 3. The demand curve for the monopolistic competitor is _________________ sloped. Consequently, the monopolistic competitor’s marginal revenue curve is (below, above) its demand, or AR curve. ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.