Principles of Economics Third Edition by Fred Gottheil
... other output? • No. The MR = MC rule always signals the firm’s most profitable output level, even if the profit is zero. Every other output level in this case would yield a loss. ...
... other output? • No. The MR = MC rule always signals the firm’s most profitable output level, even if the profit is zero. Every other output level in this case would yield a loss. ...
Applied Economics for Business Management
... What does this mean? If inputs x1 and x2 are increased by a factor λ, then output (y) will increase by λ2. ...
... What does this mean? If inputs x1 and x2 are increased by a factor λ, then output (y) will increase by λ2. ...
Chapter 8 - Monopoly and Imperfect Competition
... Under monopolistic competition—in which there are no barriers to entry and exit—the firm will not enjoy its profit for ...
... Under monopolistic competition—in which there are no barriers to entry and exit—the firm will not enjoy its profit for ...
PP - Personal.kent.edu
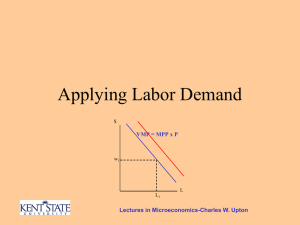
... Let’s see what happens when in the long run when the price of a product changes. Initially the firm is employing L* workers. ...
... Let’s see what happens when in the long run when the price of a product changes. Initially the firm is employing L* workers. ...
PDF
... of a resource can sell to two markets at different prices. Although only a slight variation on the model in Stiglitz (1976), which features constant elasticity of demand with zero extraction costs, our basic model does not yield the result that the monopolist extracts at the same rate as the social p ...
... of a resource can sell to two markets at different prices. Although only a slight variation on the model in Stiglitz (1976), which features constant elasticity of demand with zero extraction costs, our basic model does not yield the result that the monopolist extracts at the same rate as the social p ...
Foundations of Economics, 3e (Bade/Parkin)
... Answer: Let us consider the value of the marginal product of two workers, Alex Rodriquez, shortstop for the New York Yankees, and any kindergarten teacher in the United States. The value of marginal product of labor is the marginal product of labor multiplied by the price of the output the laborer p ...
... Answer: Let us consider the value of the marginal product of two workers, Alex Rodriquez, shortstop for the New York Yankees, and any kindergarten teacher in the United States. The value of marginal product of labor is the marginal product of labor multiplied by the price of the output the laborer p ...
Prch4
... Two Important Properties of Demand Curves 2) At every point on the demand curve, the consumer is maximizing utility by satisfying the condition that the MRS of food for clothing equals the ratio of the prices of food and clothing. ...
... Two Important Properties of Demand Curves 2) At every point on the demand curve, the consumer is maximizing utility by satisfying the condition that the MRS of food for clothing equals the ratio of the prices of food and clothing. ...
Elasticity of demand File
... In this method, the elasticity of demand is found out at a particular point in the demand curve. For example, at the middle point of the straight line demand curve, elasticity is equal to unity at the higher points of the demand curve, to the left of the middle point, elasticity is more than uni ...
... In this method, the elasticity of demand is found out at a particular point in the demand curve. For example, at the middle point of the straight line demand curve, elasticity is equal to unity at the higher points of the demand curve, to the left of the middle point, elasticity is more than uni ...
demand - Business-TES
... most exclusive perfume in the world. Only 475 bottles have been produced and bottles have been selling for £47,500 each – a classic case of paying through the nose for an exclusive good. Goods of ostentatious consumption are known as Veblen Goods and they have a high-income elasticity of demand. Tha ...
... most exclusive perfume in the world. Only 475 bottles have been produced and bottles have been selling for £47,500 each – a classic case of paying through the nose for an exclusive good. Goods of ostentatious consumption are known as Veblen Goods and they have a high-income elasticity of demand. Tha ...
Short Answer
... What is substitution effect of fall in price of a commodity on its demand.? Why does the demand of a commodity fall with the rise in price? Why do household buy more at a lower price? When does the consumer buy more of a commodity at a given price? Define Increase in Demand. What Factors causes incr ...
... What is substitution effect of fall in price of a commodity on its demand.? Why does the demand of a commodity fall with the rise in price? Why do household buy more at a lower price? When does the consumer buy more of a commodity at a given price? Define Increase in Demand. What Factors causes incr ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.