Prices and Markets
... Introduction • Prices change all the time • The reason is because of changes in supply and/or demand • This happens in a market • A market is many things, but essentially it is where suppliers and demanders meet ...
... Introduction • Prices change all the time • The reason is because of changes in supply and/or demand • This happens in a market • A market is many things, but essentially it is where suppliers and demanders meet ...
ch03-qs - uob.edu.bh
... Economic system 6. Which of the following questions is not a basic economic question? A. What goods to be produced? B. how to spend money? C. For whom to produce output? D. none of the above. 7. A negative relationship (positive slope) between P and Qd means that A When P increases, the Qd iccreases ...
... Economic system 6. Which of the following questions is not a basic economic question? A. What goods to be produced? B. how to spend money? C. For whom to produce output? D. none of the above. 7. A negative relationship (positive slope) between P and Qd means that A When P increases, the Qd iccreases ...
We assume an upward sloping supply curve → ER and SAUD are
... o Therefore, Australians increase their purchase of foreign items. To buy foreign items, they require more FC They must sell/supply their AUD to the FEM in order to receive the FC they need. The higher ER leads to foreign items being substituted for domestic items, ceteris paribus. As ER changes, ...
... o Therefore, Australians increase their purchase of foreign items. To buy foreign items, they require more FC They must sell/supply their AUD to the FEM in order to receive the FC they need. The higher ER leads to foreign items being substituted for domestic items, ceteris paribus. As ER changes, ...
Quiz1
... a) [2 marks] Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity in this market? Show your work. Answer: Equating Qd and Qs gives, 700-15 P = 25 + 10 P, which can be solved for equilibrium price: P*=27. Substitute P* for P in either the equation for the market demand or the market supply to obtain equilibr ...
... a) [2 marks] Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity in this market? Show your work. Answer: Equating Qd and Qs gives, 700-15 P = 25 + 10 P, which can be solved for equilibrium price: P*=27. Substitute P* for P in either the equation for the market demand or the market supply to obtain equilibr ...
Midterm Review Jeopardy
... reduced the risk of transmitting disease to others. This benefits the third party (society) as a whole ...
... reduced the risk of transmitting disease to others. This benefits the third party (society) as a whole ...
Equilibrium - mrsbradleysclass
... The ticket price for the concert is $30.00 per person. There are 30,000 fans in the area who are willing to pay $80.00 per seat to listen to the concert. What will happen? ...
... The ticket price for the concert is $30.00 per person. There are 30,000 fans in the area who are willing to pay $80.00 per seat to listen to the concert. What will happen? ...
Midterm Exam #1
... This exam consists of three parts. The first part requires you to provide a definition as well as an application for each concept. The second part involves solution of simple economic problems. The third part provides opportunities for students to employ economic analysis to address more complicated ...
... This exam consists of three parts. The first part requires you to provide a definition as well as an application for each concept. The second part involves solution of simple economic problems. The third part provides opportunities for students to employ economic analysis to address more complicated ...
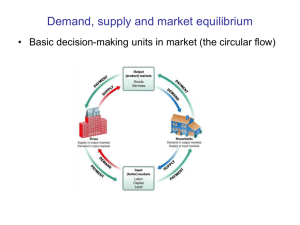
Lecture 5 The Market Equilibrium
... ► What about bargaining? Each party tries to convince the other of the powerful competition faced from alternatives ...
... ► What about bargaining? Each party tries to convince the other of the powerful competition faced from alternatives ...
Equilibrium Price
... 2. 3000 bags 3. Consumers would only buy 1000 bags while the supply would be 5000 resulting in a surplus of 4000 bags. 4. Supplier would only supply 1000 bags while demand would be 5000 resulting in a shortage of 4000 bags. 5. Demand curve is downward sloping, reflecting an inverse relationship betw ...
... 2. 3000 bags 3. Consumers would only buy 1000 bags while the supply would be 5000 resulting in a surplus of 4000 bags. 4. Supplier would only supply 1000 bags while demand would be 5000 resulting in a shortage of 4000 bags. 5. Demand curve is downward sloping, reflecting an inverse relationship betw ...
ECN 101 Economics I Student`s Summer Term Name: Final
... a. the more one is willing to pay for resources, the larger will be the possible level of production. b. increasing the production of a particular good will cause the price of good tor rise. c. in order to produce additional units of a particular good, it is necessary for society to sacrifice increa ...
... a. the more one is willing to pay for resources, the larger will be the possible level of production. b. increasing the production of a particular good will cause the price of good tor rise. c. in order to produce additional units of a particular good, it is necessary for society to sacrifice increa ...
Quiz5
... This implies P d P s 10 16 and the equilibrium quantity will be (substituting into demand) Q 50 2(16) 18 . c) [1 mark] At the equilibrium calculated in part b), what will the government’s total tax receipts be? Answer: To calculate tax receipts, take the amount of tax, $10, and multiply ...
... This implies P d P s 10 16 and the equilibrium quantity will be (substituting into demand) Q 50 2(16) 18 . c) [1 mark] At the equilibrium calculated in part b), what will the government’s total tax receipts be? Answer: To calculate tax receipts, take the amount of tax, $10, and multiply ...
EC 203
... 4. The inverse demand function for bananas is Pd=18-3Qd, and the inverse supply is Ps=6+Qs, where the prices are in Ykr. a) If there are no taxes or subsidies, what is the equilibrium quantity? 3 What is the equilibrium market price? b) If a subsidy of 2 Ykr per kilogram is paid to banana growers, w ...
... 4. The inverse demand function for bananas is Pd=18-3Qd, and the inverse supply is Ps=6+Qs, where the prices are in Ykr. a) If there are no taxes or subsidies, what is the equilibrium quantity? 3 What is the equilibrium market price? b) If a subsidy of 2 Ykr per kilogram is paid to banana growers, w ...
Basic Economics Baseball Review
... What is a surplus? What is a shortage? In order to be effective a price floor must be above or below equilibrium point? In order to be effective a price ceiling must be above or below equilibrium point? A price-floor tends to cause a shortage or a surplus. A price-ceiling tends to cause a shortage o ...
... What is a surplus? What is a shortage? In order to be effective a price floor must be above or below equilibrium point? In order to be effective a price ceiling must be above or below equilibrium point? A price-floor tends to cause a shortage or a surplus. A price-ceiling tends to cause a shortage o ...
Document
... Market equilibrium • Market equilibrium: The condition that exist when quantity supplied and quantity demanded are equal. At equilibrium there is no tendency for price to change. p ...
... Market equilibrium • Market equilibrium: The condition that exist when quantity supplied and quantity demanded are equal. At equilibrium there is no tendency for price to change. p ...
Which of the following influences does NOT shift the supply curve?
... Which of the following statements uses incorrect terminology: A: "The recent fare war among the major airlines has increased the demand for air travel.“ B: "The terrorist attack on America has caused the demand for air travel to fall." a) b) c) d) ...
... Which of the following statements uses incorrect terminology: A: "The recent fare war among the major airlines has increased the demand for air travel.“ B: "The terrorist attack on America has caused the demand for air travel to fall." a) b) c) d) ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.