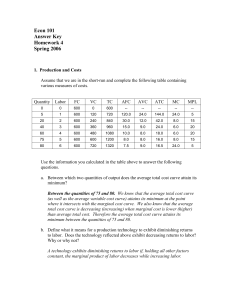
Algorithmic Game Theory and Internet Computing
... Rabbi Samuel ben Meir (12th century, France): 2nd century text: “You shall have inspectors of weights and measures but not inspectors of prices.” Commentary (Aumann): If one seller charges too high a price, then another will undercut him. ...
... Rabbi Samuel ben Meir (12th century, France): 2nd century text: “You shall have inspectors of weights and measures but not inspectors of prices.” Commentary (Aumann): If one seller charges too high a price, then another will undercut him. ...
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
... QD = 10 - P where QD is units demanded and P is price of each unit in dollars per unit. McGraw-Hill/Irwin ...
... QD = 10 - P where QD is units demanded and P is price of each unit in dollars per unit. McGraw-Hill/Irwin ...
Law of demand
... Standard 12.1.3 Monetary and non-monetary incentives and how they change behavior. Standard 12.2.1 Relationship between incentives and law of supply and law of demand. ...
... Standard 12.1.3 Monetary and non-monetary incentives and how they change behavior. Standard 12.2.1 Relationship between incentives and law of supply and law of demand. ...
Homework #2 Due: Monday >>> 3/02/2015
... 6. Supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. The model concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded by consumers (at current price) will equal the quantity supplied by p ...
... 6. Supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. The model concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded by consumers (at current price) will equal the quantity supplied by p ...
Answers to Homework #4
... before diving into the calculations.) The price from the firms’ perspective is P = 8. Once again the equilibrium price under perfect competition is determined by the minimum of the ATC curve, which is unaffected by the tax. Therefore the price received by producers is still P = 8. For consumers, sin ...
... before diving into the calculations.) The price from the firms’ perspective is P = 8. Once again the equilibrium price under perfect competition is determined by the minimum of the ATC curve, which is unaffected by the tax. Therefore the price received by producers is still P = 8. For consumers, sin ...
exam2solutions
... larger than the decrease in quantity demanded of labor. 12. B. If the MU per last dollar spent on one good (good A) is greater than the MU per last dollar spent on a second good (good B), the consumer can increase overall satisfaction by shifting fixed money income away from B allowing her to buy mo ...
... larger than the decrease in quantity demanded of labor. 12. B. If the MU per last dollar spent on one good (good A) is greater than the MU per last dollar spent on a second good (good B), the consumer can increase overall satisfaction by shifting fixed money income away from B allowing her to buy mo ...
Price Floors and Ceilings Practice
... The mayor and the city council have been considering three options: a. Let apartments rise to the market price. b. Continue the rent controls and the let people find and rent apartments on a first-come, first-served basis. Anyone convicted of collecting or paying more than the rent control price wil ...
... The mayor and the city council have been considering three options: a. Let apartments rise to the market price. b. Continue the rent controls and the let people find and rent apartments on a first-come, first-served basis. Anyone convicted of collecting or paying more than the rent control price wil ...
Lecture 1: ART OF THE ECONOMIC ARGUMENT
... • Definition of economic issue or question – May or may not be refutable – Normative question: Not refutable • The income distribution of Norway is superior to Canada • Canada’s income distribution is inferior to USA • What standard would you use to measure income distribution? Mean, Medium, ? • Wha ...
... • Definition of economic issue or question – May or may not be refutable – Normative question: Not refutable • The income distribution of Norway is superior to Canada • Canada’s income distribution is inferior to USA • What standard would you use to measure income distribution? Mean, Medium, ? • Wha ...
14.01 Fall 2010 Problem Set 1
... (a) (5 points) Computers (generally) vs. Apple MacBook Pro laptops. (b) (5 points) Stereo headphones (generally) vs. hearing aids. For each of the following goods, identify whether you would expect demand to be more (own-price) elastic in the short run or the long run. As above, please briefly explai ...
... (a) (5 points) Computers (generally) vs. Apple MacBook Pro laptops. (b) (5 points) Stereo headphones (generally) vs. hearing aids. For each of the following goods, identify whether you would expect demand to be more (own-price) elastic in the short run or the long run. As above, please briefly explai ...
Lecture4review marke..
... to sell products at various prices. This, in turn, depends on • input/raw material prices • the state of technology • the price of the good relative to the prices of other goods ...
... to sell products at various prices. This, in turn, depends on • input/raw material prices • the state of technology • the price of the good relative to the prices of other goods ...
Supply and Demand - Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas
... Disclaimer: The views expressed are those of the presenters and do not necessarily reflect those of the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas or the Federal Reserve System. ...
... Disclaimer: The views expressed are those of the presenters and do not necessarily reflect those of the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas or the Federal Reserve System. ...
Objective—Students will understand the concept of DEMAND in
... Price Effect • If the price changes, the law of demand says that the quantity will change. • It is NOT a change in demand to have the quantity change when the price changes, it is merely a movement along the curve. ...
... Price Effect • If the price changes, the law of demand says that the quantity will change. • It is NOT a change in demand to have the quantity change when the price changes, it is merely a movement along the curve. ...
VBS Pricing
... • Demand: Amt. Of goods or services customers are willing to buy at a given price • Yeild Management Pricing: Pricing strategy used whenever the quantity of a product is fixed(I.E. seats) to maximize profits by selling better tickets at higher prices or when demand increases. ...
... • Demand: Amt. Of goods or services customers are willing to buy at a given price • Yeild Management Pricing: Pricing strategy used whenever the quantity of a product is fixed(I.E. seats) to maximize profits by selling better tickets at higher prices or when demand increases. ...
Green Economics Homework 1 Essay questions. Pick any 5
... 3. Define the Second Laws of Thermodynamics. What happens to the total energy of the system when we burn oil? Would it be possible to invent an automobile that could capture its own exhaust and burn it again? ...
... 3. Define the Second Laws of Thermodynamics. What happens to the total energy of the system when we burn oil? Would it be possible to invent an automobile that could capture its own exhaust and burn it again? ...
Marketing Management Exam I Answers and suggestions: 51. Given
... market, and no business has total control over the market price. Typically, customers perceive that there are nonprice differences among the competitors' products. There are also few barriers for entry into the market, and companies feel that they have a degree of control over price. We all know wha ...
... market, and no business has total control over the market price. Typically, customers perceive that there are nonprice differences among the competitors' products. There are also few barriers for entry into the market, and companies feel that they have a degree of control over price. We all know wha ...
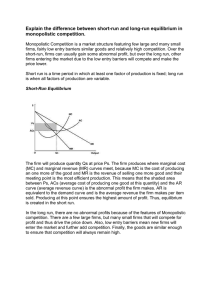
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.