Practice Exam 3
... q units of a product by consumers. The function p S (q) 3q 100 gives the price at which q units will be supplied by the producers. a. Find the equilibrium quantity and price. ...
... q units of a product by consumers. The function p S (q) 3q 100 gives the price at which q units will be supplied by the producers. a. Find the equilibrium quantity and price. ...
Demand and Supply
... an item. (positive slope, rising line) Law of demand: the quantity demanded will increase as the price of the product decreases where: p = D(x) the demand function; price per unit at which consumers will buy x units of an item. (negative slope, falling line) ...
... an item. (positive slope, rising line) Law of demand: the quantity demanded will increase as the price of the product decreases where: p = D(x) the demand function; price per unit at which consumers will buy x units of an item. (negative slope, falling line) ...
managerial-economics-sahid-pasca-market-forces-demand
... Samsung and Hynix Semiconductor to Cut Chip Production (continued) PC Solutions is a small but growing company that assembles PCs and sells them in the highly competitive market for “clones.” PC Solutions experienced 100 percent growth last year and is in the process of interviewing recent graduate ...
... Samsung and Hynix Semiconductor to Cut Chip Production (continued) PC Solutions is a small but growing company that assembles PCs and sells them in the highly competitive market for “clones.” PC Solutions experienced 100 percent growth last year and is in the process of interviewing recent graduate ...
Equilibrium price
... curves for a good in a single graph, the point at which they intersect identifies the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. • Here, the equilibrium price is $6 per pound. Consumers demand, and suppliers supply, 25 million pounds of coffee per month at this price. ...
... curves for a good in a single graph, the point at which they intersect identifies the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. • Here, the equilibrium price is $6 per pound. Consumers demand, and suppliers supply, 25 million pounds of coffee per month at this price. ...
ECONOMIC SYTEMS COMMAND VERSUS MARKET THE
... o Private Property (absolutely critical) o Freedom of Enterprise and Choice (critical) o Self-interest (assumed in all systems) o Competition (critical for efficiency) o Markets and prices (obvious) o Active but limited Government Defends private property, freedom of enterprise and choice and compet ...
... o Private Property (absolutely critical) o Freedom of Enterprise and Choice (critical) o Self-interest (assumed in all systems) o Competition (critical for efficiency) o Markets and prices (obvious) o Active but limited Government Defends private property, freedom of enterprise and choice and compet ...
supply curve - Porterville College Home
... Note: The textbook uses the Up/Down language in an example in CH 3. It may be “technically” OK, but it WILL confuse you if you use it!!! ...
... Note: The textbook uses the Up/Down language in an example in CH 3. It may be “technically” OK, but it WILL confuse you if you use it!!! ...
perfect comp
... Remember, there is perfect knowledge. So new firms move in to industry to make SNP. As they do, supply expands and price falls. The supply curve shifts rightwards; price falls; thus, in the diagram for the single firm (the black slide), the perfectly elastic demand curve (also showing price) slides ...
... Remember, there is perfect knowledge. So new firms move in to industry to make SNP. As they do, supply expands and price falls. The supply curve shifts rightwards; price falls; thus, in the diagram for the single firm (the black slide), the perfectly elastic demand curve (also showing price) slides ...
Answer Key to Practice Problem Set 1
... 6. The demand and supply of sunglasses (measured in millions) in the Republic of Rayban is given by the following equations. a. Find the equilibrium quantity and price of sunglasses. Include a graphical analysis of the equilibrium including at least 2 points on each curve. D: P = 120 - 8Q S: P = 30 ...
... 6. The demand and supply of sunglasses (measured in millions) in the Republic of Rayban is given by the following equations. a. Find the equilibrium quantity and price of sunglasses. Include a graphical analysis of the equilibrium including at least 2 points on each curve. D: P = 120 - 8Q S: P = 30 ...
DSP Revision Part 1
... Excess supply or surplus means that the quantity supplied is greater not S > D than the quantity demanded at a price which is above the equilibrium price. the condition Excess demand or shortage means that the quantity demanded is not D > S greater than the quantity supplied at a price which is belo ...
... Excess supply or surplus means that the quantity supplied is greater not S > D than the quantity demanded at a price which is above the equilibrium price. the condition Excess demand or shortage means that the quantity demanded is not D > S greater than the quantity supplied at a price which is belo ...
PART 1 - MULTIPLE CHOICE 1 - ) What is the most accurate
... If beer and wine are substitutes, a price increase by wine retailers will shift the demand curve for beer downwards. 5. An increase in the price of Pepsi would increase the quantity demanded of Cokes but not the demand of Cokes. (Pepsi and Coke are substitutes.) 6. If an economy can use its resource ...
... If beer and wine are substitutes, a price increase by wine retailers will shift the demand curve for beer downwards. 5. An increase in the price of Pepsi would increase the quantity demanded of Cokes but not the demand of Cokes. (Pepsi and Coke are substitutes.) 6. If an economy can use its resource ...
Honors Economics Unit 2 Study Guide
... 3. What is the difference between a change in quantity demanded (along the demand curve) and a shift in the demand curve? (82-83) A change in quantity demanded mean a change in price – moves along the demand curve. A shift in the demand curve comes from a change in the non-price determinants (income ...
... 3. What is the difference between a change in quantity demanded (along the demand curve) and a shift in the demand curve? (82-83) A change in quantity demanded mean a change in price – moves along the demand curve. A shift in the demand curve comes from a change in the non-price determinants (income ...
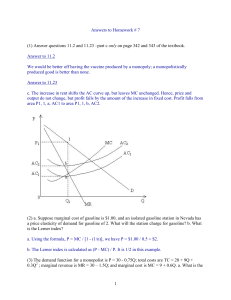
1 Answers to Homework # 7 (1) Answer questions 11.2 and 11.23
... profit-maximizing rate of output? b. What are the profits? c. What would be the price and output under perfect competition if the monopolist's marginal cost curve is the competitive industry's supply curve? d. Calculate the amount of the deadweight loss associated with the monopoly outcome. a. The ...
... profit-maximizing rate of output? b. What are the profits? c. What would be the price and output under perfect competition if the monopolist's marginal cost curve is the competitive industry's supply curve? d. Calculate the amount of the deadweight loss associated with the monopoly outcome. a. The ...
Example #1
... 13. Imagine this is the final for Econ 101. You have managed to achieve 50/100 and 70/100 on the first two midterms, which each make up 25% of your grade. The remaining 50% is decided by the final. To get 80% for the course, how much would you need to earn on the final exam out of a hundred possibl ...
... 13. Imagine this is the final for Econ 101. You have managed to achieve 50/100 and 70/100 on the first two midterms, which each make up 25% of your grade. The remaining 50% is decided by the final. To get 80% for the course, how much would you need to earn on the final exam out of a hundred possibl ...
Key Terms and Concepts: Chapter 7 Average Revenue Total
... The change in Total Revenue divided by the change in Quantity sold. In perfect competition, marginal revenue equals price. ...
... The change in Total Revenue divided by the change in Quantity sold. In perfect competition, marginal revenue equals price. ...
Part and/or Chapter Number and Title
... Productive Efficiency: Price = minimum ATC Allocative Efficiency: Price = MC Pure competition has both in its long-run equilibrium. ...
... Productive Efficiency: Price = minimum ATC Allocative Efficiency: Price = MC Pure competition has both in its long-run equilibrium. ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.