lecture-14-supply-demand
... At $15, a surplus occurs. Quantity supplied (150) is greater than quantity demanded (50). Price Falls! At $10, results is neither a surplus nor a shortage. Quantity supplied (100) is = to quantity demanded (100). Equilibrium occurs! ...
... At $15, a surplus occurs. Quantity supplied (150) is greater than quantity demanded (50). Price Falls! At $10, results is neither a surplus nor a shortage. Quantity supplied (100) is = to quantity demanded (100). Equilibrium occurs! ...
Economic Survey
... Hint: Now suppliers do not get the full price when they make a sale - they get $6 less. This changes our supply curve to: P - 6 = 20 + 2Q (Supply) P = 26 + 2Q (Supply) To find the equilibrium price, set the demand and supply equations equal to each other: ...
... Hint: Now suppliers do not get the full price when they make a sale - they get $6 less. This changes our supply curve to: P - 6 = 20 + 2Q (Supply) P = 26 + 2Q (Supply) To find the equilibrium price, set the demand and supply equations equal to each other: ...
Monopolistic Competition
... Short-Run Price and Output The monopolistically competitive firm’s production decision is similar to that of a monopolist. Production decision - The selection of the short-run rate of output (with existing plant and equipment). ...
... Short-Run Price and Output The monopolistically competitive firm’s production decision is similar to that of a monopolist. Production decision - The selection of the short-run rate of output (with existing plant and equipment). ...
Chapter 5 (35 points)
... 8. Suppose you learned that the price elasticity of demand for wheat is 0.7 between the current price for wheat and a price $2 higher per bushel. Do you think farmers collectively would try to reduce the supply of wheat and drive the price up $2 higher per bushel? Why? Assuming that they would try t ...
... 8. Suppose you learned that the price elasticity of demand for wheat is 0.7 between the current price for wheat and a price $2 higher per bushel. Do you think farmers collectively would try to reduce the supply of wheat and drive the price up $2 higher per bushel? Why? Assuming that they would try t ...
Principles of Microeconomics EXAM 1A
... Which of the following is best described by the statement “As the price of a product rises, consumers shift their purchases to the other products whose prices are now relatively lower” a. the law of demand b. the principle of normal goods c. the income effect d. the substitution effect If supply fal ...
... Which of the following is best described by the statement “As the price of a product rises, consumers shift their purchases to the other products whose prices are now relatively lower” a. the law of demand b. the principle of normal goods c. the income effect d. the substitution effect If supply fal ...
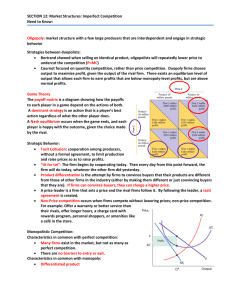
SECTION 12: Market Structures: Imperfect Competition Need to Know: : market structure with a few large producers that are interdependent and engage in strategic
... SECTION 12: Market Structures: Imperfect Competition Need to Know: ...
... SECTION 12: Market Structures: Imperfect Competition Need to Know: ...
Can spot market power translate into market power in the hedge
... The conditional cumulative function of market clearing price is: ...
... The conditional cumulative function of market clearing price is: ...
Supply - Notes Milenge
... • A measure of the extent to which the quantity supplied of a good changes when its price changes, all other factors affecting supply remaining the same (ceteris paribus). • Price Elasticity of Supply (Es) = % Change in Quantity Supplied % Change in Price ...
... • A measure of the extent to which the quantity supplied of a good changes when its price changes, all other factors affecting supply remaining the same (ceteris paribus). • Price Elasticity of Supply (Es) = % Change in Quantity Supplied % Change in Price ...
assignment 2 (winter 2007)
... such as milk, paper, towels, and cola, even though the demand and cost of production didn't change? Based on the lecture, explain why are turkeys cheapest just before Thanksgiving, when demand is highest? Traditional demand/supply theory would predict that prices should be highest when demand is hig ...
... such as milk, paper, towels, and cola, even though the demand and cost of production didn't change? Based on the lecture, explain why are turkeys cheapest just before Thanksgiving, when demand is highest? Traditional demand/supply theory would predict that prices should be highest when demand is hig ...
Intro to Linear Functions (Supply, Demand) File
... A: Remember the determinants!!! o Q: Would this be a change in supply or a change in quantity supplied? A: This would be a change in supply b/c more would be supplied at a given price. o Q: Is this number almost always negative? A: Yes, because suppliers do not like to give away their product ...
... A: Remember the determinants!!! o Q: Would this be a change in supply or a change in quantity supplied? A: This would be a change in supply b/c more would be supplied at a given price. o Q: Is this number almost always negative? A: Yes, because suppliers do not like to give away their product ...
Micterm Exam
... b. the average consumer chooses to consume the good over other similar goods. c. an increase in income increases consumption of the good. d. the average consumer chooses to consume this good at a level consistent with most other goods. ...
... b. the average consumer chooses to consume the good over other similar goods. c. an increase in income increases consumption of the good. d. the average consumer chooses to consume this good at a level consistent with most other goods. ...
1 - JustAnswer
... 1. Price elasticity of demand is calculated as (Points: 1) the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price 2. The price elasticity of demand (Points: 1) tells producers what will happen to total revenue if they change product price 3. Along a linear demand curve, ...
... 1. Price elasticity of demand is calculated as (Points: 1) the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price 2. The price elasticity of demand (Points: 1) tells producers what will happen to total revenue if they change product price 3. Along a linear demand curve, ...
answers to end-of-chapter questions
... (a) Hometown supermarket: oligopoly. Supermarkets are few in number in any one area; their size makes new entry very difficult; there is much nonprice competition. However, there is much price competition as they compete for market share, and there seems to be no collusion. In this regard, the super ...
... (a) Hometown supermarket: oligopoly. Supermarkets are few in number in any one area; their size makes new entry very difficult; there is much nonprice competition. However, there is much price competition as they compete for market share, and there seems to be no collusion. In this regard, the super ...
Monopolistic Competition
... • Result: a small percentage decrease in price will cause a large percentage increase in quantity demanded = elastic demand. ...
... • Result: a small percentage decrease in price will cause a large percentage increase in quantity demanded = elastic demand. ...
CHAPER 3 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ANSWER KEY
... farmers destroyed their herds. Since both of these shifts lead to a lower equilibrium quantity of beef, we know with certainty that equilibrium quantity will decrease. However, we cannot know with certainty whether the price of beef will rise, fall, or stay the same. The answer depends on the relati ...
... farmers destroyed their herds. Since both of these shifts lead to a lower equilibrium quantity of beef, we know with certainty that equilibrium quantity will decrease. However, we cannot know with certainty whether the price of beef will rise, fall, or stay the same. The answer depends on the relati ...
Supply, Demand, and Equilibrium
... The intersection of demand and supply curves determines equilibrium Equilibrium is stable Change in S or D causes the curve to shift A movement along the supply curve can occur when the supply curve does not move Both supply and demand can shift, but be careful of your conclusions ...
... The intersection of demand and supply curves determines equilibrium Equilibrium is stable Change in S or D causes the curve to shift A movement along the supply curve can occur when the supply curve does not move Both supply and demand can shift, but be careful of your conclusions ...
demand and supply
... quantity demanded and supplied. However changes in other factors such as incomes, population, tastes, price of other goods will affect the quantity of goods demanded. Changes in factors like cost of production, technology, seasonal factors will affect the quantity of goods supplied. ...
... quantity demanded and supplied. However changes in other factors such as incomes, population, tastes, price of other goods will affect the quantity of goods demanded. Changes in factors like cost of production, technology, seasonal factors will affect the quantity of goods supplied. ...
ECO1 REV1 – Answers
... 19. We continue production so long MB > MC and stop when they’re equal. True 20. Public goods are necessary because all can benefit regardless of income and tax contribution. True 21. The maturity stage of a product or company best demonstrates the Law of Increasing OC. True 22. When the price of a ...
... 19. We continue production so long MB > MC and stop when they’re equal. True 20. Public goods are necessary because all can benefit regardless of income and tax contribution. True 21. The maturity stage of a product or company best demonstrates the Law of Increasing OC. True 22. When the price of a ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.