Economics - Spring Branch ISD
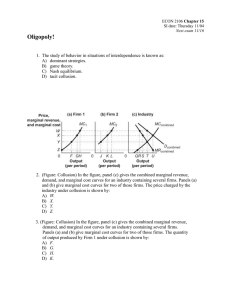
... 1. In a market system, the interaction of buyers and sellers determines the prices of most goods as well as what quantity of a good will be produced. 2. Demand is the desire to own something and the ability to pay for it. 3. The Law of Demand – When a good’s price is lower, consumers will buy more o ...
... 1. In a market system, the interaction of buyers and sellers determines the prices of most goods as well as what quantity of a good will be produced. 2. Demand is the desire to own something and the ability to pay for it. 3. The Law of Demand – When a good’s price is lower, consumers will buy more o ...
Chapter 5
... 2. As i, opportunity cost of money Quantity of Money Demanded 3. Demand curve for money has usual downward slope Supply of Supply 1. Assume that central bank controls MS and it is a fixed amount MS curve is vertical line Money Market Equilibrium 1. Occurs when MD = MS, at i* = 15% 2. If i = ...
... 2. As i, opportunity cost of money Quantity of Money Demanded 3. Demand curve for money has usual downward slope Supply of Supply 1. Assume that central bank controls MS and it is a fixed amount MS curve is vertical line Money Market Equilibrium 1. Occurs when MD = MS, at i* = 15% 2. If i = ...
content/teaching outline
... A. Explain supply and demand. 1. Supply: The amount of goods producers are willing and able to produce and sell at a given price during a certain period of time. Producers prefer to supply when the price is high; this is known as a sellers’ market. For example, when a popular music artist releases a ...
... A. Explain supply and demand. 1. Supply: The amount of goods producers are willing and able to produce and sell at a given price during a certain period of time. Producers prefer to supply when the price is high; this is known as a sellers’ market. For example, when a popular music artist releases a ...
Business Administration
... purchase the commodities offered Market price – a figure determined by the relation between the supply and the demand Equilibrium – point of intersection between supply and deman Competion – creates an inseparable conditions for the existence of any market ...
... purchase the commodities offered Market price – a figure determined by the relation between the supply and the demand Equilibrium – point of intersection between supply and deman Competion – creates an inseparable conditions for the existence of any market ...
Part II: Micro-Economics (the Market): II
... A tax on sellers (S shifts to the left) & a tax on buyers (D shifts to the left): inelastic demand, P goes up (buyers pay the tax), elastic demand, P does not change (sellers pay the tax) inelastic supply, P does not change (sellers pay the tax), elastic supply, P goes up (buyers pay the tax) change ...
... A tax on sellers (S shifts to the left) & a tax on buyers (D shifts to the left): inelastic demand, P goes up (buyers pay the tax), elastic demand, P does not change (sellers pay the tax) inelastic supply, P does not change (sellers pay the tax), elastic supply, P goes up (buyers pay the tax) change ...
Test 1 Review Outline
... 1. Motivation: Diminishing marginal utility: 2. Definition of Demand Curve 3. Determinants of Demand. 4. Changes in demand vs. changes in qty demanded. 5. The Notion of Consumer Surplus 6. An Analytical Example C. The Supply Side. 1. Driving Force. The Law of Diminishing Returns 2. Definition of Sup ...
... 1. Motivation: Diminishing marginal utility: 2. Definition of Demand Curve 3. Determinants of Demand. 4. Changes in demand vs. changes in qty demanded. 5. The Notion of Consumer Surplus 6. An Analytical Example C. The Supply Side. 1. Driving Force. The Law of Diminishing Returns 2. Definition of Sup ...
Midterm Questions and Answers, Spring 2004
... to the resulting reduction in purchasing power, holding relative prices constant. For normal goods, the income e¤ect will reinforce the substitution e¤ect, so that demand for gold should fall further. Unless you believe that gold is an inferior good, where poor people have more gold than rich people ...
... to the resulting reduction in purchasing power, holding relative prices constant. For normal goods, the income e¤ect will reinforce the substitution e¤ect, so that demand for gold should fall further. Unless you believe that gold is an inferior good, where poor people have more gold than rich people ...
Chapter 12 – Monopolistic Competition: The competitive model in a
... Result: Mon. Comp firm making profits will face competition from _______ making its demand curve more elastic ...
... Result: Mon. Comp firm making profits will face competition from _______ making its demand curve more elastic ...
File
... kidneys, no longer relying solely on the concept of “net benefit,” but also giving preference to children with small children. If total surplus is the total life span of kidney recipients, total surplus will increase. ...
... kidneys, no longer relying solely on the concept of “net benefit,” but also giving preference to children with small children. If total surplus is the total life span of kidney recipients, total surplus will increase. ...
Economics 3070 Fall 2014 Problem Set 6 Answers 1. Chapter 9
... So, if she continues to work at the grocery store, she earns an accounting profit of 80,000 plus the salary she pays herself 100,000. However, she earn negative economic profits if she continues to work at the grocery store (-120,000). But if she exits the business, her salary as a lawyer would be $ ...
... So, if she continues to work at the grocery store, she earns an accounting profit of 80,000 plus the salary she pays herself 100,000. However, she earn negative economic profits if she continues to work at the grocery store (-120,000). But if she exits the business, her salary as a lawyer would be $ ...
1st 9 weeks
... EC.19 Demonstrate how government wage and price controls, such as rent controls and minimum wage laws, create shortages and surpluses. ...
... EC.19 Demonstrate how government wage and price controls, such as rent controls and minimum wage laws, create shortages and surpluses. ...
Markets, Organizations and Corporate Strategy
... horizontal: how much of the product market the firm serves vertical: the set of activities that the firm performs itself and those it purchases from other firms corporate: the set of distinct businesses in which the firm operates ...
... horizontal: how much of the product market the firm serves vertical: the set of activities that the firm performs itself and those it purchases from other firms corporate: the set of distinct businesses in which the firm operates ...
100 - Economics @ LHS
... can make more money. If someone will pay $1.00 for a candy bar let them. If someone else would pay $2.00 then ...
... can make more money. If someone will pay $1.00 for a candy bar let them. If someone else would pay $2.00 then ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.