LESSON 6.2 Shifts of Demand and Supply Curves
... Explain how a shift of the demand curve affects equilibrium price and quantity. Explain how a shift of the supply curve affects equilibrium price and quantity. Explain what happens to equilibrium price and quantity if both curves shift. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS ...
... Explain how a shift of the demand curve affects equilibrium price and quantity. Explain how a shift of the supply curve affects equilibrium price and quantity. Explain what happens to equilibrium price and quantity if both curves shift. CONTEMPORARY ECONOMICS ...
ZOMU www.zomuedu.com Unit 3 The Elasticity of Demand Elasticity
... Elasticity measures how much demand responds to changes in its determinants The Price Elasticity of Demand measures how much quantity demanded responds to a change in price Demand of a good is said to be Elastic if the quantity demanded responds substantially to changes in the price Demand of a ...
... Elasticity measures how much demand responds to changes in its determinants The Price Elasticity of Demand measures how much quantity demanded responds to a change in price Demand of a good is said to be Elastic if the quantity demanded responds substantially to changes in the price Demand of a ...
SUPPLY
... • Supply Curves can also shift in response to the following factors: – Resource costs: cost to purchase factors of production will influence business decisions – Productivity: increases whenever more output is produced with the same amount of inputs – Technology: improvements in production increase ...
... • Supply Curves can also shift in response to the following factors: – Resource costs: cost to purchase factors of production will influence business decisions – Productivity: increases whenever more output is produced with the same amount of inputs – Technology: improvements in production increase ...
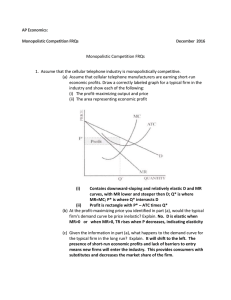
Monopolistic Competition FRQs answers
... (b) What must be true in the short run for the company to continue to produce at a loss? P > AVC butTVC
(c) Assume now that the demand for cleaning products increases and that the
company is now earning short-run economic profits. Relative to this shortrun situation, how does each of the ...
... (b) What must be true in the short run for the company to continue to produce at a loss? P > AVC but
Chapter 4 - OnCourse
... • Law of supply- tendency of suppliers to offer more for sale at higher prices and less at lower prices. • quantity varies directly with ...
... • Law of supply- tendency of suppliers to offer more for sale at higher prices and less at lower prices. • quantity varies directly with ...
demand curve
... supplied of that good. • Why? If the quantity produced of a good increases, the opportunity of producing the good also rises due to the law of diminishing returns. • Thus, firms are only willing to produce and sell more of a good if the price they get for the additional units covers the opportunity ...
... supplied of that good. • Why? If the quantity produced of a good increases, the opportunity of producing the good also rises due to the law of diminishing returns. • Thus, firms are only willing to produce and sell more of a good if the price they get for the additional units covers the opportunity ...
Demand and Supply, an Elaboration
... The effects on equilibrium price and quantity of simultaneous changes in supply and demand Why markets don’t always work well Why price ceilings create shortages Why price floors create surpluses Why demand curves might be vertical or upward ...
... The effects on equilibrium price and quantity of simultaneous changes in supply and demand Why markets don’t always work well Why price ceilings create shortages Why price floors create surpluses Why demand curves might be vertical or upward ...
Chapter 23 – Perfect Competition What are the characteristics of
... • Agricultural products (wheat, corn, etc.), metals, stocks, foreign currency, etc. ...
... • Agricultural products (wheat, corn, etc.), metals, stocks, foreign currency, etc. ...
Topic 2: Aggregate Demand, Supply and Equilibrium
... 1. Suppose the government spends $10 in the output market, I and NX are unaffected. What is the total increase in AD? ...
... 1. Suppose the government spends $10 in the output market, I and NX are unaffected. What is the total increase in AD? ...
Perfect Competition Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly Monopoly
... means that we have difficulty predicting behavior. This is why we spend so much time on Monopoly and Perfect Competition. These polar cases show the transition which occurs and know where the industry is placed in the continuum helps us understand the behavior. But when the interaction becomes perso ...
... means that we have difficulty predicting behavior. This is why we spend so much time on Monopoly and Perfect Competition. These polar cases show the transition which occurs and know where the industry is placed in the continuum helps us understand the behavior. But when the interaction becomes perso ...
Document
... food have been increasing for most of this century. High productivity in the agriculture sector, relative to income inelasticity for food, has meant that supply has increased by more than demand. As a result, prices have fallen. ...
... food have been increasing for most of this century. High productivity in the agriculture sector, relative to income inelasticity for food, has meant that supply has increased by more than demand. As a result, prices have fallen. ...
Week 2
... (Note: You must go over these slides and complete every task outlined here before Thursday, September 13) ...
... (Note: You must go over these slides and complete every task outlined here before Thursday, September 13) ...
elasticity of demand
... Price elasticity of Demand Measures responsiveness of changes in quantity demanded to changes in price. Price increases always cause a decrease in quantity demanded (law of demand). BUT For different products, the degree of responsiveness varies from elastic (very responsive) to inelastic (not v ...
... Price elasticity of Demand Measures responsiveness of changes in quantity demanded to changes in price. Price increases always cause a decrease in quantity demanded (law of demand). BUT For different products, the degree of responsiveness varies from elastic (very responsive) to inelastic (not v ...
INTRODUCTION of the Hula Hoop - Studious-Catz
... quantity demanded by buyers equals the quantity supplied by sellers; also called the marketclearing price. A surplus is the situation that results when the quantity supplied of a product exceeds the quantity demanded. This generally happens because the price of the product is above the market equili ...
... quantity demanded by buyers equals the quantity supplied by sellers; also called the marketclearing price. A surplus is the situation that results when the quantity supplied of a product exceeds the quantity demanded. This generally happens because the price of the product is above the market equili ...
supply and demand
... sitting space in the room. The couch and the armchair can be referred to as ___________________ goods. 4. When people eat french fries, they like to put ketchup on them. Due to an increase in the price of french fries, total sales of french fries decrease. At the same time, ketchup sales also decrea ...
... sitting space in the room. The couch and the armchair can be referred to as ___________________ goods. 4. When people eat french fries, they like to put ketchup on them. Due to an increase in the price of french fries, total sales of french fries decrease. At the same time, ketchup sales also decrea ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.