Demand
... • A shift to the left is a decrease. Ex: income changes, competition, consumer tastes change ...
... • A shift to the left is a decrease. Ex: income changes, competition, consumer tastes change ...
chapter 3—demand and supply
... a. an analytical expression of functional relationships. b. a visual representation of data. c. a table of electronically stored data. d. a list of economic data. e. Demand and Supply 2. The breakeven level of output occurs where: a. marginal cost equals average cost. b. marginal profit equals zero. ...
... a. an analytical expression of functional relationships. b. a visual representation of data. c. a table of electronically stored data. d. a list of economic data. e. Demand and Supply 2. The breakeven level of output occurs where: a. marginal cost equals average cost. b. marginal profit equals zero. ...
Using Economics to Quantify the Security of the Internet
... equal, the higher the price of a good, the smaller is the quantity demanded ...
... equal, the higher the price of a good, the smaller is the quantity demanded ...
Monopoly Vs. Perfect Competition PPT
... Comparing Monopoly and Perfect Competition • Because the monopolist’s marginal revenue is below its price, price and quantity will not be the same. • The monopolist’s equilibrium output is less than, and its price is higher than, for a firm in a competitive market. ...
... Comparing Monopoly and Perfect Competition • Because the monopolist’s marginal revenue is below its price, price and quantity will not be the same. • The monopolist’s equilibrium output is less than, and its price is higher than, for a firm in a competitive market. ...
ECONOMICS_1
... efficiency of the fixed and variable factors is increasing. In stage II, there is decreasing average and marginal productivity of the variable factor, but marginal product is still positive because total productivity continues to rise, though at a decreasing rate. However stage III, constitutes an i ...
... efficiency of the fixed and variable factors is increasing. In stage II, there is decreasing average and marginal productivity of the variable factor, but marginal product is still positive because total productivity continues to rise, though at a decreasing rate. However stage III, constitutes an i ...
Demand and Supply
... Demand and supply are the two words that economists use most often. Demand and supply are the forces that make market economies work. Modern microeconomics is about supply, demand, and market equilibrium. ...
... Demand and supply are the two words that economists use most often. Demand and supply are the forces that make market economies work. Modern microeconomics is about supply, demand, and market equilibrium. ...
Supply and Shifters of Supply
... 6. In-and-Out announce that they will significantly increase prices NEXT month 7. Government heavily taxes shake and fries causes their prices to quadruple. 8. In-and-Out lowers price of burgers to $1 ...
... 6. In-and-Out announce that they will significantly increase prices NEXT month 7. Government heavily taxes shake and fries causes their prices to quadruple. 8. In-and-Out lowers price of burgers to $1 ...
Chapter 3 Market Supply and Demand
... relationship between the price of a good and the quantity sellers are willing to offer for sale in a defined time period, ceteris paribus. Any price where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. A competing good. A jointly consumed good. When the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity su ...
... relationship between the price of a good and the quantity sellers are willing to offer for sale in a defined time period, ceteris paribus. Any price where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. A competing good. A jointly consumed good. When the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity su ...
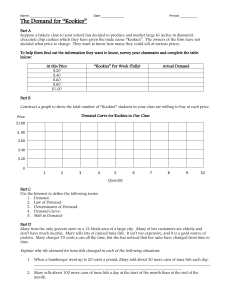
The Demand for “Kookies”
... Suppose a bakery close to your school has decided to produce and market large (6 inches in diameter) chocolate chip cookies which they have given the trade name “Kookies”. The owners of the firm have not decided what price to charge. They want to know how many they could sell at various prices. To h ...
... Suppose a bakery close to your school has decided to produce and market large (6 inches in diameter) chocolate chip cookies which they have given the trade name “Kookies”. The owners of the firm have not decided what price to charge. They want to know how many they could sell at various prices. To h ...
Elastic Demand
... Increase in the price of one decreases the demand for the other The larger the negative cross-elasticity coefficient, the greater is the complementarity between the two goods ...
... Increase in the price of one decreases the demand for the other The larger the negative cross-elasticity coefficient, the greater is the complementarity between the two goods ...
S - Unchain-vu
... More revenues through lower prices? The London city council discusses about how to reduce the public transport company's losses by raising more revenues: →The Tories argue that ticket prices should be increased in order to raise more revenues →The Labour Party suggests the opposite: Attract more peo ...
... More revenues through lower prices? The London city council discusses about how to reduce the public transport company's losses by raising more revenues: →The Tories argue that ticket prices should be increased in order to raise more revenues →The Labour Party suggests the opposite: Attract more peo ...
Level 3 Economics (90629) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... When dairy farmers are making supernormal profits, more farmers will enter the market due to no barriers to entry. This will increase the market supply to S1. As a result, the market price will fall. Because dairy farmers are price takers, they must accept the new market price so their AR / MR / P / ...
... When dairy farmers are making supernormal profits, more farmers will enter the market due to no barriers to entry. This will increase the market supply to S1. As a result, the market price will fall. Because dairy farmers are price takers, they must accept the new market price so their AR / MR / P / ...
Elasticity and its Application
... Demand for a good is elastic if the quantity demanded responds substantially to changes in the price Demand for a good is inelastic if the quantity demanded responds only slightly to changes in the price ...
... Demand for a good is elastic if the quantity demanded responds substantially to changes in the price Demand for a good is inelastic if the quantity demanded responds only slightly to changes in the price ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.