8.1.1 The Individual Firm`s Supply Curve
... 1. Prices of agricultural inputs and outputs are volatile, as they depend on the weather and global supply and demand conditions. Agricultural managers, producers, and agribusinesses would do well to pay attention to changes in relative prices. When prices change, economic conditions also change, as ...
... 1. Prices of agricultural inputs and outputs are volatile, as they depend on the weather and global supply and demand conditions. Agricultural managers, producers, and agribusinesses would do well to pay attention to changes in relative prices. When prices change, economic conditions also change, as ...
Video Information Choices & Change: Microeconomics Economics 1
... Costs of production and the development of cost curves are the foundation for understanding market structures. Simple real world examples are used to illustrate the mathematical and graphical development of cost curves. Another important aspect of this lesson is the distinction between shortrun and ...
... Costs of production and the development of cost curves are the foundation for understanding market structures. Simple real world examples are used to illustrate the mathematical and graphical development of cost curves. Another important aspect of this lesson is the distinction between shortrun and ...
Natural Monopolies
... Since the 1980s there is a global trend towards utility deregulation, in which systems of competition are intended to replace regulation by specifying or limiting firms' behaviour; the telecommunications industry is a leading example globally. ...
... Since the 1980s there is a global trend towards utility deregulation, in which systems of competition are intended to replace regulation by specifying or limiting firms' behaviour; the telecommunications industry is a leading example globally. ...
Elasticity
... White-Out when it was first introduced so its demand curve was steep or relatively inelastic. As other liquid correcting fluids were introduced, the demand curve for White-Out became flatter or more elastic. While a change in the price of White-Out had a small affect on the quantity demanded of Whit ...
... White-Out when it was first introduced so its demand curve was steep or relatively inelastic. As other liquid correcting fluids were introduced, the demand curve for White-Out became flatter or more elastic. While a change in the price of White-Out had a small affect on the quantity demanded of Whit ...
Name: JJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJ Date: JJJJJJJJJJJJJJ
... B) the level that reduces the marginal social costs of pollution to zero. C) the level of pollution at which the marginal social cost of pollution is equal to the marginal social benefit of pollution. D) the level of pollution that minimizes the average total cost of producing the product that gener ...
... B) the level that reduces the marginal social costs of pollution to zero. C) the level of pollution at which the marginal social cost of pollution is equal to the marginal social benefit of pollution. D) the level of pollution that minimizes the average total cost of producing the product that gener ...
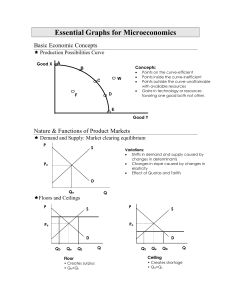
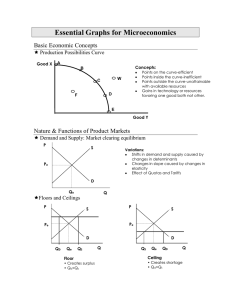
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
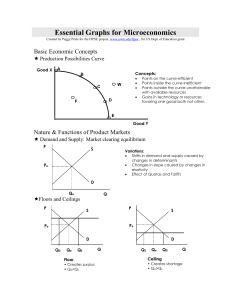
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
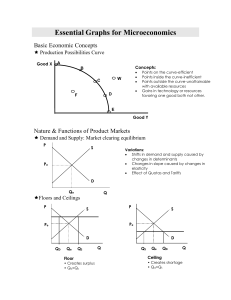
Essential Graphs for Microeconomics - pm
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
... MRP is the increase in total revenue resulting from the use of each additional variable input (like labor). The MRP curve is the resource demand curve. Location of curve depends on the productivity and the price of the product. MRP=MP x P MRC is the increase in total cost resulting from the employme ...
November 5, 2004
... 19. In the long run, each firm will operate at the minimum point on its long run average cost curve, and freedom of entry and exit will ensure that price is kept down at this level. This is a constant cost industry so we have P = 20 as the long run supply curve. Since demand is P = 48 - .005Q, we h ...
... 19. In the long run, each firm will operate at the minimum point on its long run average cost curve, and freedom of entry and exit will ensure that price is kept down at this level. This is a constant cost industry so we have P = 20 as the long run supply curve. Since demand is P = 48 - .005Q, we h ...
problem set #6: perfect competition
... d. Suppose the demand curve is Qd = 150 - 10P. What is price, quantity supplied domestically, and imports in the short-run? In the long-run? Short run. With only domestic supply, D(p)=S(p): 150 – 10p = 5p, p=$10. Since this is greater than the $8 price at which importers are willing to supply, the ...
... d. Suppose the demand curve is Qd = 150 - 10P. What is price, quantity supplied domestically, and imports in the short-run? In the long-run? Short run. With only domestic supply, D(p)=S(p): 150 – 10p = 5p, p=$10. Since this is greater than the $8 price at which importers are willing to supply, the ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter-5 Questions and Problems
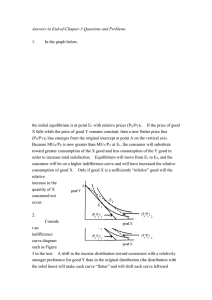
... of the Edgeworth box diagonal) yields 100 units of X output (and 0 units of Y output). Alternatively, suppose that employment of all capital and labor in the Y industry yields 200 units of Y output (and 0 units of X output). With constant returns to scale in both industries, production at the midpo ...
... of the Edgeworth box diagonal) yields 100 units of X output (and 0 units of Y output). Alternatively, suppose that employment of all capital and labor in the Y industry yields 200 units of Y output (and 0 units of X output). With constant returns to scale in both industries, production at the midpo ...
Market Failure Stakeholder Analysis (Who Wins, Loses) Monopoly
... Net Social Benefit Accounting Change in CS: P2ABP* (loss) Government Spending: P2ACP* (gain) Gain because society gets it back ...
... Net Social Benefit Accounting Change in CS: P2ABP* (loss) Government Spending: P2ACP* (gain) Gain because society gets it back ...
Taxes
... rate, the quantity of labor supplied by workers exceeds the quantity demanded by employers. There is a surplus of labor. Because employers cannot be forced to hire a greater quantity than they wish, the quantity of labor hired at the minimum wage is less than the quantity that would be hired in an u ...
... rate, the quantity of labor supplied by workers exceeds the quantity demanded by employers. There is a surplus of labor. Because employers cannot be forced to hire a greater quantity than they wish, the quantity of labor hired at the minimum wage is less than the quantity that would be hired in an u ...
Econ -Unit 2 PowerPoint
... – There is a change in the amount of a good demanded regardless of price – This is called a change in the amount demanded – There are five variables that cause a demand curve to shift – Shifts are based on quantity ...
... – There is a change in the amount of a good demanded regardless of price – This is called a change in the amount demanded – There are five variables that cause a demand curve to shift – Shifts are based on quantity ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.