PART I. Economics and Tourism
... - Give the mathematical formulation - the distinction between primary/luxury good : for luxury good, income elasticity of demand exceed 1. Question : In which category do you range tourism goods & services ? ...
... - Give the mathematical formulation - the distinction between primary/luxury good : for luxury good, income elasticity of demand exceed 1. Question : In which category do you range tourism goods & services ? ...
Slides19.pdf
... Note: going from first to second line assumes that (IC5 ) holds as an equality. ...
... Note: going from first to second line assumes that (IC5 ) holds as an equality. ...
CHAPTER OVERVIEW
... on reserve at the library to encourage students to sample the original work. You could use short excerpts as the basis for discussion or essays. “Adam Smith and the Wealth of Nations,” a 28minute video/film, is an excellent supplement. Check with your Federal Reserve District Bank’s public informati ...
... on reserve at the library to encourage students to sample the original work. You could use short excerpts as the basis for discussion or essays. “Adam Smith and the Wealth of Nations,” a 28minute video/film, is an excellent supplement. Check with your Federal Reserve District Bank’s public informati ...
Oligopoly - ILM.COM.PK
... monopolist need not always make a profit. In the long run, of course, unprofitable monopolists will either stop production or raise the price further above marginal cost until it covers average total costs. The monopolist will always try to operate on the elastic portion of the demand curve becaus ...
... monopolist need not always make a profit. In the long run, of course, unprofitable monopolists will either stop production or raise the price further above marginal cost until it covers average total costs. The monopolist will always try to operate on the elastic portion of the demand curve becaus ...
Tutorial
... coefficient throughout the length of the demand curve. d. positive slope. A. The quantity demanded by consumers is more sensitive to a price change at higher prices than at lower prices. ...
... coefficient throughout the length of the demand curve. d. positive slope. A. The quantity demanded by consumers is more sensitive to a price change at higher prices than at lower prices. ...
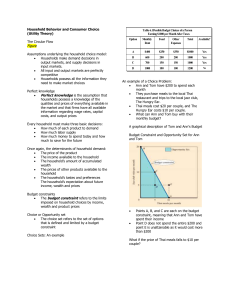
Household Behavior and Consumer Choice (Utility Theory) The
... Perfect knowledge is the assumption that households possess a knowledge of the qualities and prices of everything available in the market and that firms have all available information regarding wage rates, capital costs, and output prices Every household must make three basic decisions: ...
... Perfect knowledge is the assumption that households possess a knowledge of the qualities and prices of everything available in the market and that firms have all available information regarding wage rates, capital costs, and output prices Every household must make three basic decisions: ...
find powerpoint here
... The Effect of Trade on Price Competition • The partial equilibrium model is also useful for analyzing the gains from trade under imperfect competition. • International trade increases the number of potential suppliers, which tends to increase price competition. • Increased price competition reduces ...
... The Effect of Trade on Price Competition • The partial equilibrium model is also useful for analyzing the gains from trade under imperfect competition. • International trade increases the number of potential suppliers, which tends to increase price competition. • Increased price competition reduces ...
Slide 1
... Suppose market price is $2.50, the quantity supplied (10 burgers) exceeds the quantity demanded (4 burgers). Suppliers will increase sales by cutting the price which causes an increase in quantity demand and moves the price toward its equilibrium level. Suppose market price is $1.50, the quantity de ...
... Suppose market price is $2.50, the quantity supplied (10 burgers) exceeds the quantity demanded (4 burgers). Suppliers will increase sales by cutting the price which causes an increase in quantity demand and moves the price toward its equilibrium level. Suppose market price is $1.50, the quantity de ...
ECON 2302 - Principles of Micro-Economics
... Course Description: Fundamental principles of economics emphasize the roles and decisionmaking of the industry, firm and individual. To better illustrate this, the instructor uses many real-world examples in Vietnam. Course Objective: enable the student to analyze basic microeconomic issues and deve ...
... Course Description: Fundamental principles of economics emphasize the roles and decisionmaking of the industry, firm and individual. To better illustrate this, the instructor uses many real-world examples in Vietnam. Course Objective: enable the student to analyze basic microeconomic issues and deve ...
Lecture 01.5
... – Total Willingness-to-pay: “value in use” • Maximum total amount you would be willing to pay for x units of the good than go without? – Equals the area under the demand curve up to x units Individual's Demand Curve ...
... – Total Willingness-to-pay: “value in use” • Maximum total amount you would be willing to pay for x units of the good than go without? – Equals the area under the demand curve up to x units Individual's Demand Curve ...
Lecture 5
... Position of the demand curve depends on: 1. Income levels - higher Y is further right D curve is 2. Tastes - stronger these are, further right the D curve 3. Prices of other goods - substitutes and complements ...
... Position of the demand curve depends on: 1. Income levels - higher Y is further right D curve is 2. Tastes - stronger these are, further right the D curve 3. Prices of other goods - substitutes and complements ...
Answers to Homework #4
... c. Suppose you are told that there is an increase in input prices so that at every price the market supply changes by 90 units. What is the new market supply curve given this information? What is the new equilibrium price and quantity in this market? What quantity will a representative firm produce ...
... c. Suppose you are told that there is an increase in input prices so that at every price the market supply changes by 90 units. What is the new market supply curve given this information? What is the new equilibrium price and quantity in this market? What quantity will a representative firm produce ...
Technological Change and Dynamic Equilibrium
... world that the static model describes is one in which changes are discrete events and the expected normal state to which the economy moves is one in which prices and quantities remain constant at their equilibrium levels. But we live in a dynamic economy that is constantly in flux, rather more like ...
... world that the static model describes is one in which changes are discrete events and the expected normal state to which the economy moves is one in which prices and quantities remain constant at their equilibrium levels. But we live in a dynamic economy that is constantly in flux, rather more like ...
The Effect of Extra Border Patrols on the Market for Illicit Drugs
... • Suppose the consumer has chosen the best combination. How would the combination change if the price of one good in ( say, cones) increased? • Then, the marginal benefit from sundaes would be greater than the marginal benefit from cones. Balance is restored by reducing the consumption of cones and ...
... • Suppose the consumer has chosen the best combination. How would the combination change if the price of one good in ( say, cones) increased? • Then, the marginal benefit from sundaes would be greater than the marginal benefit from cones. Balance is restored by reducing the consumption of cones and ...
A Firm in a Compeitive Market
... desire to produce at that rate of output where ATC is at a minimum. I.e., profit max output is not necessarily at the point where ATC is the lowest. ...
... desire to produce at that rate of output where ATC is at a minimum. I.e., profit max output is not necessarily at the point where ATC is the lowest. ...
Elasticity of Demand
... total revenue (same direction) When PED < 1 You need to decrease increase price to increase total revenue (opp dir) When PED = 1 There is no effect on TR when P changes ...
... total revenue (same direction) When PED < 1 You need to decrease increase price to increase total revenue (opp dir) When PED = 1 There is no effect on TR when P changes ...
Smpfecba - University of Pittsburgh
... check with your decision on whether to produce or temporary shut down? T = TR - TC = 250(30) - 5,250 -100(30) - 2.5(30)2 = - 3,000. Yes, because the loss is less than the fixed cost, and therefore the firm will lose more money if it shut down and paid just its fixed cost. ...
... check with your decision on whether to produce or temporary shut down? T = TR - TC = 250(30) - 5,250 -100(30) - 2.5(30)2 = - 3,000. Yes, because the loss is less than the fixed cost, and therefore the firm will lose more money if it shut down and paid just its fixed cost. ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.