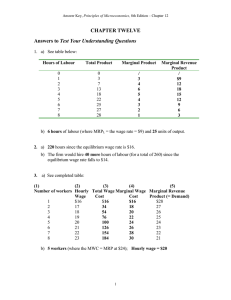
Long Problems with Solutions
... produced was less than the increase in costs. At any price above the monopoly price, MR > MC implying that if the firm could increase its output (i.e., lower its price), it would increase its revenues more than it would increase its costs, thereby resulting in an increase in profits. 5) False. When ...
... produced was less than the increase in costs. At any price above the monopoly price, MR > MC implying that if the firm could increase its output (i.e., lower its price), it would increase its revenues more than it would increase its costs, thereby resulting in an increase in profits. 5) False. When ...
economics
... crude oil (an input into making gasoline) shifts the supply curve to the left from S 1 to S2. In an unregulated market, the price would have risen from P 1 to P2. The price ceiling, however, prevents this from happening. At the binding price ceiling, consumers are willing to buy Q D, but producers o ...
... crude oil (an input into making gasoline) shifts the supply curve to the left from S 1 to S2. In an unregulated market, the price would have risen from P 1 to P2. The price ceiling, however, prevents this from happening. At the binding price ceiling, consumers are willing to buy Q D, but producers o ...
Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México Facultad de Economía
... 3.4. Análisis basado en curvas de indiferencia 3.5. El excedente del consumidor y sus aplicaciones ...
... 3.4. Análisis basado en curvas de indiferencia 3.5. El excedente del consumidor y sus aplicaciones ...
ch 4 ppt slides
... • The law of supply states that the quantity of a good supplied is directly related to the good’s price • In other words, other things equal, • Quantity supplied rises as price rises • Quantity supplied falls as price falls • The law of supply occurs because: • When prices rise, firms substitute pro ...
... • The law of supply states that the quantity of a good supplied is directly related to the good’s price • In other words, other things equal, • Quantity supplied rises as price rises • Quantity supplied falls as price falls • The law of supply occurs because: • When prices rise, firms substitute pro ...
Chapter 4: Supply and Demand
... • The law of supply states that the quantity of a good supplied is directly related to the good’s price • In other words, other things equal, • Quantity supplied rises as price rises • Quantity supplied falls as price falls • The law of supply occurs because: • When prices rise, firms substitute pro ...
... • The law of supply states that the quantity of a good supplied is directly related to the good’s price • In other words, other things equal, • Quantity supplied rises as price rises • Quantity supplied falls as price falls • The law of supply occurs because: • When prices rise, firms substitute pro ...
Chapter 5: Univariable calculus
... (c) Find the marginal propensity to save (MPS) when Y = 91. (d) Determine whether or not MPC and MPS change in the same direction as Y changes. ( for the solution see Worked Example 4.5) . Example 4.6 Marginal product In the short-run analysis of production , the production process is assumed to inv ...
... (c) Find the marginal propensity to save (MPS) when Y = 91. (d) Determine whether or not MPC and MPS change in the same direction as Y changes. ( for the solution see Worked Example 4.5) . Example 4.6 Marginal product In the short-run analysis of production , the production process is assumed to inv ...
Chapter 02 Supply and Demand Multiple Choice Questions 1
... A. makes no difference whether the consumer or the producer actually transfers the money to the government since the market effects are the same. B. is best to have the consumers pay the tax since they view cigarettes as necessities. C. is best to tax the producer since they will not cut production ...
... A. makes no difference whether the consumer or the producer actually transfers the money to the government since the market effects are the same. B. is best to have the consumers pay the tax since they view cigarettes as necessities. C. is best to tax the producer since they will not cut production ...
UNIT : 4 FORMS OF MARKET -10 marks 1. Define market. It is a real
... influence market supply or price. Similarly one buyer cannot affect market demand or price. (ii) Firms become price takers as they have to accept the equilibrium price that market demand & supply decide. So market or industry is price maker. (iii) Due to large number of buyers firm can sell any amou ...
... influence market supply or price. Similarly one buyer cannot affect market demand or price. (ii) Firms become price takers as they have to accept the equilibrium price that market demand & supply decide. So market or industry is price maker. (iii) Due to large number of buyers firm can sell any amou ...
1 Economics 101 Summer 2016 Answers to Homework #3 Due
... equal to the supply equation: thus, 500 – 10Q = 100 + 10Q 20Q = 400 Q = 20 dryers P = 500 – 10(20) = $300 per dryer Or, P = 100 + 10(20) = $300 per dryer b) The price of dryers in the domestic economy will equal the world price of $150 per dryer once this economy opens its dryer market to trade. Dom ...
... equal to the supply equation: thus, 500 – 10Q = 100 + 10Q 20Q = 400 Q = 20 dryers P = 500 – 10(20) = $300 per dryer Or, P = 100 + 10(20) = $300 per dryer b) The price of dryers in the domestic economy will equal the world price of $150 per dryer once this economy opens its dryer market to trade. Dom ...
INFORMATION AGGREGATION IN A NOISY RATIONAL
... The analysis presented here is of interest for at least two reasons. First, it provides a reasonable characterization of the economic concept of an informationally efficient market. Secondly, it introduces a definition of equilibrium which restricts prices to depend on traders’ information only thro ...
... The analysis presented here is of interest for at least two reasons. First, it provides a reasonable characterization of the economic concept of an informationally efficient market. Secondly, it introduces a definition of equilibrium which restricts prices to depend on traders’ information only thro ...
MEASURING PRODUCTION AND INCOME, Chapter 2
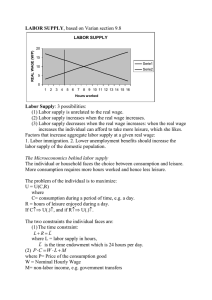
... Labor Supply: 3 possibilities: (1) Labor supply is unrelated to the real wage. (2) Labor supply increases when the real wage increases. (3) Labor supply decreases when the real wage increases: when the real wage increases the individual can afford to take more leisure, which she likes. Factors that ...
... Labor Supply: 3 possibilities: (1) Labor supply is unrelated to the real wage. (2) Labor supply increases when the real wage increases. (3) Labor supply decreases when the real wage increases: when the real wage increases the individual can afford to take more leisure, which she likes. Factors that ...
Elasticity: Measuring the Responsiveness of Demand
... Elasticity Questions 5. DishTV has lowered its subscription TV prices by 10% and its subscription base rose by 15%. (a) What is the price elasticity of demand for DishTV? Is this elastic or inelastic? Why? (b) If DirecTV sees its subscription base fall by 8%, what is the cross price elasticity of d ...
... Elasticity Questions 5. DishTV has lowered its subscription TV prices by 10% and its subscription base rose by 15%. (a) What is the price elasticity of demand for DishTV? Is this elastic or inelastic? Why? (b) If DirecTV sees its subscription base fall by 8%, what is the cross price elasticity of d ...
PPA 723: Managerial Economics
... The SR market supply curve is the horizontal summation of the firm supply curves for the firms in the market. The more firms in the market, the more elastic the SR market supply curve. ...
... The SR market supply curve is the horizontal summation of the firm supply curves for the firms in the market. The more firms in the market, the more elastic the SR market supply curve. ...
Economic equilibrium

In economics, economic equilibrium is a state where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text-book model of perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case refers to a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes and the quantity is called ""competitive quantity"" or market clearing quantity.